Dr. David A. Fishman - Hadassah Medical Center
advertisement

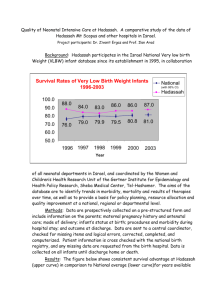
Clinical Quality איכות קלינית בעולם ובהדסה פרופ' מאיר ברזיס המרכז לאיכות ובטיחות קלינית הדסה והאוניברסיטה העברית ירושלים www.hadassah.org.il/departments/quality Definitions of Quality (Institute of Medicine) Degree to which care increases likelihood of desired health outcomes & consistent with current professional knowledge Safe Timely Effective Patient centered Equitable Efficient Overuse (antibiotics, imaging) Underuse (prevention) Misuse (errors & complications) Evidence-based Patient-centered System-minded Performance Evaluation • • • • • Voluntary Quality Indicators Mandatory Performance Evaluation Public Data Including Individual Surgeon Pay for Performance Non-payment for Preventable Complications Challenges: measurement error, socioeconomic confounders, manipulation, denial, gaming Ego bias: “I’m above the average” (Kahneman & Tversky. Heuristics and Biases. The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment) Stages of Facing Reality* Stage 1. “The data are wrong” Stage 2. “The data are right, but it’s not a problem” Stage 3. “The data are right; it is a problem; but it is not my problem.” Stage 4. “I accept the burden of improvement” * Harvard Professor Don Berwick, Institute for Health Improvement Donald M. Berwick, MD, MPP, FRCP Professor at Harvard School of Public Health President, Institute for Health Improvement, Boston, Massachusetts, USA “In short, academic medical centers should not just have best knowledge, they should model the best execution…They do not. Unreliability, waiting, lack of focus on patient’s needs and safety are every bit of characteristic of academic medical centers…and that needs not be the case. The same intellectual fervor and talent that allow places like the Brigham to raise the bar in technical clinical care can equally be used to raise the bar in the quality of medical care. …it’s going to take much more acute self-awareness among academicians and academic medical centers…. …a duty to encourage healthcare leaders and clinicians everywhere to become involved in improvement." Cycles of Improvement (Industry Model) Statistical Process Control PDSA Example: monitoring of surgical infection rate is now recognized as important tool to prevention Quality of General Intensive Care Survival at Hadassah vs. Israel Average Prof. Elisheva Simchen, Ministry of Health p<0.001 Despite higher severity score, patients had better survival at Hadassah Quality of Neonatal Intensive Care Survival at Hadassah vs. Israel Average Dr. Zivanit Ergaz, Prof. Ilan Arad & Gertner Institute Quality of Treatment in Trauma Mortality at Hadassah vs. US level I centers Dr. Yoav Mintz, Ms. Irina Gertcenchtein & Prof. Avraham Rivkind 30% 20% Hadassah - Total Mortality US National Trauma ISS 16+ Mortality Data Hadassah Bank -from 51 level-I trauma 20.9% 19.7% centers, 18.4% n= 263,524 14.4% NTDB - Total Mortality 20.2% 13.6% Hadassah data NTDB - ISS 16+ Mortality Israeli National Trauma Registry 20.5% 19.6% n=7,391 13.4% 11.5% 10% 5.3% 5.8% 5.5% 3.2% 2.6% 2.7% 5.8% 2.9% 6.7% 2.1% 0% 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Quality indicators for myocardial infarction, Hadassah vs. US data Hadassah (%) 89 90 50 83 69 44’ 102’ Referral to cardiac rehabilitation only 21% Percent of patients receiving adequate anticoagulation Before p<0.001 % After Intervention p<0.001 p<0.001 p<0.02 Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections Intervention in 108 ICU’s resulted in 66% reduction in rates of catheter-related bloodstream infection Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections I. Gross, S. Benenson, M. Cohen, C. Bloch At Hadassah, baseline observations over five months revealed a rate of infection of 13.2% (42/318 catheters), on the high side of reported ranges. Observations in ICU’s and OR: aseptic conditions not always strictly kept during catheter insertion. Intervention included discussion of results with staff, training for correct aseptic technique, use of a checklist, and authorization to nurses to feedback and stop physicians breaching asepsis. 1.0 Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections Survival Function for pat 0.9 0. 9 Cum Survi val 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 Proportion of catheters remaining without infection 0. 4 0. 3 0. 00 (Cox regression) S ur vi va l F un ct io Survival Function for pa 0.9 0.7 n 0.8 0.6 1.0 Survival Function for patterns 1 - fo r 2 NewGroup .00 1.00 1.0 0.9 0.8 Cum Survival 1. 0 urvival Cum SurvivalCum Survival Following intervention, improvement in technique 1.0 was observed;0.8 rate of infection declined by 62%, from 13.2% to 5.0% (17/337 catheters, p<0.001). 0.7 pa tt er ns 0.6 1 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00 DaysOfFollowUp 0.7 0.5 0.9 0.6 0.4 0.8 0.5 0.3 0.7 p<0.001 After the intervention 20 .0 0 40 .0 D ay 0 sO fF 60 ol .0 lo 0 w U p Days of catheter 0.00 20.00 Before the intervention 80 .0 0 40.00 10 0. 00 60.00 Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections Unit Before Intervention After Intervention Catheter days N infected Rate* Catheter days N infected Rate* Rate Reduction (%) ICU-A 1176 6 5.1 1296 3 2.3 55 ICU-B 1240 7 5.6 879 2 2.3 60 ICU Medicine 995 16 16.1 1715 6 3.5 78 Neurosurgery 225 4 17.8 173 1 5.8 67 Cardiac surgery 562 5 8.9 551 4 7.3 18 ICCU 150 4 26.7 63 1 15.9 40 Total 4348 42 9.66 4677 17 3.63 62.4** * Rate of infection per 1000 catheter-days ** p<0.001 Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections Pronovost P. et al. An intervention to decrease catheter-related bloodstream infections in the ICU. N Engl J Med 2006;355:2725 Physicians’ Hand Hygiene at Hadassah Summary of surveys in recent years Rate of hand-washing out of contacts with patients Ein Kerem Mt. Scopus Medicine 65% 55% Pediatrics 55% 62% Surgery 35% 66% Ob-Gyn 25% Use of Hadassol has been widely adopted but rate of hand hygiene unchanged Surgical Infections in General Surgery N. Minster, M. Zarhia, G. Almogy, A. Rivkind, S. Benenson, M. Cohen Rate of post-operative wound infection is 8-12%, within the range reported in the literature. Pre-operative antibiotic administration is documented as given on time in 59% of cases. A significant proportion of infections are diagnosed after discharge from the hospital. Infection monitoring is recognized as an important tool to keep rates low. Quality of Inguinal Hernia Repair in Adults and in Children at Hadassah T. Yemini, M. Badriah, Y. Mintz, R. Udassin, A. Rivkind Satisfaction high to very high in 94% of adults and children; problems: waiting & relation with staff Complications Rate of infection (95% CI) Children Adults 6% (2-13) 12% (7-20) 0.7-14%* Rate of hematoma (95% CI) Children Adults 10% (5-18) 13% (8-21) 11-15%* *Range in literature varies by motive (voluntary or mandatory) Quality of Special Surgeries Outcomes of special surgery in the Departments of Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT), Ophthalmology, Plastic and Neurosurgery ENT Snoring, tonsillectomies Ophthalmology Corneal transplant, Lasik Plastic surgery Breast reconstruction Neurosurgery Prevention of shunt infection Management of Snoring Disorders with Radiofrequency at Hadassah Optimal L. Gordon, S. Catinari, R. Eliashar p<0.005 % p<0.01 p≤0.05 Lasik (Myopic Corneal Refractive Surgery) at Hadassah Optimal (N=109) N. Orwa, A. Solomon, Y. Frucht-Peri % Evaluation of Outcomes for Tonsillectomies at Hadassah (2008) O. Frenkel, R. Eliashar % with any bleeding % needed readmission % needed reoperation Hadassah (N=106) Literature UK audit & others (N>30,000) 28 ? 20 3-10 4.7 0.5-2.0 Quality of Reconstruction Surgery After Mastectomy R. Yanko-Arzi, M. J. Cohen, R. Braunstein, E. Kaliner, R. Neuman Dept of Plastic Surgery & Center for Clinical Quality & Safety % 0 20 40 60 Severe Complications Success Satisfaction Would Recommend Hadassah moderate high 80 A survey of 140 women after reconstructive breast surgery for cancer showed satisfaction related mostly to expectations before surgery. Neurosurgical shunt infections I. Paldor, Z. Israel, C. Block with the dept of Neurosurgery % of shunts infected Intervention 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Num ber of shunts inserted 2001 10 2002 17 2003 21 2004-5 24 Mortality in infected cases dropped from 50% to 0% Is the X-ray interpretation by the junior staff on duty correct? Dr. Y. Mintz, Dr. D. Kisselgoff, Y. Gronowitz, A. Shaham, R. Hefez, Dr. D. Shaham - Departments of Surgery, Radiology, and Center for Clinical Quality & Safety % agreement resident vs. specialist Pulmonary Embolism 95% Surgery Trauma 77% 94% Effect of Translators on Understanding & Satisfaction of Arab Parents Department of Pediatrics & ER, Mt Scopus & Center for Clinical Quality & Safety, Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center The Presence of a Translator Significantly Improved Parental Understanding Regarding Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up 100 96 86 78 80 74 72 % 60 40 34 38 23 20 0 Understanding of diagnosis p<0.001, n=194 Necessary follow-up translator When return visit to ER necessary no translator Dosage & duration of medication Will patient’s empowerment improve efficacy & safety of oral anticoagulation? Self-management for Coumadin H. Goldberg, Y.Ben David, U. Izhar, L. Gordon, T. Baevsky, M.Burzstyn & M.Brezis with the Departments of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Medicine Patient’s empowerment improves efficacy & safety of oral anticoagulation 60 % of tests within target INR 50 * p<0.001 60% 40 30 38% 20 10 0 Control Intervention Patient’s knowledge & satisfaction significantly improved Communicating with Families & Satisfaction with End-of-Life Decisions Departments of Medicine & Center for Clinical Quality & Safety % of relatives agreeing with statement: Control Intervention “I felt the team didn’t care about my opinion” 35 13* “It upset me I didn’t know what was going on” 43 10* “Patient’s problems weren’t explained to me” 44 3* “Management options were not explained” 46 17* “I was afraid to ask questions” 38 10* “I felt excluded in the decision-making” 52 17* *p<0.005 in favor of the intervention group Communication with families of patients near end of life improves perceived quality of care Rate of patient’s recall for explanations on risks & alternatives: informed consent? Ward Type of procedure N Explanations about risks Discussion of alternatives Surgery Operation 178 60% 20% ObGyn Operation 198 57% 19% Medicine Diagnostic or therapeutic procedure 117 42% 40% Cardiology Angiography 120 39% 8% 613 51% 21% Total International Journal for Quality in Health Care 2008 Conclusion Projects help make healthcare at Hadassah more evidence-based, patient-centered & system-minded. Over 100 projects presented at National Meetings of Israeli Society for Quality in Healthcare; over 48 theses and 19 peerreviewed publications. Center for Clinical Quality & Safety