the slide set
advertisement
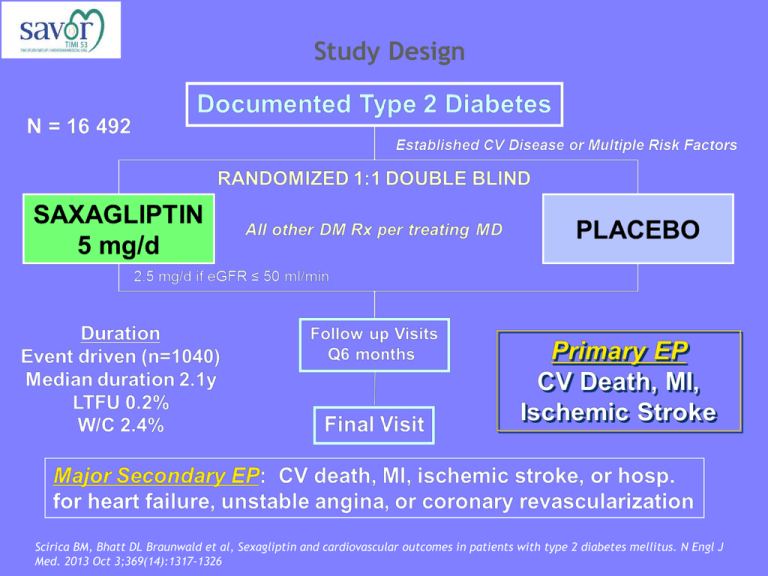
Study Design Scirica BM, Bhatt DL Braunwald et al, Sexagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 3;369(14):1317-1326 Study Design White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR et al, Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 3;369(14):1327-1335 Study Design SAVOR Primary end-point Design Treatment Patients Follow-up EXAMINE composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal ischemic stroke Multicenter, double blind and randomized Saxagliptin vs placebo Alogliptin vs placebo in addition to existing antihyperglycemic therapy in addition to existing antihyperglycemic therapy 16 492 5 380 2.1 years 18 months Change in HbA1c HbA1c (at the end of the trial) % HbA1c <7% (at the end of the trial) SAVOR EXAMINE -0.3% -0.36% 36.2% - Hypoglycemia SAVOR EXAMINE Major 2.1% (vs 1.7%; P=0.047) 0.7% (vs 0.6; P=0.86) Hospitalization 0.6% (vs 0.5%; P=0.33) - 14.2% (vs 12.5; P=0.002) - 15.3% (vs 13.4%; P<0.001) - - 6.7% (vs 6.5%; P=0.74) Minor At least 1 hypoglycemic event Any hypoglycemia* (AE) A hypoglycaemic event can be either: • An episode with symptoms and confirmed low glucose (<3 mmol/L) • An episode with low glucose • An episode with symptoms when glucose was not measured Minor hypoglycaemic events are considered when there is an awareness of the event, the event is tolerated, and the patient recovers by her/himself. In addition, the events resolved within 30 minutes of ingestion of carbohydrates (if possible confirmed with a fingerstick value). A measurement of blood glucose <54 mg/dL (<3.0 mmol/L) without symptoms is also considered an adverse event. Major hypoglycaemic events are events requiring the assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrates, glucagons, or other resuscitative actions. CV death, MI or ischemic CVA (%) Primary end point 14 HR 1.00 [0.89-1.12] P<0.001 (non-inferiority) 12 10 2y KM 8 6 Saxagliptin 7.3% Placebo 7.2% 4 2 6 12 18 24 Months Placebo 8212 7983 7761 7267 4855 Saxagliptin 8280 8071 7836 7313 4920 Scirica BM, Bhatt DL Braunwald et al, Sexagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 3;369(14):1317-1326 Individual end points Significantly more patients in the saxagliptin group than placebo were hospitalized for heart failure 2-year KM rate (%) Placebo (N=8 212) Saxagliptin (N=8 280) HR P-value for superiority CV death 2.9 3.2 1.03 (0.87-1.22) 0.72 MI 3.4 3.2 0.95 (0.80-1.12) 0.52 Ischemic stroke 1.7 1.9 1.11 (0.88-1.39) 0.38 Hosp for cor. revasc 5.6 5.2 0.91 (0.80-1.04) 0.18 Hosp for UA 1.0 1.2 1.19 (0.89-1.60) 0.24 Hosp for heart failure 2.8 3.5 1.27 (1.07-1.51) 0.007 All-cause mortality 4.2 4.9 1.11 (0.96-1.27) 0.15 Scirica BM, Bhatt DL Braunwald et al, Sexagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 3;369(14):1317-1326 Primary end point White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR et al, Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 3;369(14):1327-1335 Hospitalization for heart failure: pooled analysis Sattar N, Results from SAVOR and EXAMINE. DPP-4 inhibitors and CVD, EASD 2013 Sep 26.