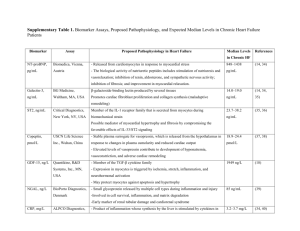
Cardiovascular Complications related to Anesthesia
advertisement

Wanawimol Saengchote M.D. Department of Anesthesiology, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol U SAFETY Anesthesia Incident Monitoring Study January to June 2007. 200,000 cases, 2537 incidents A standardized incident report form was developed in order to fill in what, where, when, how, and why it happened Arrhythmia 25% Desaturation 24% Death within 24 hrs. 20% Cardiac arrest 14% inexperience, lack of vigilance, inadequate preanesthetic evaluation, inappropriate decision, emergency condition, haste, inadequate supervision, ineffective communication. DO2 = CO x 10 x CaO2 Tissue O2 delivery = cardiac output x arterial O2 content CO = SV x HR SV ∞ preload, contractility, afterload CO = EF x LVEDV x SVR x HR Patient’s comorbid : controllability? Anesthetic management : drugs, techniques, process, anesthesia personnel Surgical procedure Hypovolemia Preop NPO Trauma-fractures Peritonitis N/v, diarrhea Bowel prep Diuretics Preoperative Blood loss Major fluid shift Tissue edema Effusion Diuresis (concealed blood loss) Intraoperative & PO. Tachycardia Peripheral vasoconstriction Low systolic blood pressure Narrow pulse pressure Cold ,clammy skin and extremities Low urine output (anemia not apparent in acute loss without adequate volume replacement) With beta blocker effect, no tachycardia detected Class I Class II Class III Class IV Pulse rate <100/min >100/min >120/min >140/min BP normal normal dropped dropped Pulse pr. normal decreased decreased decreased RR 14-20/min 20-30/min >30/min >35/min Urine >30ml/hr 20-30ml/hr 5-15ml/hr minimal Capill.refil normal delayed delayed delayed Mental st. Sl.anxious anxious confused lethargic Bl.loss(ml.,%) <750 <15% 750-1,500 15-30% 1,500-2,000 30-40% >2,000 >40% Fluid crystalloid +colloid +colloid,bl. +colloid,bl. Alert to environment, notice surgeon’s (and team) expression Good communication Adequate volume loading is all the time necessary (crystalloid – colloid) Blood and blood component as required Critical perfusion pressure should be maintained (MAP > 65 mmHg) Concern about distribution of regional blood flow - - 1. Drug effect : nearly all anesthetic agents depress myocardial contractility Potent inhalation agents Nitrous oxide in compromised heart Intravenous : thiopental , propofol, ketamine Opioid : pethidine ( arrhythmogenic effect to be discussed later) Coronary artery disease Myocardial ischemia / infarct Cardiogenic shock Valvular heart disease Congestive heart failure most common rheumatic heart disease : mitral, aortic , tricuspid valve Acute ischemic episode large or significant myocardial loss ⇨ serious ventricular arrhythmia, pulmonary congestion , hypotension ..... Hemodynamic support : inotropes , antiarrhythmic , mechanical device Cardiac markers : troponin I, AST, LDH, CKMB cTnT < 0.1 ng/L, cTnI < 2.0 ng/L, CK-MB 0-25 u/L ( > 2 x normal) Obstruction to heart, cardiac chambers or great vessels reduced stroke volume Causes : 1.Cardiac tamponade from injury, post cardiac surgery, cardiac catheterization * 2.Tension pneumothorax * 3. Pulmonary embolism * 4. Surgical manipulation in chest, esophageal, cardiac surgery 5. Supine hypotensive syndrome 1. drug interactions : concurrent drug use + anesthetic effect ACEI, CCB, opioids, IV anesthetic, inhalation agent 2. regional anesthesia : spinal, epidural an. with sympathetic blockade effect 3. various drug effect : antibiotics, protamine, 4. bone cement 5. sepsis, adrenal insufficiency, blood transfusion 20% of population with hypertensive diseases Causes of intraoperative HTN 1. Response to laryngoscopy and intubation 2. Light anesthesia 3. Hypercarbia 4. Hypoxemia 5. Drug effect 6. Hypervolemia 7. Specific surgical procedure Causes of HTN postop and at emergence 1. Stimuli from endotracheal & extubation 2. Pain 3. Hypoventilation, airway obstruction 4. Hypothermia,shivering 5. Acidosis 6. Full bladder 7. Antihypertensive withdrawal Risk Factors 1. Hypertension 2. Diabetes mellitus 3. Underlying heart disease : CAD, VHD 4. Liver disease, renal disease 5. Head injury 6. Sepsis 7. Carbon monoxide poisoning (elderly, malnutrition, hypoalbuminemia) A 62 yr-old female suspected CBD stone, scheduled for ERCP , plan for post procedural admission. Anesthetic time 1 hr 15 mins. ,uneventful an. and surgical procedure After extubation, ? Abn. breathing pattern, occ. fine crepitations BLL. Later SPO2 drop IV fluid 800 mL, minimal blood loss Diuretic given, PACU > 2 hrs. At ward SBP drop, intubate –ventilate,on dopa 1. Physiological disturbances during anesthesia Anesthetics modify body mechanism + vagal dominant, acidosis, hypoxia/ hypercarbia, electrolyte disorder, hypovolemia 2. Pathological disturbances CAD : heart block, PVC, Thyrotoxicosis, MH, pheochromocytoma 3. Pharmacological causes :ketamine, NMB 4. Anesthesia procedures : IT, CVP, SA Serious cardiac ♥arrhythmia : 6H, 5T Hypovolemia, hypoxemia, acidosis, K- Ca hypothermia, PE, ♥ tamponade tension pneumothorax Know how, Know why, Care why