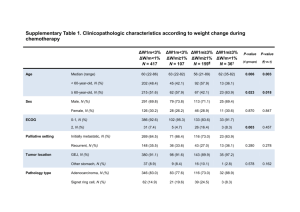
Upper gastrointestinal cancers
advertisement

Upper gastrointestinal cancers Dr Sue Darby Consultant Medical Oncologist Weston Park Hospital Sheffield Introduction • • • • • What’s UGI? Terminology Treatment intent Treatment options Clinical trials What’s upper GI? • • • • Oesophagus GOJ Stomach (Small bowel) What sorts of cancers? • Mainly adenocarcinomas (lower oesophagus downwards) • Squamous cell carcinomas (usually upper or mid oesophagus) • Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) • Lymphoma • Metastatic tumours (follicular breast, renal) Treatment intentions • • • • • Neoadjuvant (Downstaging) Adjuvant Curative Palliative Treatment types • • • • • • Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Chemoradiotherapy Biological therapy (Brachytherapy) (Surgery) Curative treatments (Neo)adjuvant chemotherapy • SqCC – 2 cycles neoadjuvant chemotherapy – 2 drugs – cisplatin and 5 fluorouracil – OEO2 trial – increases 2 year survival from 35% to 45% (surgery vs chemo+surgery) – Surgery 4-6 weeks after chemo (Neo)adjuvant chemotherapy • AdenoCa – 3 cycles neoadjuvant and 3 cycles adjuvant chemotherapy – 3 drugs – epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine – MAGIC trial – increases 5 year survival from 23% to 36.5% (surgery vs chemo+surgery) – Surgery 4-6 weeks after neoadjuvant chemotherapy ST03 • ECX +/- biological therapy • HER2 positive – +/- lapatinib – potentially operable lower oesophageal, GOJ and gastric adenoca • HER2 negative – +/- bevacizumab – gastric adenoca only Side effects • Benefits outweigh risks (in majority) • GI – nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation, mucositis • Skin – hair loss, hand-foot syndrome • Neurotoxicity – peripheral, tinnitus/deafness • Renal toxicity • Fatigue • Haematological – thrombocytopenia, anaemia, neutropenia (neutropenic sepsis) • Cardiovascular – angina/MI, arrhythmias Contraindications/Cautions • Ischaemic heart disease • Renal disease • Perfomance status • Patient choice Chemoradiotherapy • SCOPE trial – 2 yr survival >50% • 2 cycles of neoadjuvant cisplatin and capecitabine • 5 weeks of daily radiotherapy concomitantly with a further 2 cycles of capecitabine • Side effects – – – – odynophagia fatigue severe dysphagia (towards end of radiotherapy) treatment related stricture (late effect) - may require dilatation or stenting • Advantages over surgery – can treat some surgically untreatable cancers (eg locally invasive) • Disadvantages – nodal disease/field size Palliative treatments Palliative chemotherapy – line st 1 • SqCC – Cisplatin/5FU • AdenoCa – Oesophagus - EOX – epirubicin, oxaliplatin, capecitabine – adds few months on average – Gastric/GOJ • HER2 negative – EOX • HER2 positive – cisplatin, 5FU, trastuzumab (Herceptin) + maintenance trastuzumab • TOGA trial REAL2 • ECX/ECF/EOX/EOF • No significant difference in survival between arms • Around 9-11 months median survival • Trend towards best with EOX • Delivery issues • Led to change in practice from using ECF (PICC lines, continuous infusional chemo) to EOX (oral 5FU, no PICC) Palliative chemotherapy – line nd 2 • SqCC – nothing • AdenoCa – docetaxel – COUGAR trial – adds 2 months on average • Symptomatic benefit/BSC • Early phase trials (Leeds) Palliative radiotherapy • Symptomatic benefit • If local disease only can offer some local control • Good for: – Dysphagia – Bleeding – Tumour pain • Side effects minimal and short-lived – odynophagia, increased dysphagia, fatigue Clinical trials • • • • Only way to improve outcomes What current treatments are based on Form basis for future (better) treatments Importance of introducing idea to patients at early stage • Early referral of patients • Opportunity – patients – doctors Questions?