Fertility_and_Infertility_2012
advertisement

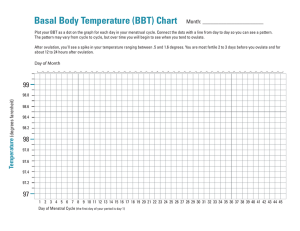
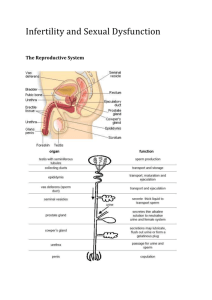
Introduction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qjSZ f43yf7k Women’s health Fertility and Infertility Developed by D. Ann Currie , R.N., M.S.N. 2012 Fertility Menstrual cycle Ovulation Cervical mucous Uterine structure Hormones Fallopian tubes Menstrual Cycle Follicular phase-days 1-14 of the cycle Menstrual phase (Menses) Proliferative phase Luteal phase-days 15-28 of the cycle Secretory phase Ischemic phase Ovulation Mature ovum comes out of the follicle Cervical Mucus Becomes more plentiful,thinner,and more stretchy consistency, and forms columns during ovulation to facilitate the transport of the sperm into the uterus Uterine Structure Normal shape and myometrium Placement of fertilizated ovum for successful implantation Unicornate Septate Bicornate Uterine Types Hormones Estrogen Progesterone FSH-Follicle stimulating hormone LH-Lutenizing hormone Fallopian Tubes Patent for sperm to reach ovum for fertilized ovum to reach uterus Male Component SpermMorphology-50% must have normal shape Count->20 million per ml. Motility-50% must have normal motion patterns Testosterone Erection Infertility Primary infertility- the individual has never conceived Secondary infertility- the individual was able to get pregnant but now can not conceive. Female component Various factors Ovulation- failure to ovulate Body fat under 14% will result in irregular menses,amenorrhea,or failure to ovulate Decrease in pituitary hormones of FSH or LH will result in fail to ovulate Structure of uterus - malformation of uterus Female Components Antibodies in vaginal or cervical mucus against sperm Scarring or blockade of fallopian tubes Smoking Other Male Components of infertility Sperm- lack of sperm, problems with shape, size,count, or motility Lack of testosterone Unable to maintain erection Failure to ejaculate Scrotal temperature Drug use-ETOH,marijuana,cocaine, smoking Male Components Mumps during teen years or adulthood Developmental factors Common Diagnostic Studies with Infertility FemaleBasal Body Temperature(BBT) Serum Hormone Testing Postcoital Exam Endometrial biopsy Hysterosalpingogram Laparoscopy BBT Temperature taken prior to arising from bed each morning sudden dip in temperature prior to ovulation followed by a rise of 0.5 1.0degrees F which indicates ovulation. Fertility awareness includes BBT and cervical mucus changes to detect ovulation Serum Hormone Testing FSH LH Postcoital Exam Couples are instructed to have intercourse 8-12 hours prior to the exam-1-2 days before ovulation 10ml syringe with catheter attached is used to collect a specimen of the secretions from the vagina the secretion is examined for s/s of infection,number of active or nonmotile sperm,sperm-mucus interaction Cont Consistency of cervical mucus. Endometrial Biopsy Obtaining an endometrial tissue sample lithotomy position or feet in stirrups paracervical block catheter into uterine to obtain sample to check the luteal phase Hysterosalingogram To detect uterine or tubal abnormalities Sedation or anesthesia iodine-based radio-opaque dye is instilled through a catheter into the uterus and tubes to outline these structures and x-ray is taken procedure should not be scheduled during menses or at time of ovulation Laparoscopy Under general or epidural anesthesia used to visualize the structures in the pelvis or to do surgical procedures Male diagnostic studies for infertility Sperm analysis-client ejaculates into container no ejaculation for several days prior to test specimen must be tested within 1/2-1 hr after ejaculation. Serum hormone testing Structural defects Psychological Factors associated with infertility Many couples will experience Shame Guilt Blame Stages of Grief Marital difficulties The nurse should Address the psychological factors discuss the couples feelings facilitate communication between the couple provide information to the couple on resources for coping and support groups and or professional counseling Educational needs of the infertile couple The educational needs of the couple with infertility problems is extensive. They will need to know about test/exams- preparation for the test, what it is, how it is done,meaning of the results of the assessment or tests. They will need to know about txsurgeries, medications, and maybe assigned reproductive technologies. Hormonal therapy Used for induction of ovulation for therapy for preparation for in vitro fertilization Medications Used to achieve induction of ovulation in cases of anovulatory menstrual cycles or to achieve multiple ova prior to in vitro fertilization Clomiphene citrate( Clomid,Serophene) Pergonal Humegon Repronex Medications Fertinex HCG Risks of ovulation induction- multiple births, ovarian hyperstimulation enlarged ovaries,abdominal distention,pain,and occasionally ovarian cysts Sperm washing For intrauterine insemination Artificial insemination Sperm collected within after ejaculation is inserted via a catheter into the uterus/vagina Donor sperm- identity of donor is confidential if sperm bank is used or the couple may know the donor In vitro fertilization (IVF) Multiple ova are harvested ova are then mixed with sperm in petri dish up to 4 embryos are placed in uterus extra embryos can be frozen for implantation at a later time. Hormone are used- FSH, progesterone Other procedures Gamete intrafallopian tranfser (GIFT) Tubal embryo tranfser(TET) Zygote intrafallopian transfer(ZIFT) Micro-epididymal sperm aspiration(MESA) Percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) Nurse’s Role with infertility Education Support Resource Advocate QUESTIONS Thank You http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=STn oSnWOLwA