Growth Hormone
advertisement

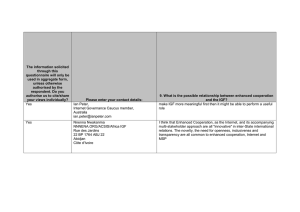
S G0 G1 G2 M Control of Secretion Hypothalamus: GHIH (or) SST (somatostatin) GHRH (+) GH Anterior Pituitary: (-) Liver: (-) (somatotropin) IGF (somatomedins) (+) GROWTH HORMONE indirect effects direct effects + + Insulin-like Growth Factor lipolysis in fat cells fat cells + carbohydrate metabolism muscle Increases FFA, glycerol, and sugars in circulation chondrocytes lipogenesis cartilage formation Protein synthesis GH/IGF/IGFBP Axis Brain Pituitary Growth Hormone (GH) IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) Liver Growth IGF Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) IGFBPs bind circulating IGF with high affinity & specificity Functions: 1. 2. 3. act as carriers of IGF in plasma prolong the half-life of IGF in circulation regulate IGF access to receptor in extracellular fluid (!) IGFBPs—two main types 1. IGFBP-3 most abundant form of IGFBP main carrier of IGF in circulation promotes IGF mediated somatic growth high IGFBP-3 associated w/ growth stimulation 2. IGFBP-1 typically present in small amounts high IGFBP-1 associated w/ growth inhibition LIVER IGF IGFBP-3 Cell IGF receptor Growth Functions LIVER IGF IGFBP-1 Cell IGF receptor Growth Functions Summary • Growth factors move cell from G0 to G1 – Initiate cell cycle • Growth Hormone – Direct effects: • Lipolysis • Carbohydrate metabolism • Increase IGF secretion from liver – Indirect effects through IGF • Increase lipogenesis in fat cells • Increase protein synthesis in muscle • Increase cartilage formation and growth in bone • IGFBPs – IGFBP3 enhances growth – IGFBP1 inhibits growth Clinical Aspects • • • • Stress effects on Growth Overproduction of GH Underproduction of GH End-organ resistance Maternal Effect: GC effect on Offspring Japanese quail implants controls Days after implantation From Hayward LS & Wingfield JC (2004) GCE 135:365-371 Human Studies 1. low birth weight 2. slow weight gain 3. smaller head size 4. are delayed in their walking 5. reduced speech development Direct Effect: Stress-induced dwarfism brought into the hospital months later GH/IGF/IGFBP Axis GCs Brain Pituitary Growth Hormone (GH) IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) Liver Growth IGF Effects of Cortisol on Plasma IGF Plasma IGF (ng/ml) 0 2 4 Time (h) Cortisol ↓ plasma IGF levels Effect takes 24 hours 10 mg/g 8 24 From Kajimura et al. (2003) JOE 178:91-99 2 mg/g control Effects of Cortisol on Plasma IGFBPs 2 mg/g control 10 mg/g ODU IGFBP-3 ↓ plasma IGFBP-3 levels plasma IGFBP-1 levels Cortisol induces rapid changes in plasma IGFBPs ODU ↑ IGFBP-1 0 2 4 Time (h) 8 24 From Kajimura et al. (2003) JOE 178:91-99 Tilapia Clinical Aspects • Stress Effects on Growth – GCs decrease growth – GCs can act through IGF or IGF binding proteins • Overproduction of GH • Underproduction of GH • End-organ resistance Acromegaly -overproduction of GH -before puberty: gigantism (excessive growth of long bones) -in adults: causes excessive growth of cartilage -symptoms Clinical Aspects • Stress Effects on Growth – GCs decrease growth – GCs can act through IGF binding proteins • Overproduction of GH – Acromegaly – gigantism • Underproduction of GH – Hypo-pituitary dwarfism • End-organ resistance IGF levels Clinical Aspects • Overproduction of GH – Acromegaly – gigantism • Underproduction of GH – hypopituitary dwarfism – Stress-induced dwarfism • End-organ resistance Laron’s Syndrome • Defective GH receptor • recessive gene • Lethal in males Clinical Aspects • Overproduction of GH – Acromegaly – gigantism • Underproduction of GH – Hypopituitary dwarfism – Stress-induced dwarfism • End-organ resistance – Laron’s Syndrome bGH in Dairy Cows? Pygmies from Central Africa