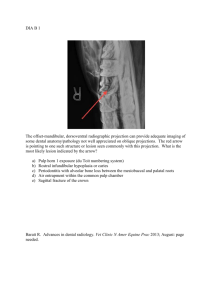
EQ Head
advertisement

Normal Radiographic Anatomy of the Equine Head Dr. Pack/Woodland April 7, 2011. Indications • Nasal Discharge – Sinusitis – Dental Disease • Head Trauma – Fractures • Facial / Neck Swelling – Guttural Pouch Tympany Technical Considerations • Head is mobile and high off the ground • Sedation – Lowers head • • • • Can use portable equipment 14x17 cassettes Film holding device Rope halter – no buckles Lateral and Oblique Views • Standing or recumbent • Can visualize sinuses, teeth and skull fractures (frontal bone) – Obliques are needed to carefully assess tooth roots • Must label correctly • Can use barium as marker on skin if needed Morgan Morgan Morgan DV/VD • Used for comparison between sides • Difficult to keep head still and straight – Can throw off symmetry • Easier to do VD when patient is under general anesthesia • Maxilla is wider than the mandible Morgan Mass on Right side Cranium • Foals: dome-shaped – Face lengthens with growth; accommodates teeth and expanding sinuses • Adult lateral view – Petrous temporal bones (tympanic bullae not visible) – Nuchal crest – Occipital condyles – Ethmoid turbinates A B C D E F Dyce et. al A - Nuchal crest B - Coronoid process C - Condylar process D - Occipital condyle E - Ramus of mandible F - Body of mandible Equine Skull • A = Petrous temporal bone • B = Cranium • C = Condyloid process • D = Coronoid process • E = Basioccipital • F = Epiglottis • G = Ethmoid turbinates A – Choncofrontal sinus A B – Maxillary sinus C – Condylar process of mandible G D – Guttoral pouch E – Stylohyoid bone G – Maxillary 3rd H – Mandibular 2nd Premolar E F F – Epiglottis Molar C B H D Equine Sinuses • Frontal – Dorsal part of the skull, medial to orbit – Combines with dorsal conchal = conchofrontal • Dorsal, ventral and middle conchal • Maxillary – Rostal and caudal – Important relationship with the molar cheek teeth • Sphenopalatine Frontal Sinus Caudal Maxillary Sinus Rostral Maxillary Sinus Dyce et. al Equine Sinuses • Normally air-filled on radiographs • Fluid or a soft tissue mass can be seen – Air-fluid lines • Hard to tell if one or both sides are affected • Maxillary sinus – PM4, M1, M2, M3 tooth roots in sinus – Tooth root infections can easily cause sinusitis Sinuses • • • • A = frontal B = dorsal conchal C = stylohyoid bone D = maxillary sinus D Sinuses • A - Nasal bone • B - Frontal sinus • C - Dorsal conchal sinus • D - Maxillary sinus • E - Mandible Post-op Tooth Repulsion Guttural Pouches • • • • Ventral diverticulum of the auditory tube Paired; lateral and medial compartments Superimposed and air-filled on radiographs Dorsal pharyngeal wall separates the ventral wall of the GP from the pharynx • Stylohyoid bones can be seen through the air filled GP’s • Retropharyngeal lymph nodes – Caudal to the GP – Infection can spread from LN to GP Guttural Pouches A A = Petrous Temporal Bone B = Basioccipital bone C = Coronoid Process of the Mandible B C Basisphenoid / Basiocciptal Fractures • Occur primarily in young horses that flip over backward – Poll strikes against ground • Clinical signs depend upon amount of displacement – Minimal = usually recover but may have residual head tilt – Severe = cerebral hemorrhage and death • If horse can stand, death is not likely Pharynx / Larynx • Pharynx – Where nasopharynx and oropharynx join • Epiglottis – Dorsal to the soft palate • Larynx – Made up of many cartilages which are rarely seen and their location is approximated anatomically on the radiograph Equine Teeth • Herbivores = hypsodont teeth – Continuously erupt to compensate for attrition (wearing) – Grinding surface • Dental enamel is more dense than bone – Sinuses will be very overexposed • Lateral, obliques +/- VD Equine Dental Formula Temporary teeth: Permanent teeth: • 3-0-3 Maxillary • 3-0-3 Mandibular – “Baby” teeth are shorter and smaller • 3-1-3(4)-3 Maxillary • 3-1-3-3 Mandibular – Maxillary premolar 1 is wolf tooth – Canine teeth • Rudimentary and commonly fail to erupt in mares Dyce et. al Numbering Teeth • Can not definitively tell which side without obliques • Make sure to call them maxillary or mandibular • Always look for wolf teeth Teeth cont. Mandibular 4th premolar = Canine Tooth Incisors P2 P3 P2 P3 P4 P4 M1 M2 M1 M2 M3 M3 Tooth root fractures (maxillary molars) Ruminants Horns: - Grow from frontal bones Dental Formula Temporary Teeth: Permanent Teeth: • 0-0-3 Maxillary • 3-1-3 Mandibular • 0-0-3-3 Maxillary • 3-1-3-3 Mandibular Lumpy Jaw (Actinomyces bovis) Test yourself • What structures can you correctly identify?