Overview of Ageing:
a
How Can We Optimize Care in the
Context of Multimorbidity?
Amy C. Justice, MD, PhD
Professor, Yale University
Schools of Medicine and Public Health
Section Chief, General Internal Medicine
VA Connecticut Healthcare System
Who is Ageing with HIV?
Everyone with access to ART and
those who contract HIV at older ages.
In US: More People Living with HIV
Infection Every Year (+38K/yr*)
Each year: 56K new infections-18K deaths=38K*
http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/surveillance/resources/slides/index.htm
Projected Proportion of those Living
With HIV in United States 50+ Years*
2001-2017
Projected
US VA in 2003
As of 2008:
•San Francisco
•NY City
33%
25%
17%
19%
21%
27%
27%
35%
37%
39%
41%
44%
45%
47%
50%
29%
22%
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
*Data from 2009, onward projected based on 2001-20078 trends (calculated by author), 2001-20078 data
from CDC Surveillance Reports 2009. New York and San Francisco data from Departments of Public Health
In New York City
HIV Epidemiology & Field Services Semiannual Report, NYCDOH. April 2010
Africa is No Exception
• An estimated 14% of adults with HIV infection
in Sub Saharan Africa are >50 years
• AIDS is leading cause of death among >50 yrs.
in Nyanza Providence, Western Kenya
Negin J. Bull World Health Organ 2010 Nov 1;88(11):847-853
Projected HIV Prevalence by Age in Hlabisa
Sub-district of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
Hontelez J. Ageing with HIV in South Africa. AIDS 2011 25:1665-73
Sex is Not Only for the Young
Proportion reporting sex in last 12 months
100.0
90.0
Men
83.7
Women
80.0
70.0
67.0
61.6
60.0
50.0
39.5
40.0
38.5
30.0
16.7
20.0
10.0
0.0
57-64
Lindau ST, et al. NEJM. 2007;357:762-774.
65-74
75-85
Sexual Risks Among Older Adults
• Newly single (widowed/divorced) status
• Ratio of men to women increasingly skewed
• Less likely to use condoms
– Postmenopausal women--pregnancy no longer possible
– Men may have erectile dysfunction complicating condom use
• Lower estrogen leads to vaginal dryness and
likely increases risk of viral transmission
Among HIV+ on ART, What Drives
Morbidity and Mortality?
Multi morbidity define as co occurrence
of health conditions that cannot be cured
and likely interact, but require ongoing
monitoring and treatment.
Delayed Presentation By Age
(NA ACCORD)
100%
350
313
300
269
277
284
275
246
203
40%
150
30%
32%
39%
90%
80%
296
293
272
261
211
41%
323
336
70%
250
200
312
333
274
261
272
273
234
41%
36%
34%
44%
42%
36%
38%
42%41%
45%
39%
46%
41%
47%
39%
266
48%
39%
60%
50%
40%
30%
100
20%
50
10%
0
0%
1997
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
Year
<50 years
Altoff K. et al. JAIDS 2011
≥50 years
<50 years
≥50 years
2006
2007
Proportion of patients with a CD4 count ≥350 cells/mm3 at first
presentation for HIV clinical care
Median CD4 count (cells/mm3) at first presentation for HIV clinical care
400
AIDS Events Increasingly Rare
ART-CC, Archives Int Med 2005: 165 416-423
AIDS Events Variably Associated with
CD4 and Survival
By Median (IQR) CD4
ART-CC, CID 2009;48:1138-51
By Relative Hazard of Death
>50% of Deaths Attributed to
Non-AIDS Events
Cumulative Mortality by COD Among Those on cART (1996-2006) ART-CC, CID 2010: 1387-1396
Death Rate Disparities by HIV,
Race/Ethnicity and Age
HIV Epidemiology & Field Services Semiannual Report, NYCDOH. April 2010
Strategies for Management of ART (SMART)
*More AIDS and “Non-AIDS” Events Among Rx. Sparing Arm (HR 1.7 in SMART) NEJM 2006;355:2283-96
HIV Associated Non AIDS(HANA)
Conditions
• After adjustment for established risk factors,
association with HIV remains
– Compare to demographically and behaviorally similar
uninfected controls
– Weaker (<2 fold) associations may be due to
inadequate adjustment for risk factors
• May be due to HIV, ART, or both
• Not necessarily closely tied to CD4 count
Premature or Accentuated Aging???
• Some studies suggest HANA conditions occur
20-30 years earlier than expected among HIV+
• Most are not adjusted for differences in the
underlying age distribution
• Others are not adjusted for differences in
established risk factors (smoking, alcohol, drug
use, or hepatitis C co-infection)
Premature or Accentuated Cancer?
A. Premature cancer : cancer
occurs earlier among those with
HIV than uninfected comparators.
Shiels MS. Ann Intern Med 2010:153:452-460.
B. Accentuated risk: cancer could
occur at the same ages but more
often than among comparators.
Multimorbidity in HIV
• In North America and Europe
– HCV co infection, alcohol, tobacco, and opioid abuse
• In Africa
– Tuberculosis, malaria, obstructive lung disease
(smoke inhalation) and alcohol abuse
• Among all those ageing: HANA conditions
– Vascular disease, liver disease, renal disease,
osteoporosis, and specific cancers
Justice AC. HIV and Aging: time for a new paradigm. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2010: &:69-76
What are the Implications of
Multimorbidity?
In the US General Population
• Screening and Treatment Guidelines do not
consider it (RCTs exclude multimorbidity)
• 50% of >65 years have >3 comorbid conditions
• A disconnect between healthcare focusing on
individual patient vs. individual disease
• Multimorbidity represents the next frontier in
the evolution of Evidence Based Medicine
Campbell-Scherer D. Multimorbidity: a challenge for EBM. Evid Based Med 2010: 15:165-166
Guidelines do not Consider
• Harms from polypharmacy
• Interactions with substance use or depression
• Hepatitis B or C
• Social issues which compete with ability to
adhere to complex treatment regimens
Guideline Overload
• Considered guidelines for 10 chronic diseases to
a panel of 2500 with age, sex, and chronic
disease prevalence matched to US
• Did not allow for new patients
• Estimated MD time required assuming
– All stable (3.5 hours/day)
– Some active disease (10.6 hours/day)
– Did not allow for new problems
Ostbye T, Ann Fam Med 2005;3:209-14
Multimorbidity is a Game Changer
• Increases treatment benefit if condition
interacts with other conditions (e.g. HCV)
• Decreases time to benefit from screening
(e.g. cancer screening)
• Increases risk of toxicity
• Creates competing demands: there isn’t time
to address HIV and primary care guidelines
and adequately care for active problems
We Need a New Paradigm
and a New Approach to
Measuring Disease to Guide Us
We Need to Prioritize Synergies
• Hypertension causes cardiovascular disease,
stroke, and renal disease
• Smoking increases risk of cardio- vascular
disease, stroke, lung disease, and cancer
• Alcohol causes microbial translocation, elevates
bp, speeds HCV progression, causes liver
cirrhosis and cancer, impedes adherence, and
may substantially contribute to vascular disease
And to Tailor Screening and
Treatment to Individual Risk
• Use prediction tools to estimate net benefit
– Rather than relative benefit
– Account for treatment disutilities
• Requires two inputs:
– Accurate estimation of risk
– Risk reduction associated with interventions
Hayward RA. et al. Optimizing Statin Treatment for Primary Prevention of CAD. Ann Int Med 2010:152:69-77
Eddy DM. et al. Individualized Guidelines: The Potential for Increasing Quality and Reducing Costs Ann Intern
Med 2011;154:627-634.
Veterans Aging Cohort Study
Risk Index (VACS Index)
An index composed of routinely
collected laboratory values that
accurately predicts all cause
mortality among those with HIV
infection
Justice, AC. et. al, HIV Med. 2010 Feb;11(2):143-51. Epub 2009 Sep 14.
The Veterans Aging Cohort Study (VACS)
• Well characterized NIAAA cohort
• >40,000 HIV+ matched to >80,000 HIV– Matched on age, race/ethnicity, region
– All HIV+ entering care since 1998
– Controls had to be seen in VA in same year
• ~10 yrs. of longitudinal data
• Clinically arbitrated endpoints for MI, stroke,
cancer, pneumonia, and cirrhosis
• Nested in-depth cohort of >7,000 (half HIV+)
31
Validated in Cross Cohort
Collaborations
• Collaborations
– ART-CC: Largely European, 19 cohorts
– NA-ACCORD: North American, 21 cohorts
• VA mortality rates are somewhat higher and
population is older and more likely to be male
• Associations with outcomes very consistent
Veterans Aging Cohort Study
Risk Index (VACS Index)
• Composed of age and laboratory tests currently
recommended for clinical management
– HIV Biomarkers: HIV-1 RNA and CD4 Count
– “non HIV Biomarkers”: Hemoglobin, hepatitis C,
composite markers for liver and renal injury
Composite Biomarkers
FIB 4 =
AGE * AST
PLT * sqrt(ALT )
eGFR = 186.3 * CREAT -1.154 * AGE -0.203 * FEM_VAL * BLACK_VAL
FEM_VAL =
0.742 if female, 1 if male
BLACK_VAL = 1.21 if black, 1 otherwise
34
34
VACS Index Thresholds and
Weights
Age (years)
<50
50 to 64
> 65
0
23
44
0
12
27
CD4
cells/mm3
> 500
350 to 499
200 to 349
100 to 199
50 to 99
< 50
0
10
10
19
40
46
0
6
6
10
28
29
HIV-1 RNA
copies/ml
< 500
500 to 1x105
> 1x105
0
11
25
0
7
14
Hemoglobin
g/dL
> 14
12 to 13.9
10 to 11.9
< 10
0
10
22
38
FIB-4
< 1.45
1.45 to 3.25
> 3.25
0
6
25
eGFR mL/min
> 60
45 to 59.9
30 to 44.9
< 30
0
6
8
26
Age
HIV
Specific
Biomarkers
Biomarkers
of General
Organ
System
Injury
Index Score
Restricted
VACS
Hepatitis C Infection
Tate J. et al. IDSA 2010 Vancouver, BC October 21-24th. Poster 1136
5
VACS Index Highly Predictive of Long Term
(5 Year) All Cause Mortality
100%
Aggregated Scores
60%
100%
40%
y = 0.0091x - 0.0318
R2 = 0.9916
80%
20%
0%
0
20
40
60
Risk Score
80
Mortality
Mortality
80%
100
60%
40%
20%
0%
Individual Scores
0
20
40
60
Risk Score
80
100
Justice, AC. et. al, HIV Med. 2010 Feb;11(2):143-51. Epub 2009 Sep 14.
Justice AC. HIV and Aging: Time for a New Paradigm. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2010 May;7(2):69-76
36
Discrimination of VACS vs.
Restricted Index
Subgroup
VACS Index Restricted Index p-value**
C-stat
C-stat
Overall
Male
Female
0.80
0.81
0.81
0.75
0.75
0.77
<0.0001
<0.001
<0.001
White
Black
Hispanic
Age
<50
>= 50
HIV-1 RNA
<500
>=500
0.79
0.81
0.90
0.74
0.76
0.78
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
0.81
0.74
0.75
0.69
<0.001
<0.0001
0.77
0.78
0.68
0.74
<0.0001
<0.0001
Justice AC. et al. A Prognostic Index for those Aging with HIV. CROI 2011 Poster # 793
Calibration of VACS vs.
Restricted Index (5 Year Mortality)
Justice AC. et al. A Prognostic Index for those Aging with HIV. CROI 2011 Poster # 793
VACS Index Response to 1st Year of cART
(+/- 80% adherence)
Solid lines indicate >80% adherence
Tate J. et al. IDSA 2010 Vancouver, BC October 21-24th. Poster 1136
39
VACS Index Correlated with
Biomarkers of Inflammation
VACS index
Rest. index
IL-6
sCD14
d-Dimer
CD4 count
FIB-4
Hemoglo…
HIV-1 RNA
Age
eGFR
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
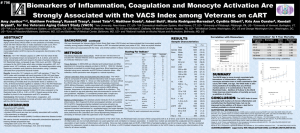
Justice AC et al,“Biomarkers of Inflammation, Coagulation, and Monocyte Activation are Strongly
Associated with the VACS Index among Veterans on cART” CROI 2011 Poster # 796
VACS Vs. Restricted Index Summary
• More accurately predicts mortality among
patients in North America and Europe
• More responsive to antiretroviral treatment
• More strongly correlated with markers of
hyper-coagulability, microbial translocation,
and inflammation
Why Should Clinicians Care?
• Uses lab tests currently part of routine care
• Identifies modifiable risk at lower test thresholds
• Incorporates age, and effects of HANA and toxicity
• Computation easy, can be included in lab reports
and available through websites/apps
• Offers approach that incorporates multifaceted
HIV effects, multimorbidity, and toxicity
Case
• HIV+ 45 yr old man. After 1 yr. of ART, CD4
count is 500 cells/mm3, HIV-1 RNA
undetectable. HCV+ and has a FIB-4 >3.25.
• Restricted Index
– Score=0
– Expected 5 yr mortality 2%
• VACS Index
– Score=30 (5 pts HCV ;25 pts FIB-4)
– Expected 5 yr mortality 12%
Case Continued
• Just as Framingham charts CVD risk over time the
VACS Index can chart overall health over time
• For this patient, we would target sources of liver
injury: HCV, alcohol, toxic medications, and obesity
• If we achieve a SVR and his FIB-4 normalizes score
drops to 0; new 5 yr mortality 2%
• If we decrease his FIB-4 from “high” to “moderate”
his score would drop to 11; new 5 yr mortality 3-fold
lower (from 12% to 4%)
Future Work
• Informatics: tools to calculate index, counsel on
risk, identify modifiable risk, and suggest
patient and provider action
• Observational Analyses: estimate likely effect
size for potential interventions: eg, alcohol
cessation, HCV treatment, adherence, etc.
• RCT: compare VACS Index guided management
to usual care among multimorbid HIV+ patients
– Possible outcomes: hospitalization, MICU
admission, nursing home placement, or death
National VACS Project Team 2010
Veterans Aging Cohort Study
•
PI and Co-PI: AC Justice, DA Fiellin
•
Scientific Officer (NIAAA): K Bryant
•
Participating VA Medical Centers: Atlanta (D. Rimland), Baltimore (KA Oursler, R Titanji), Bronx
(S Brown, S Garrison), Houston (M Rodriguez-Barradas, N Masozera), Los Angeles (M Goetz, D
Leaf), Manhattan-Brooklyn (M Simberkoff, D Blumenthal, H Leaf, J Leung), Pittsburgh (A Butt, E
Hoffman), and Washington DC (C Gibert, R Peck)
•
Core Faculty: K Akgun, S Braithwaite, C Brandt, K Bryant, R Cook, K Crothers, J Chang, S
Crystal, N Day, R Dubrow, M Duggal, J Erdos, M Freiberg, M Gaziano, M Gerschenson, A
Gordon, J Goulet, N Kim, M Kozal, K Kraemer, V LoRe, S Maisto, K Mattocks, P Miller, P
O’Connor, C Parikh, C Rinaldo, J Samet
•
Staff: H Bathulapalli, T Bohan, D Cohen, A Consorte, P Cunningham, A Dinh, C Frank, K Gordon,
J Huston, F Kidwai, F Levin, K McGinnis, L Park, C Rogina, J Rogers, L Sacchetti, M Skanderson,
J Tate, E Williams
•
Major Collaborators: VA Public Health Strategic Healthcare Group, VA Pharmacy Benefits
Management, Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center
(MAVERIC), Yale Center for Interdisciplinary Research on AIDS (CIRA), Center for Health Equity
Research and Promotion (CHERP), ART-CC, NA-ACCORD, HIV-Causal
•
Major Funding by: National Institutes of Health: NIAAA (U10-AA13566), NIA (R01-AG029154),
NHLBI (R01-HL095136; R01-HL090342; RCI-HL100347) , NIAID (U01-A1069918), NIMH (P30MH062294), and the Veterans Health Administration Office of Research and Development (VA
REA 08-266) and Office of Academic Affiliations (Medical Informatics Fellowship).