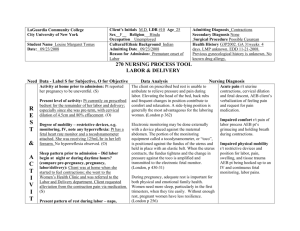
Complications of Labor & Delivery
advertisement

Normal labor is characterized by progress. Dystocia is a general term that applies to any difficult labor or birth. Causes › The Powers › The Passenger › The Passageway › The Psyche Ineffective uterine contractions › Uterine Dystocia Hypertonic Contractions Hypotonic Contractions Ineffective Maternal Pushing Hypotonic contractions › › › › Weak Infrequent Short Pt comfortable Nursing interventions › › › › Walking Position changes Amniotomy Oxytocin Hypertonic Contractions › › › › › Uncoordinated and eratic Painful but ineffective Usually occurs in latent phase High resting tone Maternal fatigue › › › › › Pain management Promote relaxation Analgesics Oxytocin or amniotomy Tocolytics may be ordered Nursing interventions Incorrect technique Fear Decreased urge Exhaustion Fetal Size Malpositions Malpresentations Multifetal pregnancy Fetal Anomalies Vacuum extraction Forcep delivery › Risks of both to the baby › Risks of both to the mother Pelvis › Pelvic Dystocia (Cephalopelvic Disproportion) Bladder Interventions Monica, a G1, P0 @ 39.4wks is admitted to L&D with occasional uterine contractions that started soon after her BOW broke an hour ago. She pauses during conversation to breath during contractions and gives a pain rating of 5. Monica states she will probably want an epidural. While performing the admission history/assessment you notice that Monica’s contractions are occurring every 2 minutes and palpate strong. Monica is beginning to demonstrate difficulty with coping during contractions. Monica grunts during her last contraction. What nursing interventions will you provide? Pain Stress Fear Support Prolonged Labor › Once in active phase should proceed at 1-2 cm/hr › Risk Factors › Nursing interventions Precipitous Labor › Birth that occurs within 3 hours of the onset of labor › Causes › Nursing interventions Spontaneous rupture of membranes prior to the onset of labor Associated conditions: › Infection STDs, UTI, GBS › Previous history of PROM › Amniotic sac with a weak structure › Fetal abnormalities › Overdistention of the urterus › Maternal stress › Trauma Determine time of PROM Verification of PROM: • Visualization • Sterile speculum exam for ferning • pH Nursing Assessment › Vital signs (temp q 2hr) › Fetal monitoring › Nature of fluid › WBC count Administration of Celestone betamethasone › PROM: preterm If leak seals, discharge instructions Defined as: labor that occurs between 20 and 37 weeks gestation. Associated conditions › › › › › › › Multiple gestation Hydraminos UTI Abdominal trauma Infection No prenatal care Low socio-economic status Cervical Length Fetal Fibronectin test › 99% accurate predictor of NO preterm birth within 7 day Infections Treat the underlying cause › Preeclampsia › Hypovolemia › Serious Infection Promote rest Hydration Tocolytics Medications prescribed to stop preterm labor › Terbutaline – B adrenergic receptor agonist › Indomethacin- Prostaglandin inhibitor › Magnesium sulfate – CNS depressant › Nifedipine - Calcium channel blocker Necessary if infant < 34 weeks (24-34 weeks) Betamethasone › Every 7 days › Birth should be delayed by 24 hours Occurs when the umbilical cord precedes the presenting part. Primary Risk Factor › Fetal head is not engaged or at a high station Vessels carrying blood to & from the fetus are compressed, usually results in fetal distress or possible demise Nursing Interventions › Knee chest position › Administer O2 › Manual lift of fetal head off the cord Causes: › Long difficult labor › Injudicious use of Pitocin › Dehisence › High parity › Blunt abdominal trauma Pain Chest pain Hypovolemic shock Impaired fetal oxygenation Absent fetal heart sounds Cessation of uterine contractions Palpation of fetus Identify the risks Use oxytocin cautiously Monitor bleeding In the presence of a small tear in the amnion and chorion, a small amount of amniotic fluid may leak into the chorionic plate and enter the maternal blood system. Can also occurs at areas of placental separation, cervical tears or during trumultuous labor The more debris (meconium, vernix, lanugo) in the amnionic fluid, the greater the maternal problems caused by possible anaphylactic reaction to fetal antigens Assessment Findings: Sudden onset Respiratory distress (dyspnea) Circulatory collapse (cyanosis) › First the right ventricle, then left Tachycardia Hypotension Acute hemorrhage › DIC Obstetrical Emergency Interventions: › CPR › Mechanical ventilation › Correction of hypotension › Blood transfusion - DIC › Emergency C/S if pregnant Prognosis – 50% of women die with the first hour of symptoms