Basics in glaucoma
advertisement

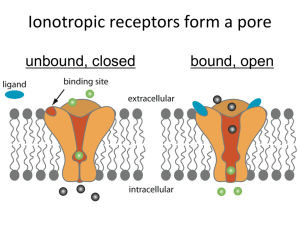
Basics in Glaucoma Dr. Sharmila Glaucoma clinic Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy with characteristic appearance of the optic disc and specific pattern of visual field defects that is associated frequently but not invariably with raised IOP Classification of glaucoma Open angle glaucoma Angle-closure glaucoma POAG NTG Juvenile open angle glaucoma Glaaucoma suspect Secondary open angle glaucoma childhood glaucoma PACG with pupillary block Acute angle closure Primary congenital/infantile glaucoma subacute angle closure CACG Secondary angle closure glaucoma with pupillary block Secondary angle closure glaucoma without pupillary block Glaucoma associated with congenital anomalies Secondary glaucoma In children Classification of glaucoma OPEN ANGLE GLAUCOMA CLOSED ANGLE GLAUCOMA DEVELOPMENTAL GLAUCOMA SECONDARY GLAUCOMA POAG Adult onset IOP > 21mm Hg Open Angles Glaucomatous nerve damage Visual field loss Risk factors Age > 65 Black race Positive family history Myopia Thin Corneas Pathogenesis Increased resistance to aqueous outflow Ischaemic Theory Mechanical theory Pathogenesis pathogenesis Symptoms Usually asymtomatic Rarely decreased visual fields Diagnosis of glaucoma History taking Visual acuity and refractive state Tonometry Gonioscopy Ophthalmoscopy Perimetry Tonometry Indentation tonometry-schiotz tonometer Applanation tonometry variable force-goldmann Tonopen variable area- maklakov Non contact tonometer Schiotz indentation Tonometry Body –footplaterests on the cornea Plunger Weights5.5gm – permanently fixed. additional weights7.5g.10g,15g Technique of schiotz tonometry Anaesthetise cornea Patient in supine position Fixes on the target Eyelids gently separated Plunger rests on cornea. Look for movement of the needle Additional weights –if reading is <4 IOP derived from conversion table Sources of error Ocular rigidity High ocular rigidity-high hyperopia,long standing glaucoma,ARMD Low ocular rigidity –high myopia,osteogenesis imperfecta,miotic therapy,retinal surgeries Thick cornea-high value Other tonometers TONOPEN GOLDMAN APPLANATION PERKINS TONOMETER Gonioscopy Goniolens[direct] Koeppe, layden, barken Gonioprism Goldman single mirror, two mirror, three mirror Zeiss four mirror Posner four mirror Normal angle structures Ciliary body band Scleral spur Trabecular meshwork Schwalbe’s line Ophthalmoscopy Disc Focal atropy Concentric atrophy Deepening of the cup Advanced glaucomatous cupping Vascular changes Haemorrhage,baring of vessels, bayonetting Retinal nerve fiber layer changes Peripapillary atrophy Perimetry Kinetic Static Visual fied defects Paracentral scotoma Seidel scotoma Arcuate scotoma Double arcuate scotoma Nasal step Angle Closure Glaucoma With pupillary block Without pupillary block Diagnosis depends on : Anterior segment examination Gonioscopy Risk factors Age Gender Asians, Chinese, Eskimos Family history Hypermetropia Pathogenesis Increased opposition between iris and lens enhance the degree of pupillary block Increased pressure in posterior chamber Increased peripheral iris bowing Iris Bombe High IOP Types Latent Subacute Acute congestive Post congestive Chronic Absolute Acute Congestive Glaucoma Symptoms Severe pain and vomiting Unilateral visual loss coloured haloes Headache and vomiting Signs Shallow AC Corneal edema Semi dilated pupil High IOP Closed angles Treatment Immediately 2% Pilocarpine Steroid eye drops Β blockers Analgesics and antiemetics Lie in supine position I.V. Mannitol + Oral T. Diamox Treatment MEDICAL AFTER CORNEA CLEARS LASER PI IF NOT POSSIBLE TRABECULECTOMY Cont.d… After 1 hr: Pilocarpine 2% Yag PI After 11/2 hr: If IOP is still high 50% oral glycerol 20% Mannitol (1-2g/kg) I.V. over 45minutes Laser Iridotomy Clear corneas Less than 1800 of angle by PAS Surgery: Trabeculectomy Congenital Glaucoma 1:10,000 births 65% are boys Pathogenesis: Maldevelopment of the angle of anterior chamber Classification Congenital Glaucoma Infantile Glaucoma Juvenile Glaucoma Clinical Features Corneal edema Buphthalmos Breaks in DM Optic disc cupping Diagnosis Increased IOP Increased Corneal diameter > 11mm at 1yr > 13mm Treatment: Goniotomy Trabeculotomy trabeculectomy Lens related Glaucomas Phacolytic: Hyper mature cataract Corneal edema AC reaction – psuedo hypopyon Open angles Treatment Anti glaucoma drugs Topical antibiotic steroids surgery Phacomorphic Galucoma Intumscent cataractous lens Shallow anterior chamber Treatment: Antiglaucoma drugs Laser iridotomy surgery Neo vascular Glaucoma Retinal ischaemia NVI NVA OPEN ANGLE ANGLE CLOSURE Causes Ischeamic CRVO Diabetes Mellitus Miscellaneous Carotid disease Intra ocular tumor Long standing RD Symptoms & Signs Decreased visual acuity Congestion of Globe Very high IOP and corneal edema Severe pain Aqueous flare NVI Gonioscopy - NVA Treatment Medical – topical Atropine & steroids Retinal ablation / - DIODE CPC Surgery: Trab with MMC Aqueous drainage shunts Retrobulbar alcohol injection Enucleation Treatment Modalities in glaucoma Medical Laser Surgery – Trabeculectomy combined surgery Anti Glaucoma Drugs Β blockers Decreases IOP by decreasing aqueous secretion Contra indications: Congestive cardiac failure Heart block Bradycardia Bronchial asthma Side effects Iotim, Nyolol, Glucomol 0.5% bd Ocular Systemic allergy Bradycardia, Hypotention SPK’s Broncho spasm tear secretion Hallucination, head ache nausea, dizziness Alpha 2 Agonists Brimonidine, apraclonidine Mechanism: Decreases aqueous secretion Increases uveo scleral outflow Side Effects: Allergic conjunctiviti s Xerostomia Drowsiness and headache PROSTAGLANDIN ANALOGUES Mechanism Decreases IOP by increasing uveoscleral outflow Latanoprost F2 α analogue.005% Travoprost 0.004% Bimatorpost 0.3% Unoprostone 0.15% BD Side Effects Conjunctival hypereamia Eye lash growth and hyperpigmentation of periorbital skin Anterior uveitis Cystoid macular edema MIOTICS Pilocarpine 1% 2% 3% 4% QID Parasympathomimetic stimulates muscarinic receptors in sphincter pupillae & ciliary body In POAG – increases aqueous outflow In PACG – opens the angles Side Effects Miosis Browache Myopic shift Visual field defect Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Inhibits aqueous secretion Topical CAI Dorzolamide (Trusopt) Brinzolamide (Azopt) Systemic CAI Acetazolamide 250mg BD Side Effect Parasthesia Malaise GI upset Renal Stone Blood dyscrasias Hyper Osmotic Agents Glycerol 1g / kg in 50% solution Mannitol 1-2g/kg in 20% solution Side Effects: Cardiac or renal failure Urinary retention Head ache, nausea Lasers in Glaucoma Laser Iridotomy: Indications: PACG Occludable angles SACG with pupillary block Combined mechanism glaucoma Laser PI prerequisites Instil 1% Apraclonidine Miotic pupil Laser settings 4-8 mJ Post laser steroid eye drops Abraham lens Complications Bleeding Iritis Corneal burn Glare Diplopia Surgery Trabeculectomy: A conventional filtering procedure creates a new channel for aqueous outflow between the anterior chamber and subtenons space without the use of an artificial device Partial thickness Full thickness Management of coexistent cataract and glaucoma Complications Wound leak Excessive filteration Pupillary block Malignant glaucoma Hypotony Choroidal detachment Failing bleb SIGNS • Injection • Vascularisation • Thickening • Localization • High domed Bleb • Normal / High IOP • Low IOP Initial few weeks critical Failing filtration Frame work for Classification • IOP • Bleb Failing filter – High IOP Low localized Bleb External Internal - Subconjunctival fibrosis - Tight scleral flap sutures - Sclerectomy obstruction Failing filter – High IOP High domed bleb – encapsulated bleb or Tenon’s cyst Failing filter - Low IOP Low bleb - Bleb leak Elevated diffuse bleb - Over Filtration hypotony Bleb Failure Argon laser suturolysis 0.2sec 50µ 500-700mw Digital massage Topical steroids 5FU injection DF Nd yag laser Needling of tenons cyst REFRACTORY GLAUCOMA AQUEOUS DRAINAGE IMPLANTS Refractory glaucomas Cyclo destructive procedures New diagnostic and surgical procedures Central corneal thickness assessment OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY ULTRASOUND BIOMICROSCOPY Classification of glaucoma OPEN ANGLE GLAUCOMA CLOSED ANGLE GLAUCOMA DEVELOPMENTAL GLAUCOMA SECONDARY GLAUCOMA