classification of vascular anomalies
advertisement

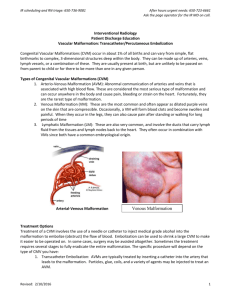
Updated ISSVA (International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies) Department of diangosis imaging Children’s Hospital 2 INTRODUCTION • Vascular anomalies are among the most common congenital abnormalities observed in infants and children. • Older nomenclature continues to cause confusion, misunderstood diagnoses, and potential mismanagement • In 1982, Mulliken and Glowacki proposed a classification system for vascular anomalies based on their clinical behavior and endothelial cell characteristics into two groups: hemangiomas and vascular malformations.This system, which was adopted by the ISSVA, has since been expanded and is now widely accepted. • Radiologists can use the ISSVA classification system by correlating imaging findings with patient history and physical findings. Consistent use of this system will help patients receive the correct diagnosis and treatment. Traditional classification • • • • • • • • • Capillary hemangioma Strawberry hemangioma Strawberry nevus Port wine stain Flame nevus Cavernous hemangioma Venous angioma Lymphangioma Arteriovenous malformation CLASSIFICATION(ISSVA) Vascular anomalies Vascular tumors Infantile hemangioma Vascular malformations Slow-flow Fast-flow vascular malformations vascular malformations Capillary malformation(CM) Venous malformation(VM) Lymphatic malformation(LM) Arterial malformation(AM) Arteriovenous fistula(AVF) Arteriovenous malformation(AVM) Updated ISSVA classification of vascular anomalies. Vascular tumors • • • • • • • Infantile hemangiomas Congenital hemangiomas (RICH and NICH) Tufted angioma (with or without KasabachMerritt syndrome) Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (with or without Kasabach-Merritt syndrome) Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma Other, rare hemangioendotheliomas (epithelioid, composite, retiform, polymorphous, Dabska tumor, lymphangioendotheliomatosis, etc.) Dermatologic acquired vascular tumors (pyogenic granuloma, targetoid hemangioma, glomeruloid hemangioma, microvenular hemangioma, etc.) Vascular malformations 1..Slow-flow vascular malformations: • Capillary malformation (CM) – – – • Port-wine stain Telangiectasia Angiokeratoma Venous malformation (VM) – – – – – Common sporadic VM Bean syndrome Familial cutaneous and mucosal venous malformation (VMCM) Glomuvenous malformation (GVM)(glomangioma) Maffucci syndrome • Lymphatic malformation (LM) 2. Fast-flow vascular malformations: • Arterial malformation (AM) • Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) • Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 3.Complex-combined vascular malformations: • CVM, CLM, LVM, CLVM, • AVM-LM, CM-AVM C:capillary; V:venous; L:lymphatic; AV:arteriovenous; M:malformation. RICH:rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma; NICH:noninvoluting congenital hemangioma. Differentiating Features Hemangioma •True tumors, with proliferation of the vascular endothelium • >3:1 female:male •Small or absent at birth •Rapid growth during infancy •“self-limited” •Diagnosis:Clinical history+ appearance Vascular Malformations •No tumor, Comprised of dysplastic vessels •1:1 female:male •Present at birth •Growth proportional to child • never disappear •Diagnosis: MRI,Doppler ultrasonography,angiography Comparison of Previous Terminology and New ISSVA Terminology Previous ISSVA •Capillary or cavernous Hemangioma of any organ • •Infantile hemangioendothelioma of the liver •Hepatic or infantile hemangioma •hepatic hemangioma, cavernous hemangioma • Infantile hemangioma Venous malformation • Lymphatic Malformation •Lymphangioma,Cystic hygroma •Port-wine stain,Capillary Hemangioma • Capillary Malformation Key Imaging Features of the Most Common Pediatric Vascular Anomalies Differentiation between Hemangioma and Hemangioendothelioma of the liver Classification of Vascular Tumors • Benign tumors and tumor-like conditions – Hemangiomas – Spindle cell hemangioma (‘hemangioendotheliomas’) – Epithelioid hemangioma • Low-grade malignant tumors – – – – Retinform hemangioendotheliomas Composite hemangioendotheliomas Polymorphous hemangioendotheliomas Kaposiform hemangioendotheliomas • Malignant tumors – Epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas – Angiosarcoma HEMANGIOMA Arterio-Venous Malformation(AVM) congenital hemangioma Infantile hemangioma HEMANGIOMA Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma with Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon Hemangioma • Benign endothelial cell tumor • 2 main types 1. Infantile Hemangioma • • • • Most common tumor of infancy/childhood Usually has overlying patch of redness Appears weeks/months after birth Natural course - 3 stages 1. Proliferating - first year 2. Involuting - few years 3. Involuted - most resolved by age 10 Hemangioma(cont) 2. Congenital Hemangioma • • • • Present at birth Rare (compared to infantile) Blue/gray hue w/ pale halo (skin) 2 types – Non-Involuting (NICH) - persistent – Rapidly Involuting (RICH) - resolved by 1-2 yrs Lymphatic malformations • Commonly occur in the cervicofacial region, Lymphatic malformations in an extremity can cause diffuse or localized swelling with soft-tissue and skeletal overgrowth Venous Malformation (VM) • Present at birth • skin discoloration, local swelling, and pain • Thin-walled, dilated veins:Inadequate smooth muscle layer • Complications: Thrombosis, bleeding Venous Malformation (VM) Arterio-Venous Malformation (AVM) • Present at birth • Reddish vascular hue (skin), often warm pulsations, thrill, and bruit • High-flow arterio-venous communication absence of developed capillary bed • Complications: ulceration, bleeding,pain, compression/displacement of organs, highoutputcardiac failure Arterio-Venous Malformation (AVM) AVM Summary of Regional and Diffuse Syndromes Associated With Vascular Malformations • Regional syndromes with associated vascular malformations – – – Sturge–Weber: facial capillary malformation with intracranial capillary malformation, venous malformation, or AVM. Klippel–Trenaunay: limb/trunk capillary venous lymphatic malformations with overgrowth. Parkes Weber: CAVM with overgrowth; lymphatic malformation. • Diffuse syndromes associated slow-flow malformations – – – – Proteus syndrome: vascular malformations (capillary or venous), hamartomatous syndrome with overgrowth(hemihypertrophy and macrodactyly), lipomas, pigmented nevi. Blue rubber bleb nevus (Bean) syndrome: multiple cutaneous, musculoskeletal, and gastrointestinal tract venous malformations. Epidermal nevus syndrome (Solomon syndrome): vascular malformations (intracranial AVM), epidermal nevi, various developmental abnormalities of the skin, eyes, nervous, skeletal, cardiovascular, and urogenital systems. Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome: vascular malformations (cutaneous, intracranial), macrocephaly, ectodermal dysplasia, lipomatous masses, and intestinal hamartomatous polyps, PTEN suppressor gene mutation association. • Diffuse syndromes associated fast flow malformations – Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler–Weber–Rendu): telangiectasias (skin, mucous membranes, gastrointestinal mucosa) and AVMs (lungs, liver, brain, spinal cord). AVM, arteriovenous malformation; CAVM, capillary arterial venous malformation; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog. OVERGROWTH SYNDROMES: • Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome which is a lowflow combined vascular anomaly (capillarylymphatic-venous malformation) usually associated with marked overgrowth of the leg and capillary stains. • Parkes-Weber syndrome consists of an AVM-like high-flow malformation that involves the entire extremity (usually a lower limb), and it is usually associated with a capillary malformation over the enlarged limb. Simple malformations • slow flow – capillary – lymphatic – venous • fast flow – arterial • aneurysm • coarctation • ectasia – arteriovenous fistulae (with one ore more shunts) – arteriovenous malformations (with a nidus of multiple shunts) Complex malformations • regional – Sturge-Weber syndrome – Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome – F. P. Weber syndrome • diffuse – Maffucci syndrome – Solomon syndrome – Proteus syndrome Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) Low flow malformations • Lymphatic Malformations -Microcystic -Macrocystic • Venous Malformations • Capillary Malformations • Combined types