Edible Tectonics
advertisement
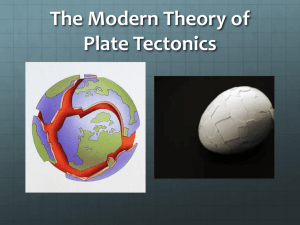
Edible Tectonics Bellwork Agenda: Create 4 part foldable about the types of boundaries. Clear off desk except for journal. Add to your layers of the Earth illustration, label, and explanation. With the vocabulary words, try to match the words to the correct definition. Layer that is thinner than the others and nearly all solid rock. This layer is about 750 mi thick and is the hottest layer. It is solid made up of very hot iron and nickel. High pressure here keeps these metals from melting. This layer has both solid and melted parts. The melted, yet still solid part flows very slowly. The solid upper layer of the mantle and the crust join to form this. This layer is the only liquid layer on Earth. It is about 1400 mi thick. This liquid is extremely hot. Today’s Journey 0507.7.1 Create a model to illustrate geologic events responsible for changes in the earth’s crust. 0507.7.2 Prepare a chart to compare how volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting, and plate movements affect the earth’s surface features. State Performance Indicators SPI 0507.7.1 Describe internal forces such as volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting, and plate movements that are responsible for the earth’s major geological features such as mountains, valleys, etc. Edible Tectonics As you know the Earth’s crust and upper mantle combine to make the lithosphere. These plates “float” on the asthenosphere or middle mantle. As the convection currents rise and fall, the plates move in a variety of ways. These ways are known as boundaries. There are 4 main types of boundaries. Divergent Convergent Subduction(a type of convergent boundary) Transform With your 3-4 person team, get the picture and label cards that represent these boundaries and try to match them together. (Save the descriptions for later.) Edible Milky Way Tectonics Each of you have 2 fun size milky ways. We are going to use these to demonstrate the types of boundaries present that cause geologic features such as volcanoes, earthquakes, mountains. trenches, etc. 1-Take a moment with your team and come up with an operational definition for plate tectonics Look at one of the fun size candy bars. Observe the cross-section of the candy bar. Carefully pull the candy-bar apart in half. Illustrate this and label it candy-bar cross-section in your journal. Illustrate your observations. Label it “pulled apart.”Talk with your partners; what do you notice? The candy-bar will be used as a model of Earth. Identify Characteristics of the candy-bar which make it suitable to model the layers of the Earth. Draw the inside cross-section of the candy-bar and label what each part could represent. Divergent Boundaries Also called spreading centers because they are fractures in the lithosphere where the plates are moving apart, as in the Mid-Ocean Ridge system or rift valleys like the one running through eastern Africa. As the plates separate, pressure on the mantle directly below decreases. The decrease in pressure causes the temperature in that portion of the mantle to rise above its melting point. The small amount of melting mantle produced rises to the surface and erupts creating new crust, as well as earthquakes and volcanoes. Diverging Boundaries What types of geologic features could be created by this? Now take the candy-bar and gently push it back together. What happens to the chocolate? Illustrate what the candy-bar looks like now. Label it “pushed together.” What type of geologic features could this make? Convergent Boundaries When two plates with continental crust at the leading edge collide, they buckle and are pushed upward, creating towering mountain ranges like the Himalayas, the Alps and the Appalachians. (The Rockies were not created by convergent plates. They were formed by glaciers.) Another type Now take the candy bar and force it even harder together. What happens? Illustrate this cross-section now. You should notice that the parts pushed hard together are forced so tightly that one half goes below the other. What types of features do you think this makes? Subduction Boundaries Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust and considerably less dense. When dense ocean crust collides with a continental crust, the ocean crust bends and slides under the continental crust. As it plunges deep into the mantle the plate going under dehydrates. The super hot water coming out of it, causes the overlying mantle to melt and create volcanoes. When oceanic crust on one plate collides with oceanic crust on another plate, one plate will slide under the other. A deep oceanic trench forms at the boundary. The molten rock of the plate that went under rises through the overriding plate, erupting on the surface to create volcanic mountains or chains of volcanic islands. How are subduction boundaries similar to converging boundaries? These are similar because they are both being pushed together! However, in subducting boundaries, the denser crust will bend and slide under the continental crust. One side goes under like a submarine! Now open your other candy-bar. Place both candy-bars side by side- one in each hand. Now gently push the right hand piece of candy away from you while pulling the left hand piece toward you. The sides may stick together so you may have to increase the force of your push. What do you observe? Transform Boundaries A place where two plates slide past each other is another type of boundary. These plates catch and grind causing powerful earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault, responsible for the devastating earthquakes in San Francisco and Los Angeles, is this type of boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. Let’s look at a couple videos! Basic Boundaries http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/animations/basic_pl ate_boundaries.htm http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/conte nt/visualizations/es0804/es0804page01.cfm?chapter_no=vi sualization Divergent http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/animations/the_pro cess_of_rifting.htm Subducting: http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/animations/the_pro cess_of_subduction.htm Let’s look at all the types. Can you identify them? http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/animations/earth3e Brainpop-Plate Tectonics /04.htm http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/platetectonics/ Today’s Journey 0507.7.1 Create a model to illustrate geologic events responsible for changes in the earth’s crust. 0507.7.2 Prepare a chart to compare how volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting, and plate movements affect the earth’s surface features. State Performance Indicators SPI 0507.7.1 Describe internal forces such as volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting, and plate movements that are responsible for the earth’s major geological features such as mountains, valleys, etc. Use the worksheet given to answer more about what you know about plate tectonics.