15.05.14 Revision Plate Boundaries
advertisement

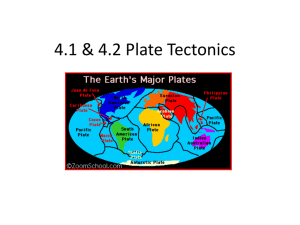
Layout and Revision for Summer Test • Short Questions – – – – – Plate Tectonics The Rock Cycle Earthquakes Volcanoes Fold Mountains • 3 Long Questions – Physical Geography – Formation of rock type and landscape – Regional Geography – Factors that influence Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Activities in a Core/Peripheral Region you have studied – An Irish Core Region (GDA) –An Irish Peripheral Region (BMW) – Sketch Map of a region you have studied ms cummins PLATE BOUNDARIES EXAM PAPERS (LONG QUESTIONS – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY) – 2007 QUESTION 1 PART B “Plate boundaries are zones where crust is both created and destroyed”. Examine the above statement, with reference to examples you have studied. (30 marks) • Marking Scheme • Name one example of each boundary: 2 marks + 2 marks • Discussion re creation/destruction: 7 (6) SRPs or 6 (7) SRPs • KEY WORDS • Crust created at divergent plate boundaries • Convection currents • Magma cools and solidifies • Crust destroyed at converging plate boundaries • Heavier plate subducts (destructing plate) • Trench marks point of subduction • Volcanic landforms may be created • Fold mountains Types of Plate Boundaries Constructive Plate Boundary (Divergent) Destructive Plate Boundary (Convergent) Transverse/Transform Plate Boundary (slide) Divergent (Constructive) Plate Boundary – Plates separating • Crust is created at a Divergent (Constructive) Plate Boundary (2M) • These Boundaries occur where plates are pulled apart by convection currents below (2M) • The crust splits allowing magma to rise and fill the gap making new crust (2M) • Over millions of year repeated separations and eruptions have formed the ocean floors. (2M) • An example of a landform resulting from Sea Floor Spreading is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (2M) • The sub-merged Mountain Range stretches over 40,000 km from the North to the South Pole (2M) • Iceland has formed where the Mid-Atlantic Ridge appears above the sea. (2M) • Iceland is getting wider due to the process of sea floor spreading. On one side of the country is the North Atlantic Plate on the other side is the Eurasian Plate. (2M) • The crust is moving apart at a rate of 5cm a year. Working out at about 25km per million years. (2M) Divergent/Constructive Plate Boundary Convergent (Destructive) Plate Boundaries – Crust Colliding • At destructive Plate Boundaries plates crash together and crust is destroyed. (2M) • There are 3 situations where this can happen: 1. Oceanic and Continental Plates collide 2. Oceanic and Oceanic Plates Collide 3. Oceanic and Continental Plates Collide (2M) 1. Oceanic and Continental Plates collide – Andes Mountains • When an Oceanic Plate collides with a Continental Plate the heavier oceanic plate is submerged under the Continental plate and is destroyed. (2M) • Sediments are sliced off from the sea floor of the Oceanic Plate as it descends. These sediments create “terrains” of land which stick to the continental plate, eventually building up to form fold mountains. (2M) • As the Oceanic plate slides under the Continental plate it melts and is recycled into magma – sub-duction. (2M) • The newly formed magma moves up through the continental crust above creating volcanoes (2M) • The Pacific ring of fire is named so because many active volcanoes created at sub-duction zones mark the edge of the pacific plate (example Mount Fuji) (2M) The Andes Plate Boundary – Nasca Plate slides under South American Plate Oceanic – Oceanic example: The Marina Trench Continental – Continental example: The Himalayas Continental-Continental Convergence Complete the following Revision Questions on Physical Geography: • Chapter 1 - Plate Tectonics – Revision Questions – 4, 6, 8, 10,12, 13, 14 • Chapter 2 – Earthquakes – Short Questions, 9, 10, 11, 12 – Long Questions, 13, 14 • Chapter 3 – Volcanoes – Short Question 9Long Questions, 10/13 and 14