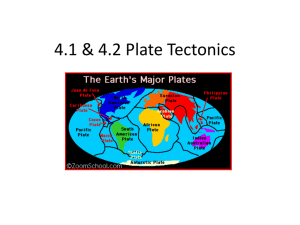
Plate Tectonics - Ms. Hilgefort`s Science Classroom
advertisement

Bell Ringer Freshwater reptile Mesosaurus • Fossils of a fresh water swimming reptile, Mesosaurus (Figure 2) have been found on the east coast of southern Brazil and the west coast of Africa. This reptile could not possibly have swum the 3,000-mile distance across the South Atlantic Ocean. • How could we possibly explain this? Discovering Plate Tectonics: The Mystery of the Brachiosaurus • Mystery of the Brachiosaurus Uncovered Puzzle Key and Landmasses • Try to figure out how to answer the question of how Mesosaurus appeared on two continents 1. Assemble the pieces so that they fit together like a puzzle 2. When finished, raise your hand to be checked. 3. Answer the questions #1-5 in Part 1 on your worksheet Continental Puzzle Analysis Questions 1. What made you put the puzzle pieces the way that you did? Were there any clues that helped you put the pieces a certain way? 2. What three kinds of evidence support Wegner’s theory that South America was at one time joined with Africa? Be specific! (hint: look at the key) 3. What dinosaur is found on almost every continent? 4. Since a dinosaur cannot swim, explain how a fossil can be found on all continents? 5. It is generally considered that dinosaurs live in warm climates, yet fossil remains are found in Antarctica. Convection Current Demonstration • • http://www.teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=137741 http://teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=261126&title=Convection_Currents Action of the Red Dye • What temperature was the red dye? • In what direction did the red dye move? • What do you think the density of the red dye is compared to the water? Why? Foam Plates • What caused the foam plates to move? • Describe the movement of the foam pieces when the dye started to rise. Could you see a pattern? Topic: The Lithosphere, Pangaea, and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Cornell Notes Key Terms Summary: Notes 1. Q: What is the lithosphere made up of? A: Crust and Upper Mantle Continental Drift • Wegener came up with a theory in 1910 called Continental Drift. • His theory said that the continents had started as one big “super continent” called Pangea. Continental Drift • Over millions of years, Pangaea broke apart into the 7 continents. Continental Drift • During Pangaea, continents had completely different environments.. Evidence that supported Wegener’s Theory • Landforms – Example: Some mountain chains, have very similar rocks and structures (i.e., folds and faults) to mountain belts found on other continents • Fossil Evidence - There are many examples of fossils found on two continents that are currently separated by vast oceans – Example: Mesosaurus Evidence that supported Wegener’s Theory • Climate –Example: Glacial striations, the parallel "scrape" marks on rocks caused by moving glaciers, have been found on rocks in South America, Africa and Australia and are of similar orientation to striations found on Antarctica • Puzzle-like Fit of the Continents-in several cases, modern shorelines of continents look as though they were once joined – Example: Africa and South America are the best example of these “puzzle pieces” Continental Drift Rejection • Scientists at the time rejected his theory because he could not come up with an explanation why the continents were actually moving. Plate Tectonics • Plate Tectonics is the theory that the lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) is made of moving plates that float on the mantle. • Convection currents cause magma in the asthenosphere to rise and sink. • The plates are slowly moving and bump into each other Discovering Plate Tectonics: Changes in Earth’s Surface Plate Tectonics: Understanding Earth’s Shifty Surface Versatile • Finish for homework –Write letter and word for answers –Cite evidence for each questions by highlighting/underlining passage in reading that supports answer –All 12 numbers should be displayed on reading Continental Drift Reading “Draw a picture”- As I read the passage aloud, draw (pictures) of what you are hearing about evidence of continental drift. *Try to draw at least one picture per paragraph Pangea Writing Prompt • You are Wegener’s defense attorney. Using your knowledge of the lithosphere, asthenosphere, Pangaea, and evidence for continental drift (190-195), write two paragraphs that defend his hypothesis. • (Think: What do we know about the lithosphere? The asthenosphere? Pangea?) Lithospheric Movement Review 1. What is Alfred Wagner’s hypothesis? a.The continents have always been where they were now? b.Today’s continents were once part of a single land mass that split apart c. The continents are made of rock d.The continents will one day join to form a single continent. 2. List three pieces of evidence for Pangaea: 3. What causes earth’s tectonic plates to move? Use the words density and convection current to explain what’s happening? Bell Ringer Answer the following questions 1.Draw arrows convection currents in the mantle of the earth—label hot, cold and High density, Low density. 2. What is Pangaea? 3. Describe what causes the lithospheric plates to move. Evidence Our first evidence of tectonic motion is based on similar fossils and rock types on opposing sides of the ocean Lithospheric Plates Review • The earth’s crust is divided into plates, and these plates move (that’s why Pangaea broke apart) • The plates move because of convection currents underneath the Earth (PLAY VIDEO!) • But other than Pangaea breaking apart, what happens when the plates move? Types of Plate Boundaries • Plate Boundaries: Where two lithospheric plates meet –Divergent (what does “diverge” mean?) –Convergent (what does “converge” mean?) –Transform Plate Boundaries Brainpop • http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/platete ctonics/ 1. Match the definitions with the words 2. For each geologic feature, write down which plate boundary could cause it. Use Convergent (C), Divergent (D), or Transform (T) Plate Boundaries Tree Diagram Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent Convergent Transform Description Description Description Landforms Landforms Landforms Picture Picture Picture Tectonic Plates Versatiles • Finish for homework –Write letter and word for answers –Cite evidence for each questions by highlighting/underlining passage in reading that supports answer –All 12 numbers should be displayed on reading Bell Ringer 1. Scientists found fossils of identical creatures on Africa and South America. What does this tell you about the Earth? a. Africa and South America are the same continent b. Africa and South America used to be next to each other c. All animals are on each continent d. All of these animals can swim or fly long distances 1. Which of the following has caused the continents to spread apart? a. The eruption of volcanoes b. Huge plates moving underneath the ground have moved the continents apart c. The shaking of the ground caused by earthquakes d. The continents have always been spread apart. Divergent Plate Boundaries Divergent Video Divergent Cornell Notes Key Terms Summary: Notes Divergent Boundary • When two plates move or spread apart from each other – Connection: What causes them to move apart from each other? – What hand motion would you use? • http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0804/es0804page0 1.cfm?chapter_no=visualization What does this actually look like? Video 1: http://www.videosurf.com/video/divergent-boundary-119597587 And Video 2: http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=2ED78244-ED66438C-B2DD-55C2D810C4A1&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Two Oceanic Plates Diverging • Causes Sea-Floor Spreading • As plates spread, magma comes up and cools and hardens, forming new crust. • As new rock piles on top of each other, mountain form under the ocean • Mid-ocean ridge- Mountain range on ocean floor Age of Rocks • As the plates spread and magma hardens to form rocks—we get the newest rocks on Earth near diverging plates. Two Continental Plates Diverging • Creates a Rift Valley or Ocean Basin • As the continental plates diverge, they sink and can fill with water making a sea! --the Great Rift Valley, East Africa --the Red Sea Ireland: Hikers walk in the shadow of cliffs. The divergent Mid-Atlantic Ridge rises above sea level, with the North American plate to the west and the Eurasian plate to the east. Divergent Plates- Plates move apart Oceanic Continental What happens Sea-floor spreading happens and magma comes up and cools – forms new rock Plates spread and then sink to form a basin (bowl shape) or rift valley What forms Mid-ocean ridges Seas Example: the Mid- Example: the Red Atlantic ridge Sea Sea-Floor Spreading Lab • Using the model, answer the questions with your partner • When finished, begin “Divergent Homework” Bell Ringer #4 • Create a venn diagram that compares and contrasts continental plates diverging and oceanic plates diverging Continental Both Oceanic • Divergent boundaries • Convergent boundaries • Transform boundaries Today we are learning about CONVERGENT! Convergent Boundaries • There are two things that can happen when two plates move towards one another –1. One sinks under the other and starts to melt –2. They both collide and start to crumble and pile up. Types of Convergent Boundaries • Oceanic - Oceanic • Oceanic - Continental • Continental - Continental • The only difference between the two type of plates is the rock composition and the density. Oceanic – Continental (subduction) • Oceanic plates is more dense than continental plate • Ocean lithospheric plate will always sink under (subduction) continental plates because it is more dense! • Volcanoes • Ring of Fire in Pacific Ocean Oceanic – Oceanic (subduction) • Same density; • Oldest plate will go under (subduction) younger plate • Trenches & Volcanoes • Mariana Trench DRAW IT OUT! Continental-Continental (collision) • Plates have the same density • Plates collide and crash into each other– lithosphere folds like wrinkles • Mountains • Himalayan Mountains Types of Convergent Boundaries Relative Density What happens OceanicOceanic OceanicContinental ContinentalContinental Both have same density, but one is older Older plate goes under the other (subduction) Oceanic is more dense than continental Ocean plate goes under the continental plate (subduction) Volcanoes Exp: Ring of Fire Both have same density Landforms Volcanoes and ocean trench Exp: Mariana Trench They hit each other and squish upwards Mountains Exp: Himalaya Mountains Convergent Plates The Big Picture Where are we going? We appear to be headed for another super continent as North America, South America, Asia and Australia converge in the ever shrinking Pacific Ocean Convergent Inquiry Lab 1. What does Map 1 represent or have on it (hint: look at the title and extras on the map)? – Location of volcanoes 2. What does Map 2 represent or have on it (hint: look at the title, key and colors)? – Plate boundaries: Red Convergent, Blue Divergent, Green Transform 3. Place Map 1 and Map 2 side by side. Convergent Inquiry Lab 4. What do you notice now that the two maps are together? • The large clumps of volcanoes line up with the plate boundaries 5. What color line/boundary do the volcanoes line up with? • Red lines 6. What does this color mean (hint: look at the key)? • Convergent Plate Boundaries (2 plates are coming towards one another) 7. Why do you think that these plate boundary lines and volcano lines match up? • Volcanoes are formed at convergent boundaries/subduction zones Convergent Inquiry Lab • Independently answer question 8 • Based on what you have seen and what you know about Continental Drift and Convection Currents, how do you think volcanoes form? • When finished with #8, begin “Convergent Homework” Bell Ringer #5 1. Explain what the Ring of Fire is and why it occurs in the Pacific Ocean. – Areas in the Pacific Ocean that contain large amount of volcanoes because plates are converging/subducting 2. What is happening to the sizes of the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean? Explain. – Pacific ocean is getting smaller because it contains subduction zones; Atlantic ocean is getting larger because plates are diverging and new crust is being formed (Mid-Atlantic ridge) Ring of Fire= Subduction Zones Transform Plate Boundaries Explaining the Phenomenon of Earthquakes • Divergent boundaries • Convergent boundaries • Transform boundaries Today we are learning about TRANSFORM! Earthquake Brainpop Earth’s Structure Brainpop • How do earthquakes help scientists study the interior of the earth? – Seismic waves (earthquake waves) bend differently through different materials, so scientists observe the way the waves bend to determine the temperature, density, and composition of each layer Transform K.I.M Chart Key Term (K) Information (I) Memory Cue (M) Transform boundaries • Two plates slide past each other http://www.classzone.com/b ooks/earth_science/terc/con tent/visualizations/es0804/e s0804page01.cfm?chapter_ no=visualization Earthquakes • Occur at transform boundaries because great tension can build in the plates • Eventually the plates snap and release all of the stored tension and shake the earth Faults • Cracks in the earth crust that occur when plates snap • Example: San Andreas Fault (California) Focus • The point deep underground in which the fault fails Epicenter • Spot on earth’s surface directly above the focus Seismograph • Instrument that detects, measures, and records various seismic waves (Primary, Secondary, and Surface waves) Primary (P) Waves • Quickest wave and detected first; travel through solids, liquids, and gases Secondary (S) Waves • Second fastest waves; only travels through solids Surface Waves • Slowest and most damaging waves Tsunami • “Harbor Wave” in Japanese • Giant waves caused by earthquakes occurring on the ocean floor – Japanese Tsunami – Mega tsunami Frequent Earthquake Areas • The pink lines show where transform boundaries exist: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dyna micearth/plate.html • News about Haiti: http://www.cbsnews.com/news /four-years-after-earthquakehaiti-says-its-makingcomeback/ HAITI CALIFORNIA JAPAN INDIA Think Earthquakes are rare? • Think again: http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=eart hquake • Over half a million magnitude 1 earthquakes a year! Earthquake Versatiles • Finish for homework –Write letter and word for answers –Cite evidence for each questions by highlighting/underlining passage in reading that supports answer –All 12 numbers should be displayed on reading Transform Review 1. Draw a transform boundary. 2. What natural disaster or physical feature is caused at a transform plate boundary? 3. How are volcanoes and earthquakes related? Bell Ringer • Classify the following as constructive (C), destructive (D), or both (B) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Volcanoes resulting in islands Erosion Deposition Physical Weathering Chemical Weathering Plate Tectonics Gizmo • Volcanoes, earthquakes, mountains, and other features of Earth’s surface owe their origin to the movements of plates: enormous, slowly-moving sections of Earth’s crust. At plate boundaries, plates collide, move apart, move under or over each other, or slide past one another. The theory of plate tectonics describes how the plates move, interact, and change the physical landscape. • Turn on Show labels. What are the layers of Earth that you can see? • Turn on Boundary name, and click on each boundary. What four boundaries do you see? Plate Boundary Organizer • When finished, organize the information about convergent (subduction and collision), divergent, and, transform boundaries using the information in your notebooks. • Homework if not finished in class. Bell Ringer • Write down the three words: Divergent, Transform, and Convergent • Put the words below under the correct term –Moving together –Moving apart –Sliding past –Earthquakes –San Andreas Fault -Trenches -Mountains -New crust -Mid-Atlantic ridge -Volcanoes Snack Plate Tectonic Lab! Follow directions and work hard or you won’t get to eat it! Expectations! Snack Tectonic Lab Questions • Like all labs, this comes with questions as well. When you are done performing the step, answer the questions. • If you fall behind, make sure you go back and complete the questions before turning in your lab. 1:03 1:32 1:53 Snack Tectonic Lab Closure • From the lab questions, be prepared to share with the class your answers to question #16 and #17. • Homework: Plate Boundaries Map Worksheet (1/2) Bell Ringer 1. Give one example of how plate movement directly affects the construction of earth’s surface (#16 on lab) 2. Give one example of how plate movement directly affects the destruction of earth’s surface (#17 on lab) THE OCEAN FLOOR THE OCEAN FLOOR • Many of today’s continent’s were once underground • Georgia was under an inland sea hundreds of millions of years ago • Just like the continents, the ocean floor has mountains, valleys, volcanoes, and plains • How do we get information about the ocean floor? • http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/news/env ironment-news/us-ocean-floor-mapping-vin/ OCEAN FLOOR FEATURES • Continental Shelf: A long, gently inclined area where continent enters ocean • Continental Slope: Steep side of continental shelf that is the end of the continent OCEAN FLOOR FEATURES • Mid ocean ridge= An underwater mountain range where new crust forms when plates move apart. • Mid-Atlantic Ridge-world’s longest ridge formed by the North and South American plates diverging from the Africa and Eurasian plate OCEAN FLOOR FEATURES • Abyssal plain= flat areas on the ocean floor between the continental slope or trench and a midocean ridge OCEAN FLOOR FEATURES • Seamount: Underwater Volcano • Beach: Forms as a result of waves and currents moving sand and sediment toward the shore OCEAN FLOOR FEATURES • Trench= steep, deep cavern on the ocean floor that forms when plates converge and one plate is subducted under another • Mariana Trench : 36,201 feet (near Guam) • It’s so deep that you could fit Mt. Everest inside of it! THE OCEAN FLOOR Label the picture of the ocean floor using your K.I.M Chart. Disney Ride Task • You have been hired by Disney to create a new ride at Disney World modeling the ocean floor. You need to have a script for your Disney imagineer to say to the patrons during the ride (describing the features), as well as a picture of your ride. The sketch of the ride and the script must include: – Label 7 features on your picture of the ride – Highlight/Underline 7 features in your script 1. 2. 3. 4. Continental Slope Abyssal Plain Seamount Mid-Ocean Ridge 5. Continental Shelf 6. Beach 7. Trench Rubric: – – – – Diagram of ride: 35 points (5 points each feature) Imagineer Script: 35 points (5 points DESCRIBING each feature) Neat/Colorful: 10 points On-Task: 20 points (10 points/day)