Folding and Faulting
advertisement

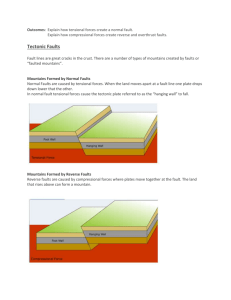
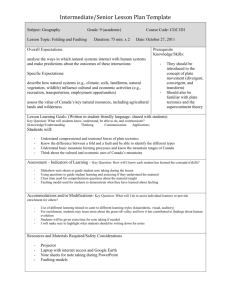
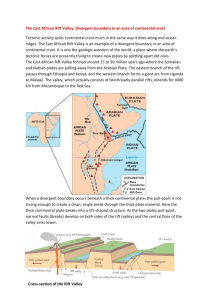
anticline dipping syncline recumbent fold fault overthrust fault The compressional force exerted on the crust is a result of movement of earth’s plates. When the plates converge, the weak rocks and sediments lying between the 2 plates get squeezed and get folded. Parallel folds give rise to long chains of parallel mountain ranges with high peaks. The up-folds form fold mountains while the down folds form longitudinal valleys. The Valley of Ten Peaks, Banff National Park Faults are large scale internal movements causing large scale physical features especially mountains and valleys If the force is moderate only cracks may appear in the rocks. The displacement that occurs results in formation of faults. Such fractures are divided into Joints & Faults. A joint is a fracture where a rock seems to be joined together without any movement it may become a fault when displacement takes place Normal faults occur when tensional forces act in opposite directions and cause one slab of the rock to be displaced up and the other slab down Reverse faults develop when compressional forces exist Compression causes one block to be pushed up and over the other block. A graben fault is produced when tensional stresses result in the subsidence of a block of rock. On a large scale these features are known as Rift Valleys Major relief feature of Faulting Activity is Rift Valley. A Rift Valley may be formed in two ways : (1) When the middle portion between two normal faults is dropped downward the sides remain stable. (2) When the middle portion remains stable and the two sides are raised upward These valleys have flat bottoms and steep sides http://georgengondo.hubpages.com/hub/About-The-Great-Rift-Valley-in-Africa The Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben (also known as the Ottawa Graben), with its branch the Timiskaming Graben, is an ancient rift valley in the Canadian Shield of Northeastern Ontario and Quebec, Canada This rift valley was formed when the Earth's crust moved downward about a kilometre between two major fault zones known as the Mattawa and Petawawa faults These ancient faults are still active and occasionally release stress in the form of earthquakes, such as the 1935 Timiskaming earthquake and the 2000 Kipawa earthquake. The length of the graben is about 700 km (435 mi) Runs from the Montreal area on the east to near Sudbury and Lake Nipissing on the west A horst fault is the development of two reverse faults causing a block of rock to be pushed up - In German Horst = 'heap' Block mountains are another important feature of Faulting caused by the Tensional features in the Earth’s crust The mechanism of formation of Block mountains is same as the Rift valley The Block mountains are often found on the sides of the Rift valley It is because the land between two parallel faults is either subsides to form a Rift valley or rises to form Block mountains strike-slip http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?NR=1&v=tIuk2blBzHs transform fault








!["Human Origins in Africa" [BB09]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005801692_1-b5b40078f7d5ae773e8789f2ec514d2f-300x300.png)