Primary Headwater Habitats
advertisement

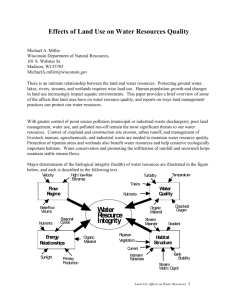
Primary Headwater Habitats (PHWH) The Basics - What is a Primary Headwater Stream? Characteristics: A Watercourse1 with: A defined BED2 and BANK3 Either continuous4 or periodic5 FLOWING water A drainage6 generally less than one square mile Deepest pools7 < 40cm Widely divergent8 communities based upon in- stream Biology Why Classify PHWH Streams? To provide standardized information for making decisions affecting water quality in primary headwater streams To help maintain the quality of water and biological communities in larger streams, lakes and wetlands The turbid PHWH stream at the top flows into the clear PHWH stream below degrading downstream waters to the left A traditional stream classification system: Classification by the Stream Continuum Concept Ohio EPA’s Classes of PHWH Streams Class I – EPHEMERAL1 stream, normally dry channel with little to no aquatic life; native fauna when flowing Class II – INTERSTITIAL2 to PERENNIAL3 moderately diverse aquatic life with native fauna4 adapted to warm water Class III –diverse aquatic life adapted to cool/cold PERENNIAL flowing water Stream Flow Types Ephemeral flow = Channel dry phase present annually, flow during rain or snow melt , permanent pools absent Class I PHWH Streams Characteristics Flow - ephemeral Channel1 - dry phase present annually, flow during rain or snow melt Permanent pools - absent Aquatic life - absent or present seasonally Aquatic life - diversity low Class I PHWH Stream - Example Natural channel, Geauga Co More Examples of Class I (click) Class II PHWH Streams Characteristics Flow – intermittent Channel – no continuous channel - only shallow groundwater connection between pools Permanent pools - present most years Aquatic life - abundance high Aquatic life diversity - moderate and warm water adapted Class II PHWH Stream - Example Natural channel, Geauga Co. More Examples of Class II (click) Class III PHWH Streams Characteristics Flow - perennial, deep groundwater Channel - present Permanent pools - present Aquatic life diversity1 & abundance Presence of one or more of the following at all times: 2 Obligate aquatic salamanders Cold water or pioneering fish species 3 Cool water adapted benthic macro-invertebrates Class III PHWH Stream - Example Delaware Co. More Examples of Class III (click) Quick Quiz What class PHWH stream is this? What characteristics did you use to classify the stream? Quiz Question 2 What PHWH Stream Class is shown here? How do you know you have chosen the correct class of PHWH stream? Glossary Terms as used for PHWH streams Bank- The lateral confines of a stream. Bed- The bottom of the stream. The physical boundary of normal water flow. Benthic- Organisms that live on the bed (bottom) of the stream. Channel- The course of the bed of a stream, river, or waterway. Continuous- Uninterrupted flow. Continuum-. Divergent-. Diverse- Different kinds, characters, or forms. Drainage- Water flowing off and from an area. Ephemeral- Usually flowing for only a short amount of time, dry at some time annually. Fauna- Animals of a given area. Intermittent- Flow that stops or ceases for a period of time. Interstitial- Flow interrupted by dry channel (sub-surface between pools). Obligate- Able to exist or survive only in a particular environment. Perennial- Flowing year round. Periodic- Happening over regular intervals. Pioneering Pools- A relatively deep, slow flowing or still place in a stream. Watercourse- Channel. Watershed- Region or area that drains into a given stream, river, or water body.