PowerPoint - Susan Schwinning
advertisement
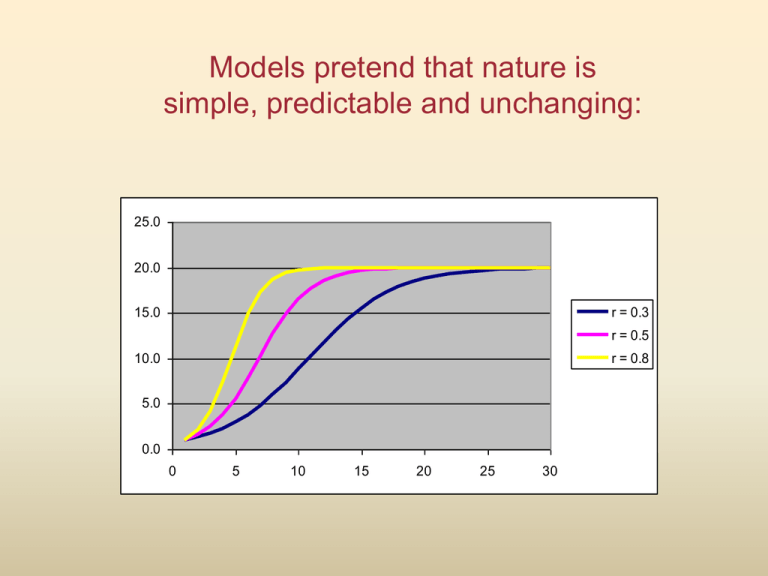
Models pretend that nature is simple, predictable and unchanging: 25.0 20.0 15.0 r = 0.3 r = 0.5 10.0 r = 0.8 5.0 0.0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 The real world is messy. Saether et al. 2002 Does this “messiness” matter to populations and communities? (“messiness” = heterogeneity, variability) Causes of variability Patterns of variability How does variability matter to populations? Causes of variability Environmental weather related: temperature, precipitation, light,… site related: soil properties, slope, vegetation cover,… biological: the number of competitors, predators,… Demographic stochasticity Random variability in the growth rates of small populations arising chance events in individual survival and reproduction. Can lead to chance extinction in small populations. Chaotic dynamics Random-like variability from strong and non-linear interactions between variables. Environmental variability Patterns in space or time spatial variation: when sites differ temporal variation: when conditions change over time Deterministic or random variability deterministic: predictable variation that follows precise rules random: has only statistical properties: mean, variance, etc. Types of deterministic variability periodic (in time or space) progressive change (spatial gradient, temporal trend) Patterns in time: 40 30 Average monthly temperature in Tucson Precipitation in Moab, Utah 300 250 Winter Summer 200 20 150 100 10 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011 12 Month of the year 0 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 Year 1980 1990 2000 Patterns in time: Patterns in time: Patterns in space: Patterns in space: Demographic stochasticity: High per-capita variability in growth rate due to random fluctuation in individual survivorship, and fecundity. Small populations can go extinct, even though average growth rates are positive. Excel Worksheets: • Demographic Stochasticity Demographic stochasticity N 50 Exponential model with N0 = 20 45 40 35 30 b = 0.01 per year d = 0.002 per year 25 20 15 10 5 29 36 43 50 57 64 71 78 85 92 99 97 22 91 15 16 14 N0 = 5 12 10 8 6 4 2 85 79 73 67 61 43 37 31 25 19 13 7 0 1 N 8 55 1 49 0 A documented extirpation Three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus) The population disappeared from a pond in Wales in 2000 (Wootton 2010) Chaotic fluctuations: Some entirely deterministic processes can produce fluctuations indistinguishable from random fluctuations. This was first discovered by the meteorologist Edward Lorenz who worked the prediction of weather patterns. Edward N. Lorenz (1917-2008) The Butterfly Effect Whether or not a hurricane forms may depend on whether or not a butterfly flapped its wings several weeks before Chaotic dynamics have extreme sensitivity to initial conditions. The Butterfly Effect (Slingo and Palmer 2011) The Discrete Logistic Model: N t 1 N t rmax Nt N t 1 K Equilibrium defined as Nt+1 = Nt N*,1 = 0 N*,2 = K Excel Worksheets: • Discrete logistic equation The existence of the various forms and changing patterns of variability drives evolution and creates and maintains biodiversity. A prairie Six species of Solidago (golden rod) are found in old fields and prairies. nemoralis canadensis missouriensis gigantea speciosa graminifolia Frequency of occurrence species Species usually occupy only a subset of an environments range of conditions. Oklahoma Prairie Hour of day Species are active only during a fraction of the total available time. Summary: There are various sources and patterns of variability in nature producing spatial and temporal heterogeneity. Forms of patterns: random, cyclic, or persistent trends (both in space and time). A special case of variability is called: demographic stochasticity: the random fluctuations of small populations (which can have large and important consequences) . Chaos is a special case of variability that is seemingly random but actually caused by deterministic processes. Much of ecology is concerned with understanding species’ responses to variability in its various forms in evolutionary and ecological time.