The Ecosystem - washburnsciencelies

THE ECOSYSTEM
2.6 Changes
Assessment Statements
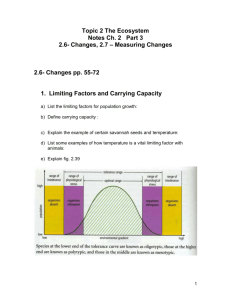
2.6.1 Explain the concepts of limiting factors and carrying capacity in the context of population growth.
2.6.2 Describe and explain S- and J- population curves.
2.6.3 Describe the role of density-dependent and density-independent factors, and internal and external factors, in the regulation of populations.
2.6.4 Describe the principles associated with survivorship curves including, K- and r-strategists.
Assessment Statements Cont.
2.6.5 Describe the concept and processes of succession in a named habitat.
2.6.6 Explain the changes in energy flow, gross and net productivity, diversity, and mineral cycling in different stages of succession.
2.6.7 Describe factors affecting the nature of climax communities.
2.6.1 Explain the concepts of limiting factors and carrying capacity in the context of population growth.
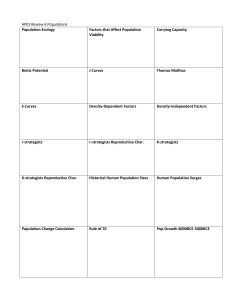
Limiting Factors – Factors that limit the distribution or numbers of a particular population.
They are environmental factors that slow down population growth.
Usually involve an optimal range, with upper and lower tolerances.
Temperature
Water
Nutrient Availability
2.6.1 Explain the concepts of limiting factors and carrying capacity in the context of population growth.
Carrying capacity– the number of organisms or size of population that an area or ecosystem can support sustainably over a long period of time.
2.6.2 Describe and explain S- and J- population curves.
S-population curve: Three
Stages
Exponential growth stage
– population grows at increasingly rapid rate
Transitional phase – continues to grow, but slows considerably
Plateau or stationary phase – number of individuals stabilizes and population growth stabilizes
2.6.2 Describe and explain S- and J- population curves.
J-population curve:
Only has the exponential growth stage. Growth is initially slow and becomes increasingly rapid. It does not slow down.
2.6.3 Describe the role of density-dependent and densityindependent factors, and internal and external factors, in the regulation of populations.
Density-dependent – factors that lower the birth rate or raise the death rate as a population grows in size.
Operate as negative feedback mechanisms.
Examples: resources, space, disease, parasitism, and predation
2.6.3 Describe the role of density-dependent and densityindependent factors, and internal and external factors, in the regulation of populations.
Density-independent – factors that lower the birth rate or raise the death rate irrespective of population density.
Examples: Natural disasters, and long term climate change.
2.6.3 Describe the role of density-dependent and densityindependent factors, and internal and external factors, in the regulation of populations.
Internal factors include density-dependent fertility or size of breeding territory.
External factors include predation or disease.
Physical environmental factors: water and nutrient availability, and temperature
Biological environmental factors: Predation, and competition.
2.6.4 Describe the principles associated with survivorship curves including, K- and r-strategists.
K-strategists species:
Grow and mature slowly
Produce few large offspring
Stable environments r-strategists species:
Grow and mature quickly
Produce many small offspring
Disturbed or new environments
Those that lie between are called C-strategists
2.6.4 Describe the principles associated with survivorship curves including, K- and r-strategists.
K-strategists survivorship curve:
Almost all survive potential lifespan, and then die almost simultaneously
Salmon and humans r-strategists survivorship curve:
Most die at a very young age, but those that survive are likely to live a very long time
Turtles and oysters
2.6.5 Describe the concept and processes of succession in a named habitat.
Succession – Orderly process of change over time in a community divided into stages called serals
Zonation – The arrangement or patterning of plant communities or ecosystems into bands in response to change, over a distance, in some environmental factor.
2.6.5 Describe the concept and processes of succession in a named habitat.
Primary Succession –
Succession on previously uncolonized substrate
Secondary Succession
– Succession where a previous community has been disturbed
2.6.6 Explain the changes in energy flow, gross and net productivity, diversity, and mineral cycling in different stages of succession.
Pioneer community –
Earliest seral stage
Early Stages of
Succession:
Gross Productivity: low
Respiration loss: low
Net Productivity: high
System: Growing
Biomass: Accumulating
2.6.6 Explain the changes in energy flow, gross and net productivity, diversity, and mineral cycling in different stages of succession.
Climax community –
Final seral stage
Final Stages of
Succession:
Gross Productivity: high
Respiration loss: high
Net Productivity: near
0
Production/Respiration
Ratio: Near 1
2.6.7 Describe factors affecting the nature of climax communities.
Climax community features:
Greater biomass
Higher levels of diversity
Favorable soil conditions
Lower pH
Taller and longer-living plant species
More K-strategists or fewer rstrategists
Greater community complexity and stability
Greater habitat diversity
Steady-state equilibrium
Plagioclimax – interrupted succession