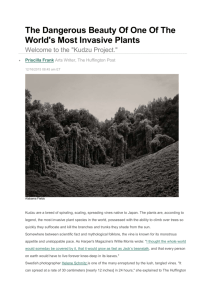
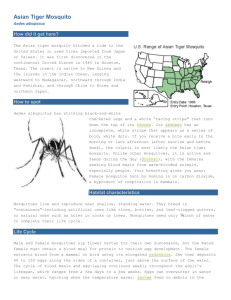
Kudzu
advertisement

Effects On Native Vegetation •extremely rapid growth rate and habit of growing over objects threatens natural areas by killing native vegetation through crowding and shading and basically chokes native vegetation • vines kill trees through girdling and the added weight of vines can lead to uprooting trees. • kudzu blankets the floor with its vines and runners and prevents the growth of any new trees • indigenous animals lose a great proportion of their natural food source. •Kudzu takes over farm fields and destroys many valuable crop plants. Such as its relative the soybean which leaves farmers with no way to control it without risking their crop •Many of the pesticides, such as Tordon, used to rid Kudzu have a lasting effect on the native vegetation through seeping into the soil •Kudzu has massive tap roots 7 inches or more in diameter, 6 feet or more in length, and weighing as much as 400 pounds Severity of the Problem Also known as “the vegetable form of cancer” Causes huge loses in agriculture power companies in the South devote around $1.5 million a year to controlling kudzu infestations Where productive forest land has been overtaken, lost productivity is estimated at $48 per acre per year Kudzu control costs exceed $200 per acre per year for five years. Mostly made of water so is hard to burn out Can transmit foreign disease and parasites In Mississippi, it is estimated that the forestry industry loses over $20 million a year because land which could be used for forestry is infested with kudzu Grows 7+ feet / week, 1+ foot / day and grows 50 feet in one growing season The Geography of Kudzu In the U.S: Kudzu can be found in the southeastern U.S, as far south as Key West, Florida, and as far North as Pennsylvania Kudzu can also be found in the Clackamas and Multnomah counties of Oregon Local Geography Kudzu can grow on just about anything: Method of Destrution Covers anything in its path blocking out sunlight to plants Competes with native species for food and territory Invasions can be accidental or intentional Can change predator/ prey relationships Damage to ecosystems and economy Some other problems, food chain disruption, reduced biodiversity, clogging of water intakes, increased weed growth, and is hard to eliminate without causing harm to other species How do you get rid of kudzu? You don’t! Roots grow over 10 feet deep. Each seed pod has 100 seeds and can blow miles away and can germinate in just about in conditions. Benefits of Kudzu Can be used as a supplement to help lower cravings of alcohol Used in Chinese medicine to treat angina Helps with alergies, headaches, and digestive problems Erosion control The nutritious leaves are high in vitamins C and A Kudzu vines can be woven into baskets and furniture Kudzu powder or kudzu root tea is used to treat a wide array of ailments such as inflammation, hangovers, sexual apathy, indigestion, respiratory disorders, headaches, sinus troubles, muscle stiffness, kidney trouble, breast-feeding complications, and skin rashes. Kudzu can be used to reclaim poor agricultural land where fertility has diminished and weeds are abundant. Kudzu will out compete weeds as well as return nutrients and biomass to the soil.