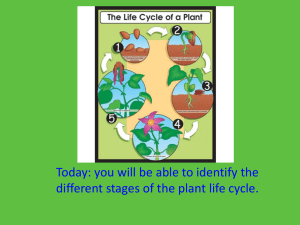
Discuss
advertisement

Which of the following most directly controls the flowering response in short-day plants? a. length of the light period b. length of the dark period c. relative amounts of blue light available d. intensity of light during the light period e. air temperature during the dark period Answer: b The coiling of a vine around a pole is due to a. phototropism b. gravitropism c. thigmotropism d. circadian rhythms e. photoperiodism Answer: c In plants, the initiation of flowering in response to photoperiod is triggered by changes in a. ethylene b. gibberellic acid c. auxin d. phytochrome e. cytokinin Answer: d a. Indoleactic acid (IAA) b. Cytokinin c. Gibberellin d. Ethylene e. Abscisic acid 1. A gas the hastens fruit ripening Answer: d 2. Promotes germination Answer: c 3. Stimulates activation of proteins for mitosis Answer: b (coleoptile) SAR= Systemic acquired resistance • Chemicals that spread the “alarm” of infection Salicylic acid The coiling of a vine around a pole is due to a. phototropism b. gravitropism c. thigmotropism d. circadian rhythms e. photoperiodism Answer: c Which of the following most directly controls the flowering response in short-day plants? a. length of the light period b. length of the dark period c. relative amounts of blue light available d. intensity of light during the light period e. air temperature during the dark period Answer: b a. Indoleactic acid (IAA) b. Cytokinin c. Gibberellin d. Ethylene e. Abscisic acid 1. A gas the hastens fruit ripening Answer: d 2. Promotes germination Answer: c 3. Stimulates activation of proteins for mitosis Answer: b In plants, the initiation of flowering in response to photoperiod is triggered by changes in a. ethylene b. gibberellic acid c. auxin d. phytochrome e. cytokinin Answer: d Only female gametes are produced in which of the following structures? a. antheridia b. stamens c. protonemata d. flowers e. archegonia Answer: e Which is true of seeds? a. They contain the gametophyte. b. They are characteristic of all plants. c. They are a mechanism for pollen dispersal. d. They are not characteristic of conifers. e. They contain the cotyledon. Answer: e Which of the following occurs after fertilization? a. The ovule becomes the seed, the ovary becomes the fruit. b. The ovary becomes the seed, the ovule becomes the fruit. c. The micropyle becomes the seed, the sepals become the fruit. d. The stigma becomes the seed, the ovule becomes the fruit. e. The micropyle becomes the seed, the ovary becomes the fruit. Answer: a Which of the following structures is NOT part of the pistil? a. ovule b. ovary c. style d. anther e. stigma Answer: d Angiosperms (flowering plants) have wide distribution in the biosphere and the largest number of species in the plant kingdom. (a) Discuss the function of FOUR structures for reproduction found in angiosperms and the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of each. (b) Mosses (Bryophytes) have not achieved the widespread terrestrial success of angiosperms. Discuss how the anatomy and reproductive strategies of mosses limit their distribution. (c) Explain alternation of generations in either angiosperms or mosses. (Carpel) Which is true of seeds? a. They contain the gametophyte. b. They are characteristic of all plants. c. They contain the cotyledon. d. They are a mechanism for pollen dispersal. e. They are not characteristic of conifers. Answer: c Which of the following structures is NOT part of the pistil? a. ovule b. ovary c. style d. stigma e. anther Answer: e Which of the following occurs after fertilization? a. The ovule becomes the seed, the ovary becomes the fruit. b. The ovary becomes the seed, the ovule becomes the fruit. c. The micropyle becomes the seed, the sepals become the fruit. d. The stigma becomes the seed, the ovule becomes the fruit. e. The micropyle becomes the seed, the ovary becomes the fruit. Answer: a Only female gametes are produced in which of the following structures? a. antheridia b. archegonia c. stamens d. protonemata e. flowers Answer: b Angiosperms (flowering plants) have wide distribution in the biosphere and the largest number of species in the plant kingdom. (a) Discuss the function of FOUR structures for reproduction found in angiosperms and the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of each. (b) Mosses (Bryophytes) have not achieved the widespread terrestrial success of angiosperms. Discuss how the anatomy and reproductive strategies of mosses limit their distribution. (c) Explain alternation of generations in either angiosperms or mosses. Flowering plants have evolved various strategies for fertilization. (a) Describe the process of fertilization in flowering plants. (b) Discuss TWO mechanisms of pollen transfer and the adaptations that facilitate each transfer. Some species of flowering plants have evolved Mechanisms to prevent self-fertilization. (a) Discuss an evolutionary advantage of preventing self-fertilization. (b) Describe TWO mechanisms that prevent self-fertilization.