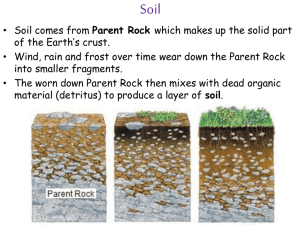
Permafrost - University of Alaska
advertisement

Northern Ecohydrology Jessica M. Cable and W. Robert Bolton International Arctic Research Center (Fairbanks) Environment and Natural Resources Institute (Anchorage) University of Alaska permafrost Miriam Jones J. Cable J. Cable J. Cable J. Cable L. Hinzman L Hinzman freshwater systems in Alaska Map by Robert Simmon D. White freshwater systems in Alaska climate ecology permafrost hydrology boreal hydrology How does permafrost distribution and active layer dynamics impact streamflow and soil moisture? Discontinuous warm permafrost region with boreal forest Storage dominated watersheds, on the margins Caribou Poker Creek Research Watershed near Fairbanks, Alaska boreal hydrology streamflow Permafrost dominated watersheds - higher specific discharge, lower specific base flow, and longer recessions than low permafrost watersheds boreal hydrology soil moisture Permafrost free area Area with permafrost 5cm, organic soil 40cm, mineral soil Permafrost free systems – lower soil moisture than systems with permafrost ecology ecosystem water use evapotranspiration = evaporation + transpiration transpiration (vascular plants) physiologically controlled ET affects soil moisture E → surface moisture (0-15cm) T → surface & deep moisture (> 5cm) How are plants tied into soil moisture? Where in the soil do plants take water? evaporation (moss, soil) physically controlled water uptake profiles fractional uptake from each layer 0.2 0.6 0.8 0.0 0.2 0.4 a.Sedge, C. bigelowii 0-5 * 5-10 0.6 0.8 1.0 b. V. uliginosum 0-5 * blueberry * 5-10 * 10-20 10-20 20-30 * 20-30 * 30-40 30-40 40-50 Depth (cm) 0-5 mound trough * mound trough c. B. nana shruband trough mound * d. R. chamaemorus mound and trough 40-50 0-5 5-10 5-10 10-20 10-20 20-30 20-30 30-40 30-40 40-50 40-50 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 fractional uptake from each layer 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 fractional uptake from each layer 1.0 Depth (cm) Depth (cm) 0.4 Depth (cm) 0.0 fractional uptake from each layer EcoHydrology Permafrost free area Surface and subsurface soil moisture are disconnected EcoHydrology “water limited”, less residual soil water Not “water limited”, more residual soil water for other processes How do vegetation water use and permafrost dynamics impact stream flow in the boreal forest discontinuous permafrost zone? Holistic approach by integrating ecological and hydrological processes, including storage, soil moisture, active layer dynamics, and transpiration EcoHydrology Coniferous CDE Deciduous DDE Likely varies over the growing season Soil drainage Permafrost Transpiration coniferous deciduous poor yes low well no high Changes in permafrost AND vegetation Growing season Autumn senesce, T decreases CDE - Active layer deepens DDE- Plants leaf out, T increases Spring snow melt period Integration Plant water use Hydrological variables Field work Ti ~ N (mi,t) Bayesian Data analysis Storage-based model Model integration Pathway and timing of water movement Acknowledgements Alaska EPSCoR NSF OPP International Arctic Research Center Larry Hinzman Kiona Ogle Bill Cable Miriam Jones Arctic Regions Supercomputing Center