Soil
advertisement
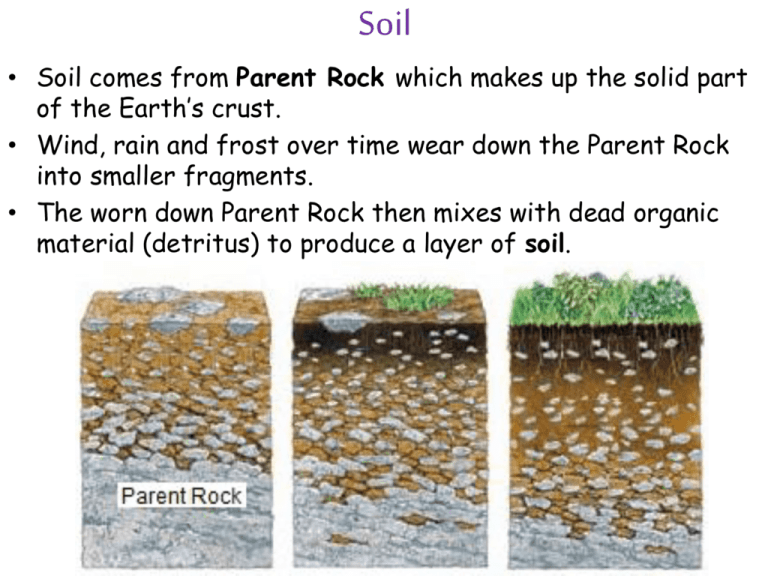
Soil • Soil comes from Parent Rock which makes up the solid part of the Earth’s crust. • Wind, rain and frost over time wear down the Parent Rock into smaller fragments. • The worn down Parent Rock then mixes with dead organic material (detritus) to produce a layer of soil. Soil Horizons • As soil develops in layers called horizons. • The horizons are identified by their color, texture and composition. There are 3 conditions necessary for soil to be able to support plant life: 1) Sufficient amount of minerals 2) Enough moisture 3) Appropriate soil pH Permafrost • Ground whose temperature has been 0 ̊C or below for at least 2 years • Can be found in polar regions or at high latitudes Permafrost • In certain regions, the upper layer of permafrost thaws in the summer and certain plants are able to grow. This top layer is called the active layer. When winter returns, the ground freezes again. • Permafrost makes it difficult for plant roots to grow deep into the ground. For this reason, very small/no plants are able to survive. • Permafrost makes agriculture impossible and construction difficult. Permafrost & Climate Change • As temperatures continue to rise, permafrost will continue to thaw. • As permafrost melts, the once-frozen land becomes unstable which results in landslides. The soil is then more vulnerable to erosion. Permafrost & Climate Change • Permafrost stores a lot of carbon (C). • As permafrost melts, this carbon is released into the atmosphere in the form of methane (CH4), a powerful greenhouse gas responsible for warming the planet. • This leads to more climate change and the cycle aggravates itself. Try This! 1. Permafrost is: a) all the frozen water on the Earth’s surface. b) a layer of permanently frozen soil. c) the snow which accumulates on the surface of glaciers. d) the upper layer of water which freezes when in contact with cold air. 2. Chose the statement which is false. Areas of permafrost can be challenging to live in because: a) agriculture is not possible. b) buildings can collapse. c) sunshine is lacking. d) the ground is usually frozen. Try This! 1. Which of the following is not a possible consequence of melting permafrost? a) Decreased primary productivity b) Increased erosion c) Increased Global Warming d) Increased decomposition of soil 2. In an area of permafrost, global warming can increase the depth, as well as the length of time, during which the active layer is present. How does this affect: a) the lithosphere? b) plant life? c) human life?











