BadgerPowerPoint
advertisement

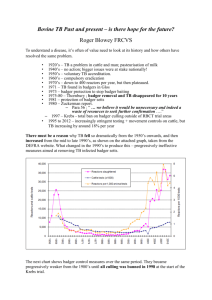
Badger Bother To cull or not to cull? Badgers are blamed for spreading the bovine tuberculosis (bTB) disease to dairy cows . . . by some people Why cull badgers? Bovine tuberculosis (bTB) What • Infectious is fatal bovine disease • Caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (bTB)? Bovis • Affects mammals, including cows, badgers, rats, foxes, deer and people • The disease is fatal to cows Why is bTB a problem? • The milk from infected cows can’t be sold • Cows with the disease have to be killed because people can catch the disease if they drink the milk How is bTB spread? Cows can catch it from other cows as well as from wildlife such as badgers Badgers can catch it from other badgers as well as from cows Distribution of badgers and bovine TB in the UK Badgers Cases of cattle TB 2006 – 2010 Badger cull areas Distribution of badgers and TB in the UK West Gloucestershire West Somerset bTB history Tuberculin testing suspended due to Foot & Mouth disease (FMD) fuelling a dramatic rise in bovine TB 2001 - 2002 Randomised Badger Culling Trial (RBCT) 1998 - 2007 1960 All cattle in the UK tested & reactors removed 1987 Relaxation of cattle testing, slaughter and movement controls Culling using gassing 1975 - 1981 2013 Pilot culls in Somerset and Gloucestershire Pilot cull supported by: •DEFRA (government department for farming and rural affairs) •NFU (National Farmers’ Union) •To run over four years •Selected areas in Gloucestershire and Somerset •Free-running badgers to be shot at night by farmers using rifles •70% of badger population to be killed •Anticipated 16% fall in TB after 4 years •To go nationwide if ‘successful’ Pilot cull opposed by: •Most leading scientists (including Professor Krebs who organised the biggest scientific study into the issue) •Most wildlife societies and animal protection groups •Most MPs (voted 147 to 28 against in Oct 2012) They say: •Shooting badgers is cruel •It won’t work •It will cost too much Protesters at Badger Camp in Gloucestershire Shooting a fleeing badger humanely is not easy . . . at night it’s even more difficult The Krebs Trial Randomised badger culling trial • Key scientific study into whether badgers reduces bovine TB culling • Carried out between 1998 and 2007 - culling for 5 years, and follow-up studies for 4 years • 30 areas of the country selected, each 100 square km in size • 10 culled proactively, 10 reactively (in response to outbreaks), 10 not culled • Badgers culled through being caught in cages and then shot • Incidence of bovine TB measured on farms inside and outside study areas • Reactive culling suspended early after significant rise in infection • More than 11,000 badgers killed Key conclusions ‘Badger culling can make no meaningful contribution to cattle TB control’ [We] ‘recommend that TB control efforts focus on measures other than culling’ Shooting badgers upsets their family groups, causing surviving animals to move out of the area, spreading TB further afield. What’s the alternative? 1) Vaccinate badgers against bTB 2) Improve testing of and biosecurity cattle 3) Improve the living conditions and health of cows so they are less likely to become ill Arguments for the cull 28,000 cattle were slaughtered due to bTB in Something has to be done England in 2012 a 7% increase on 2011 need be controlled Badgers are toto blame for spreading TB on to cattle The Republic of works Ireland has been culling badgers Culling badgers since 2004 and the number of cows with TB has fallen dramatically At £662isper vaccinating Culling theanimal most cost effectivebadgers methodcosts way too much compared to shooting Arguments against the cull Badgers Infected cattle are being passing usedthe asdisease a scapegoat onto other by the dairy cattleindustry is the main cause of the disease spreading to new areas Culling badgers doesn’t work Scientific evidence shows that culling badgers is counter productive The cull method is inhumane Shooting free-running badgers in the dark is cruel and will cause a great deal of animal suffering Cure not kill badgers – culling is is the the more wrongeffective method Vaccinating and humane method of controlling bTB Animal Aid: www.animalaid.org.uk NFU: www.tbfreeengland.co.uk Extra pic Extra pic Extra pic Extra pic