Platyhelminthes
advertisement

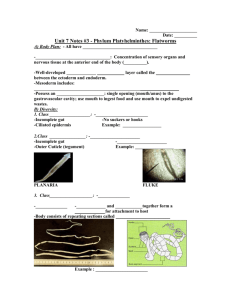
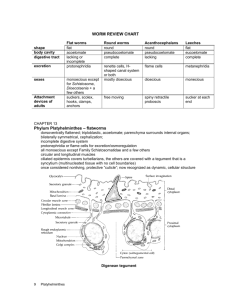
Daniel Jaffe Paige Minteer Zoey ZoBell http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.divetrip.com /wakatobi/flatworm02.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.divetrip.com/pho t0410d.htm&usg=__j9Bk4Alyot44vGWORfQmnPD2gI=&h=480&w=640&sz=123&hl=en&st art=2&um=1&itbs=1&tbnid=9H_cUbqZEqAXM:&tbnh=103&tbnw=137&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dflatworm%26u m%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dsafari%26rls%3Den%26tbs%3Dis ch:1 Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class Examples and Characteristics Turbellaria Dugisea: Marine, freshwater, predator and scavenger, ciliated body surface Monogenia Monogians: Marine and freshwater parasites, ciliated bodies, infect outer layer of fish skin. Trematoda Trematodes and Flukes: Parasites, two suckers attached to host, most life cycles attach to intermediate Cestoda Tapeworm: Parasites of vertebrates, no head or digestive system, one or more intermediate hosts Sample Animals Dugisea Tapeworm http://gurungeblog.files.wordpress.com/2008/11/platyhelm_turbellaria_dugesia.jpg http://www.britishbeef.co.uk/tapeworm.gif Body Cavity No body cavity exists within the Platyhelminthes Considered an Acoelomates, which means without a cavity http://biology.unm.edu/ccouncil/Biology_203/Images/SimpleAnimals/Acoelomate.JPG Body Symmetry Platyhelminthes exhibit bilateral symmetry, which means it has one line of symmetry, similar to humans. A bilateral animal has a dorsal side and a ventral side A bilateral animal has an anterior end and a posterior end. http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/labs/bilateral.jpg Nervous System Central Nervous system that processes information from the eyes and other sensory structures The bilateral symmetry of this phylum allows for sensory equipment concentrated at the anterior end along with the central nervous system and the brain This evolutionary tend is known as cephalization Circulatory System No body or organs for circulation Open system http://www.seaslugforum.net/images/flatworm.jpg Digestive System Pharynx: a muscular tube in which the mouth is located Extends form ventral side Digestive juices are sprayed onto pray, and small pieces are sucked into pharynx, where digestion continues Undigested wastes are egested through the mouth Excretory System “Flat” shape in which nitrogenous waste (ammonia) is removed through diffusion across the body surface. No organs specialized for gas exchange or circulation. They have a basic structure excretory system is through osmotic balance with their surroundings. Locomotion/Musculature Motility a.k.a “Going Dumb” Move by using cilia on their ventral epidermis, gliding along a film of mucus that they secrete. Some use muscles to swim through water with an upand-down form of motion. http://www.glogster.com/media/2/3/71/6/3710611.jpg Skeletal Type Platyhelminthes do NOT contain a skeleton type. They can literally do the “worm” without risking any bone fractures.…holy biology! http://cyberportfolio.st-joseph.qc.ca/classes/carriere/archives/surprised-girl-reading-book.jpg Sensory Structures/Features Ganglia: Located at the anterior end of the worm, they are dense clusters of nerve cells also known as eye spots Ventral nerve cords: Coming from the ganglia, a pair of nerve cords that run down the lenth of the body. Reproduction Methods Sexual and asexual reproduction Regenerative tissues allow one split individual to regenerate into two separate worms Mostly homaphrodite Self fertilization as well as cross fertilization is seen Direct development (no larva stage) http://cas.bellarmine.edu/tietjen/images/Chlonorchis01.gif Gas Exchange Lack respiratory systems Flat bodies permits flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide by diffusion http://cas.bellarmine.edu/tietjen/images/platyh16.jpg Unique Features Restricted to living in wet environments because of the nature of their open gas exchange making them susceptible to dehydration Their bodies are soft, unsegmented, and resemble ribbons Some of these species are carnivorous, while the rest are parasitic Tapeworm disease, or, Cestodiasis is caused by a parasitic type of Platyhelminthes The End Thanks for listening!