The Age of Exploration
advertisement

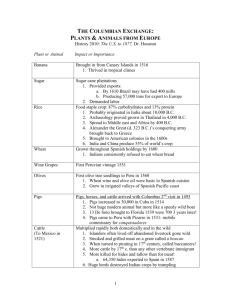
The Age of Exploration MesoAmerica North American Colonies BACKGROUND Rise of Monarchies • Kings and queens paid for the exploration trips • • Prestige More territory Printing Press • • Fed rise of humanism • Access to books, more people read accounts of new lands Scientific and intellectual inquiry • • Access to maps, navigation tools BACKGROUND How did it start? ◦ Prince Henry “The Navigator” of Portugal ◦ Started a school of navigation in 1420 ◦ Didn’t sail, but planned voyages and analyzed their reports ◦ Astronomers, geographers, mathematicians shared info with Portuguese sailors and shipbuilders. ◦ Expert mapmakers updated maps/charts GEOGRAPHY GEOGRAPHY How did geography play a factor in the pursuit of new lands? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ The Turks blocked the trade route from the Mediterranean Sea to the land route to Asia. Crusades—European countries tried to regain control of holy sites that had been taken over by the Muslims and were exposed to trade items. Portugal—They didn’t have a Mediterranean port location and needed an option. Arabs’ prices were too high. (Middle Man) SOCIAL European explorers conquered three major MesoAmerican empires, greatly changing their lives and destinies: ◦ Aztecs ◦ Mayans ◦ Incas All three empires easily conquered ◦ Feared white man: armor, guns = gods ◦ Unrest within SOCIAL: AZTEC SPRITE 1200 AD – 1535 AD G: Central Mexico ◦Built capital city of Tenochtitlan ◦Legend: priest had dream, locate city where he found an eagle holding a snake in his claws on top of a cactus. Mexico City Modern day Mexican flag S: Ruler, priests and nobles, warriors merchants and artisans, farmers, and slaves P: Empire ruled by emperor SOCIAL: AZTEC SPRITE R: Religion many gods. was polytheistic: Believed in ◦Used human sacrifices to please the gods. I: Created writing system using hieroglyphics. T: Built irrigation for crops E: Traded cacao beans, tools, clothes, jewelry at local markets; caravans to present day Guatemala, Belize, Honduras SOCIAL: MAYA SPRITE 200 AD – 900’s AD G: Southern Mexico into Central America S: Social Classes based on birth P: Built city-states ruled by kings. R: Polytheistic; Used humans as sacrifice SOCIAL: MAYA SPRITE I: Very accomplished: ◦Studied stars ◦Developed calendar ◦Created writing system using hieroglyphics ◦Invented system of mathematics with concept of 0 T: Built pyramids as temples E: Traded among empire/city-states ◦ As currency, cacao beads gave way to stone beads ◦ Gold, jade and copper = more expensive items SOCIAL: INCA SPRITE ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 1200 AD – 1535 AD G: Modern day Peru along Pacific Ocean S: “Inka” means ruler Adapted to Inca by Spanish conquistadors to refer the people of the area, not the ruler or his family Inca a patchwork of people from different lands P: Government run by emperor Civil war within empire favored Spanish conquest R: Polytheistic Believed in reincarnation SOCIAL: INCA SPRITE ◦ ◦ I: Architecture most important of Inca arts Machu Picchu Temples constructed using mortar less construction ◦ ◦ ◦ knife couldn’t fit between! T: Built vast network of roads and bridges Terrace farming E: Traded within empire High degree of central planning: govt planned for citizens needs POLITICAL Treaty of Tordesillas (Line of Demarcation) Spain got the West (new world) and Portugal got the East (old world) ◦ This is why Brazilians speak Portuguese but the rest of SA speaks Spanish POLITICAL POLITICAL OCEAN EXPLORERS ◦ Spain Columbus: Carribean Vespucci: South American coast; “Americas” deBalboa: Hiked mountains; first to see Pacific Magellan: circumnavigated world; named Pacific ◦ Portugal Dias: Explored Africa DaGama: Sailed around tip of Africa to India Cabral: Explored Brazilian coast; sailed on to India POLITICAL INLAND EXPLORERS ◦ Cortez-(Mexico) Conquered the Aztecs, put the Aztec emperor, Montezuma in prison. ◦ Pizarro-(Peru) Conquered the Incas, executed their leader, Atahualpa. Spanish explorers were known as conquistadors They received grants, or special permission, to explore and claim land. POLITICAL NORTH AMERICAN EXPLORERS ◦ Henry Hudson Sailed for England & Holland/Netherlands Hudson River (NYC) named for him Pilgrims ◦ See religion RELIGION MesoAmerica ◦ Native Americas = polytheistic ◦ Europeans = monotheistic / CHRISTIAN, considered Indian ways barbaric ENCOMIENDA: Spanish granted land & Native Americans to colonists in South America. In return, convert Indians to Christianity Result = Disease, overwork killed millions of Indians Lends itself to African slave trade RELIGION North America ◦ Pilgrims leave England to escape religious persecution ◦ Settle in Plymouth, Massachusetts ◦ Indians taught Pilgrims to hunt/fish Pilgrims still wary/distrusted Indians Long term = leads to displacement of Indians from their land Trail of Tears INTELLECTUAL/TECHNOLOGY What were technology changes that increased exploration? Better ships ◦ triangular sail, sturdy rudder Better tools ◦ Astrolabe, magnetic compass Better maps ◦ Cartographer—a person who makes/studies maps Included ocean currents and latitude lines ECONOMIC Columbian Exchange ◦ Exchange of plants, animals between continents ◦ Provided new goods to sell, new means of transportation ◦ Also brought diseases: killed millions of Indians Mercantilism ◦ Economic principal: nation’s strength depended on its wealth Intense competition between nations 1500-1600’s ECONOMIC Wrap Up: 1-2-3-4-5-6 Foldable Name 1 way the Catholic Church was involved in exploration. Do you agree or disagree with the Church’s position? Why? Who were the 2 Spanish conquistadors responsible for colonizing South American? How might SA be different today had they not been successful? Name 3 Native American groups we examined and the geographic locations of their civilizations. In what ways did the Columbian Exchange effect the New World? Name 2 positive and 2 negative effects. What 5 items involved in the Columbian Exchange do you consider most important? Defend your response. Discuss at least 6 pros and cons of continued exploration in our world today.