Chapter 5 PPT pt1
advertisement

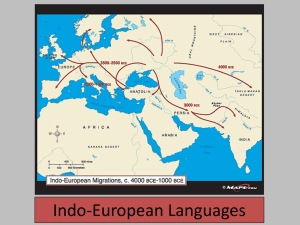
Chapter 6 Language Language Language – a set of sounds, combinations of sounds, and symbols that are used for communication. World Language Families Major Language Families Percentage of World Population Fig. 5-11a: The percentage of world population speaking each of the main language families. Indo-European and Sino-Tibetan together represent almost 75% of the world’s people. Major World Languages Major World Languages Language Terms • Standard language-an official language sustained by the state in the form of state examination for teachers, civil servants and others. • Dialect-regional variation of a standard language. • Language family-a group of languages descended from a single, earlier tongue. • Language subfamily-a further division of language groups. E.g. Romance language is a subfamily of Indo-European. • Regional differences in a standard language; – Syntax-the way words are put together – Vocabulary – Pronunciation – Cadence or rhythm – Accents can reveal the regional home of a person. • Isogloss-a geographic boundary within which a particular linguistic feature is found. Dialect-variants of a standard language along regional or ethnic lines- vocabulary-syntax- pronunciation- cadence-pace of speech Isogloss -A geographic boundary within which a particular linguistic feature occurs Origin & Diffusion of Languages • Mother Tongue-the first language spoken by Homo sapiens about 200,000 years ago. • Deep reconstruction-by studying sound shifts, linguists try to re-create an extinct language. • Language divergence-the differentiation that takes place over time and distance. • Language convergence-when long isolated languages make contact through diffusion. • Language replacement-traditional languages of small groups of less advanced people were replaced or greatly modified by an invading tongue. • Linguists can find linkages among languages by examining sound shifts – a slight change in a word across languages over time. • An example of sound shift: – – – – Latin for milk is lacte Italian is latta Spanish is leche French is lait • Another example of sound shift is: – German vater – Dutch vader – English father • Still another example is – Latin for eight is octo – Spanish is ocho – French is huit How are Languages Formed? Language divergence – when a lack of spatial interaction among speakers of a language breaks the language into dialects and then new languages. Language convergence – when peoples with different languages have consistent spatial interaction and their languages collapse into one. Mutual Intelligibility- means two people can understand each other when speaking. Problems: • Cannot measure mutual intelligibility • Many “languages” fail the test of mutual intelligibility • Standard languages and governments impact what is a “language” and what is a “dialect” How do Languages Diffuse? • human interaction-2,000 years ago-Han China, Roman Empire-spread languages over vast empires • print distribution-Gutenberg’s movable type printing press (1452-first Gutenberg Bible) helped to diffuse, standardize & stabilize European languages • Migration-ancient & more recent migration from 16th century to now diffused languages e.g. Spanish, Portuguese, English & French • Trade-encouraged the spread of goods & languages • Rise of nation-states-stabilized & standardized languages • Colonialism-mercantilism & colonies spread European languages in the Americas, Africa & Asia Spatial Interaction helps create: • Lingua franca – A language used among speakers of different languages for the purposes of trade and commerce. • Pidgin language – a language created when people combine parts of two or more languages into a simplified structure and vocabulary. • Creole language – a pidgin language that has developed a more complex structure and vocabulary and has become the native language of a group of people. Monolingual State a country in which only one language is spoken Multilingual State a country in which more than one language is in use Official Language should a multilingual state adopt an official language? • The vocabulary of a ancient language can reveal its cultural hearth. • The Indo-European branches of the language tree at right illustrates the concept of language divergence. • August Schleicher was the first to compare the world’s language families to the branches of a tree. Language Family Trees Proto-Indo-European • Russian scholars have led the way on research of ancient languages • Nostratic-the ancient ancestor of Indo-European languages-were huntergatherers of 14,000 yrs. ago • Nostratic is the ancestor of Indo-European, Kartvelian, Uralic-Altaic , Afro-Asiatic & Dravidian • Hearth of Indo-European was Black Sea or east-central Europe some 5,000 to 9000 years ago • Postulated diffusion of an Indo-European protolanguage • The approximate timing of the westward dispersal of the Indo-European languages. Renfrew Hypothesis • British scholar Colin Renfrew proposed 3 hearth areas near the Fertile Crescent. • Renfrew hypothesis claims that Anatolia was the source of Europe’s Indo-European languages, from the western Fertile Crescent North African & Arabic languages, from the eastern Fertile Crescent the languages of Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan & India • Michael Oppenheimer claims that Indo-European languages originated in India over 50,000 years ago Indo-European Language Family The main branches of the Indo-European language family include Germanic, Romance, Balto-Slavic, and Indo-Iranian. • Indo-European is the largest and most widespread language family. Languages of Europe • Dominated by IndoEuropean. • Subfamilies include: • Germanic • Romance • Slavic • Celtic • There is a high correlation between languages and political organization. • Pockets of Ural-Altaic Romance Branch of Indo-European Fig. 5-8: The Romance branch includes three of the world’s 12 most widely spoken languages (Spanish, French, and Portuguese), as well as a number of smaller languages and dialects. Invasions of England 5th–11th centuries Fig. 5-2: The groups that brought what became English to England included Jutes, Angles, Saxons, and Vikings. The Normans later brought French vocabulary to English. Germanic Branch of Indo-European Fig. 5-6: The Germanic branch today is divided into North and West Germanic groups. English is in the West Germanic group. Euskera The Basque speak the Euskera language, which is in no way related to any other language family in Europe. How did Euskera survive?