Another
Presentation
© 2013 - All rights Reserved
MAGIC
SQUARE
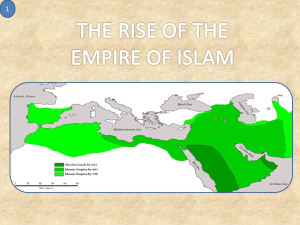
Islam’s Influence on West Africa
1
6
11
16
2
7
12
17
3
8
13
18
4
9
14
19
5
10
15
20
How did Islam first reach Ghana?
A.
B.
C.
D.
by the Arab Muslim armies that conquered Ghana
after a Ghanaian king had a vision of Muhammad
through Muslim traders and missionaries
after Ghanaian scholars traveled to the Middle East
for their studies
1
West Africans began to celebrate the festival of Eid
al-Fitr, which marks the end of the holy month of
A. Songhai.
B. Eid al-Adha.
C. Ramadan.
D. Ibn Battuta.
6
At the University of Sankore, the highest degree a
student could earn required
A.
B.
C.
D.
one year of intensive study.
about ten years of study.
at least twenty years of study.
a lifetime of study.
11
When people began to build mosques in West Africa, they
A. imported materials from the Middle East to keep
all mosques consistent.
B. built Islamic architectural styles with local
materials.
C. used only stone, because it lasted longer than
other materials
D. avoided Islamic styles in favor of traditional local
architectural styles.
16
What was the impact of Islam's view toward
traditional religious practices in West Africa?
A. The Muslims' opposition to traditional religious practices
slowed down the acceptance of Islam.
B. The tolerance shown by Muslims toward traditional
religious practices helped Islam to spread.
C. The Muslims banned all traditional religious practices,
which drove non-Muslims into hiding.
D. Muslims borrowed freely from other religious traditions,
which encouraged non-Muslims to convert.
2
After they became Muslim, West Africans
preserved some of their old religious practices,
such as
A.
B.
C.
D.
learning the Five Pillars of Islam.
making pilgrimages to Makkah.
making sacrifices to the spirits of dead ancestors.
worshipping in mosques.
7
The turbans worn by students at the University of
Sankore symbolized wisdom, knowledge, excellent
moral character, and
A. kindness.
B. divine light.
C. high social status.
D. maturity.
12
How did the builders of Djingareyber plan ahead to
make the building easier to repair in future years?
A. They built the structure only one story high to make it
more accessible.
B. They used interchangeable wall panels that could be easily
replaced.
C. They built the mosque into the side of a hill, leaving only
one wall exposed.
D. They placed beams in the walls that could be used as
scaffolding.
17
Which statement about Mansa Musa is true?
A. Mansa Musa was the first leader of Mali to accept Islam,
though he did not practice devoutly.
B. Mansa Musa's pilgrimage to Makkah was an enormous
and impressive undertaking.
C. Mansa Musa was happy to kneel before the sultan in
Cairo, because he admired the sultan greatly.
D. Mansa Musa was isolationist and tried to cut off all
contact between Mali and the outside world.
3
How did Muslim rulers change the line of succession
in West Africa?
A. Leadership now passed from mother to daughter.
B. Rulers now decided who would succeed them to
the throne.
C. The people now elected their rulers.
D. The right to rule now became patrilineal.
8
Why did Muslims set up schools for children in
Timbuktu?
A.
B.
C.
D.
to train them in philosophy
to prepare them for careers in medicine or law
to teach them to interpret the Qur'an
to care for them while their parents worked.
13
How did the architect Al-Saheli change the
look of houses in West Africa?
A. He built round stone houses surrounded by four
minarets.
B. He built plain, rectangular houses out of brick
with flat roofs.
C. He built lightweight homes of thatch that could
be easily moved.
D. He built brightly-colored, heavily decorated
homes with many windows.
18
Under the rule of Askia Mohammed Toure, the
Songhai empire
A. covered a territory as large as western Europe.
B. began a prolonged war against the Byzantine empire.
C. conquered the empire of Ghana and ruled all of West
Africa.
D. abandoned Islam and returned to traditional religions.
4
Which of the following is a major change that
Muslim rulers adopted in West Africa?
A. They decentralized the government according to
longstanding Muslim tradition.
B. They used local names for their leaders, rather than
Arabic terms sultan, amir, or emir.
C. They adopted the use of "trial by wood" to test the guilt
or innocence of an accused person.
D. They replaced the customary laws of West Africa with
the shari'ah.
9
Which statement about language is true?
A. Arabic allowed West African traders to
communicate more easily.
B. West Africans completely abandoned their
native languages.
C. Muslim rulers in West Africa insisted on using
their native languages at all times.
D. Many people in West Africa learned Arabic as
they converted to Christianity.
14
Why did the architect Al-Saheli introduce clay
drain-pipes to houses?
A. They prevented damage to houses from
rainwater.
B. They brought in fresh drinking water to each
house.
C. They stopped the spread of disease by carrying
away waste water.
D. They served as the only decorative element in
the houses' exteriors.
19
In West Africa, Muslims
A. took part in both Muslim and their traditional religious
practices.
B. abandoned their traditional religious practices when they
adopted Islam.
C. quickly reverted to their traditional religion after their
initial contact with Islam.
D. continued to practice their traditional religion, but gave
each celebration an Arabic name.
5
A major center of learning in West
Africa was
A.
B.
C.
D.
Cairo.
Baghdad.
Timbuktu.
Istanbul.
10
How did the spread of Islam help spread the Arabic
language?
A. Arabic was only used in the language of religion.
B. Arabic was the language of learning.
C. Native languages were used as the language of trade and
government.
D. none of the above
15
Which statement about decorative arts is true?
A. West Africans continued using their traditional designs
for art and textiles.
B. West Africans preferred to use images of animals in their
art, rather than geometric designs.
C. West Africans rarely used calligraphy and preferred their
traditional ways of writing.
D. West Africans adopted calligraphy and geometric patterns
in their decorative arts.
20