slides - myWeb
advertisement

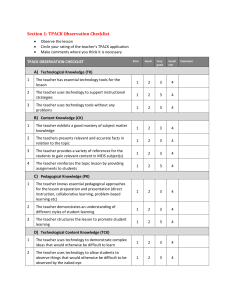
Technology in Professional Development: TechKnowLogia Aslı Lidice Gokturk asli.saglam@ozyegin.edu.tr http://aslisaglam.edublogs.org 27.05.2012 TEACHER KNOWLEDGE Think about factors that make up our knowledge. You may have more than one answer but prioritise... Tell us the most important one Nature of teachers’ knowledge & learning (Fisher et.al. 2006) How do teachers know? Shulman and Shulman’s Model (2004) Vision Motivation Capability Understanding Practice Reflection Community = «being ready, willing and able» (Fisher et. al. 2006; Chen, 2012) What do teachers know? Shulman’s Categorization(1987) Content knowledge General Pedagogical knowledge Curriculum knowledge Pedagogical content knowledge Knowledge of learners & their characteristics Knowledge of educational contexts Knowledge of educational purposes, values and aims EFFECT OF TECHNOLOGY?? How do you think technology affects teacher knowledge? VOXOPOP (an online message board) Do you use web tools in your teaching? How did you learn about them? Did you receive any training? Pre-service? In-service? Others??? http://www.voxopop.com/topic/cb455b6f-5f81-4bf7-ba6ecd91b9842b41 Effect of Technology : Brief description of constructs in the 'TPACK framework from Mishra and Koehler (2006) in Graham, 2011. Technological knowledge knowledge of operating systems and computer hardware, and the ability to use standard sets of software tools such as word processors, spreadsheets, browsers,...etc.) Technological pedagogical knowledge knowledge of how teaching might change as the result of using particular technologies Technological Content Knowledge knowledge about how technology and content are related. Technological pedagogical content knowledge the basis of good teaching with technology • teach content • how technology can help readress some of the problems that students face • knowledge of students’ prior knowledge • and knowledge of how technologies can be used to build on existing knowledge and to develop new methods or strengthen old ones.” (p. 1029) TPCK What do teachers know? Strongly agree Agree Neither agree or Disagree Disagree The purpose of this section is to gather information about combining technology, pedagogy and content knowledge in the teaching and learning process. For each item choose only one option that best describes you. 1 I can use technology to develop activities based on students needs to enrich the teaching and learning process. 2 I can implement effective classroom management in the teaching and learning process in which technology is used. 3 I can use technology for implementing educational activities such as homework, projects, etc. 4 I can use technology based communication tools ( blog, froum, chat, e-mail, etc. ) in the teaching process. 5 I can use innovative technologies ( facebook, blogs, twitter, podcastingi etc.) to support the teaching and learning process. 6 I can use technology to update my knowledge and skilss in the area that I will teach. 7 I can troubleshoot problems that could be encountered with online educational environments ( Moodle, Web CT, etc) 8 I can use technology in every phase of the teaching and learning process by considering the copyright issues(e.g. licence) Ican become a leader in spreading the use of technological innovations in my future teaching community. Strongly disagree A technological pedagogical content knowledge scale (Yurdakul et.al. 2012) TPACK is: Knowing how to present the subject matter with technology in pedagocially sound ways So & Kim, 2009 A teacher’s knowledge of how to coordinate and combine the use of subject-specific activities and topic-specific activities using emerging technologies to facilitate student learning Cox&Graham ,2009 TPACK is not simply: ....adding technology to existing teaching and content... Yurdakul et al,2011 INTERACTION BETWEEN EDUCATIONAL TECH & TEACHER DEVELOPMENT The “new” models of staff development study groups, teacher networks, mentoring relationships, committee or task force, internship, individual research project, or teacher resource center (Alberta Commission on Learning, 2006; Birman et al., 2000; Sikora & Alexander, 2004). INTERACTION BETWEEN EDUCATIONAL TECH & TEACHER DEVELOPMENT Other promising adult learning environments include exchange of information, collaborative work, critical thinking, active/exploratory/inquiry-based learning, informed decisionmaking, and authentic, real-world context (ISTE &Thomas, 2007). Clusters of Purposeful Activity with Digital Technologies in Professional Development Knowledge Building Distributed Cognition Community and Communication Engagement Knowledge building: http://teacherchallenge.edublogs.org/ You can start your own blog blogging and copyrights issues ...and reflect your intake; http://aslisaglam.edublogs.org/2011/01/29/how-do-bloggers-make-use-of-images/ OR you can start a class blog Spice up your class with a blog; http://sallgood.edublogs.org/ Input from teacher challange; how to embed media http://teacherchallenge.edublogs.org/2011/01/27/ kick-start-activity-6-%e2%80%93-beginner%e2%80%93-enhancing-posts-by-embeddingmedia/ Hands on experience in my class blog; http://ourupperintclass.edublogs.org/ Are you familiar with these? CoP WIA Web 2.0 tools EVO Worldbridges Secondlife Virtual round table WEBHEADS Online Community of Practice of Teachers and Educators Practicing Peace and Professional Development through Web 2.0 and Computer Mediated Communication HOW DOES WEBHEADS WORK? COMMUNICATION PLATFORM : Yahoo Participants send messages about various issues, ask for help, respond to each other’s questions & even share important events in their lives Webheads meet online (live) on a regular basis ( each Sunday via Wiki) http:// learning2gether.pbworks.com explore the latest communications technologies, brainstorm on how to adapt Web 2.0 & Social networking tools. Webheadsinaction.org TESOL CALL Interest Section Electronic Village Online (EVO) Sessions more social scaffolding: collaborative spirit of WIA EVO &WORLDBRIDGES online discussions &workshops varying from simple discussions to virtual hands-on workshops, discussion of an issue in the field of teaching language to experiments with and pedagogy of new technology tools Provides invaluable service to teachers all over the globe, Brings the convention to those who cannot travel.. The sessions are again free and open to all interested parties. An example; a course on digital story telling Syllabus: http://digitalstorytelling4kids.pbworks.com/w/page/ 45606035/Syllabus%29 Tasks: http://digitalstorytelling4kids.pbworks.com/w/pag e/47970204/Week1 http://teacherbootcamp.edublogs.org/ Resources about the effective integration of technology with ELT teachers Virtual Round Table E-Conference http://www.virtual-round-table.com/page/vrtwebconprogram an annual web conference for language learning Technologies Virtual Round Table E-Conference http://www.virtual-round-table.com http://www.scoop.it/t/learning-technology & explore Web 2.0 Tools http://quickshout.blogspot.co.uk/2011/11/on-surface-of-it-justword-looks-just.html TEACHING ENGLISH http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/blogs/asligokturk/wikisworking-interactively-a-kool-way-i-nternet TEACHING ENGLISH Facebook Groups Free on-line videos for teacher training: Blogging http://www.teachertrainingvideos.com/newBlogger/i ndex.html Elecronic Village Online; Mentoring http://evosessions.pbworks.com/w/page/48514837 /Mentoring2012 http://www.techknowlogia.org/tkl_active_pages2/TableOfContents/main.asp ?IssueNumber=18 TechknowLogia Facebook Groups; http://www.facebook.com/groups/IATEFL.TTEdSIG/ Back to effect of technology PLN PATHS http://davidwarlick.com/images/manypaths-20090725-074436.jpg Back to teacher knowledge& learning; «being ready, willing and able» In conclusion, considering the examples, How can digital technologies support; 1) the development of teachers’ vision for education? 2) teachers’ motivation to learn and develop their practice? 3) teachers’ professional knowledge, understanding and practice? 4) teachers' reflection? 5) teachers’ learning in the community? ARIOĞUL, S. (2007). UNDERSTANDING FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHERS’ PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE: WHAT’S THE ROLE OF PRIOR LANGUAGE LEARNING EXPERIENCE?. JOURNAL OF LANGUAGE AND LINGUISTIC STUDIES, 3,(1), P. 1-14. BOGDAN, R.C & BIKLEN, S.K. (1998). NEEDHAM HEIGHTS: ALLYN & BACON PUBLISHING. BORG, S. (2003). TEACHER COGNITION IN LANGUAGE TEACHING: A REVIEW OF RESEARCH ON WHAT LANGUAGE TEACHERS THINK, KNOW, BELIEVE, AND DO. LANGUAGE TEACHING, 36(2), P. 81-109. BORG, S. (2006). TEACHER COGNITION AND LANGUAGE EDUCATION. LONDON: CONTINUUM. CHARLES, G. (2011). THEORETICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR UNDERSTANDING TECHNOLOGICAL PEDAGOGICAL CONTENT KNOWLEDGE (TPACK), COMPUTERS AND EDUCATION, 57, 1953-1960. CHOU, C. (2008). EXPLORING ELEMENTARY ENGLISH TEACHERS’ PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE: A CASE STUDY OF EFL TEACHERS IN TAIWAN. ASIA PACIFIC EDUCATION REVIEW, 9(4), P.529-541. DENZIN, N.K. & LINCOLN, Y.S. (2005). THE SAGE HANDBOOK OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH. CALIFORNIA: SAGE PUBLICATIONS, INC. ELBAZ, F. (1981). THE TEACHER’S “PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE”: REPORT OF A CASE STUDY. CURRICULUM INQUIRY, 11(1), P.43-71. FISHER,T. , HIGGINS, C. & LOVELESS, A. (2006). TECAHERS LEARNING WITH DIGITAL TECHNOLOGIES, RETRIEVED FROM: HTTP://ARCHIVE.FUTURELAB.ORG.UK/RESOURCES/PUBLICATIONS-REPORTS-ARTICLES/LITERATUREREVIEWS/LITERATURE-REVIEW129 IM, S. (2010). CONTEMPLATIVE TEACHERS’ PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE: TOWARDS HOLISTIC TEACHER EDUCATION. AN UNPUBLISHED DOCTORATE THESIS TO GRADUATE DEPARTMENT OF CURRICULUM, TEACHING AND LEARNING ONTARIO INSTITUTE FOR STUDIES IN EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF ONTARIO. REFERENCES MILES, M.B. & HUBERMAN, A.M. (1994). QUALITATIVE DATA ANALYSIS, THOUSAND OAKS, CA: SAGE. SHAVELSON, R.J AND STERN, P. (1981). RESEARCH ON TEACHERS’ PEDAGOGICAL THOUGHTS, JUDGEMENTS, DECISIONS, AND BEHAVIOUR. REVIEW OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH, 51(4), P. 455498. SHULMAN, L.S. (1987). KNOWLEDGE AND TEACHING: FOUNDATIONS OF THE NEW REFORM. HARWARD EDUCATIONAL REVIEW, 57(1), P.1-22. PATTON, M.Q. (2002). QUALITATIVE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION METHODS. CALIFORNIA: SAGE PUBLISHING. PERETZ-BEN, M. (2011). TEACHER KNOWLEDGE: WHAT IS IT? HOW DO WE UNCOVER IT? WHAT ARE ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR SCHOOLING? TEACHING AND TEACHER EDUCATION, 27, P.3-9. TAMIR, P. (1991). PROFESSIONAL AND PERSONAL KNOWLEDGE OF TEACHERS AND TEACHER EDUCATORS. TEACHING AND TEACHER EDUCATION, 7(3), P.263-268. ZANTIG, A. ET. AL (2003). USING INTERVIEWS AND CONCEPT MAPS TO ACCESS MENTOR TEACHERS’’ PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE. HIGHER EDUCATION 46, P.195-214. REFERENCES Thank you for listening :) Aslı Sağlam