Chapter 8 Power Point
advertisement

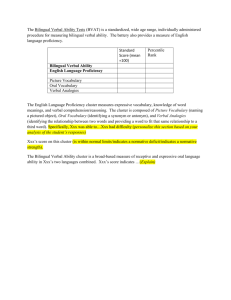
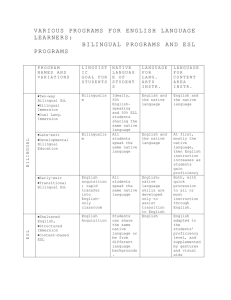
Language and Learning Style Do you remember learning how to talk? Think about a time when someone didn’t understand you. What did you do to help them understand you? What is the difference between an accent and a dialect? What is an appropriate distance to stand when talking to someone? What do you think about bilingual education? Organized Everyone for activity participates Collaborative Building relationships communities of learners Alternate assessments Language is the first institutionobjectifies, interprets, and justifies reality for the child. External, objective, has the power of moral authority and is historical Accent- the way words are pronounced Dialect- variation of some standard language form that includes differences in pronunciation, word usage, and syntax • • • • Black English(Ebonics) Rural English Mountain English Standard English Bidialectalism- refers to the ability to speak two or more dialects. American Sign Language Body movements and facial expressions 50%-90% of messages we send/receive Functions • • • • Convey messages Augment verbal communication Contradict verbal communication Replace verbal communication Proxemics- distance between people Kinesics- body movements Paralanguage- sounds Field independent • Abstract, analytical, individualistic, prefers working alone, intrinsically motivated Field dependent • Well-developed social skills, perceives globally, observational approach to learning, extrinsically motivated Multiple Intelligences History 1839Ohio passes first bilingual education law 1968Title VII Bilingual Education Act 1920sWWI fears lead to Englishonly laws 1981limited English proficient (LEP) 1974- Lau vs. Nichols 1990sbacklash English Language Learners (ELLs) • Silent/receptive/preproduction stage • Early production stage • Speech emergence stage • Intermediate language proficiency stage • Advanced language proficiency stage Curriculum Assessment Globalization