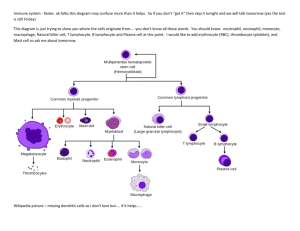
Mast cell-orchestrated immunity to pathogens
advertisement

Mast cell-orchestrated immunity to pathogens Soman N. Abraham and Ashley L. St. John Nature Reviews Immunology June 2010 Sentinels of host defence • Host-environment interface Blood vessels Neurons Sentinels of host defence • Host-environment interface Lymphatic vessels Dendritic cells Mast cell mediators Carboxy peptidase Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Chymase Platelet activating factor Lipid derived Proteases Tryptase TNF IL-5 Chemokines IL-12 Bactericidals VEGF Histamine IL-6 Cytokines IL-4 IL-3 Heparin Serotonin Mast cell heterogeneity • Different types – mucosal and connective tissue • Different granule composition - proteases • Different stimuli- IL4, Il10 • Different receptors (C5aR) • Different response to stimuli – cytokine, phenotype Recognition of pathogens • Recognize PAMPs by PRR – TLR , Fc receptors, others • TLR heterogeneity • Direct and indirect recognition • Pathogen associated substance – mastoparan, vector borne • Endogenous inflammatory factors – neurotensin, substance P, endothelin 1, complement; feedback mechanism • IgG and IgE, cross linking, superantigens Two waves of mediator release Nature, duration, specificity • 1) Degranulation – temporal advantage • Some soluble, most insoluble • Insoluble: slow, prolonged release • Long distance delivery • 2) De novo synthesis Cytokines Mediator functions • Protease: Neutrophil recruitment • Leukotrienes: rolling and extravasation through chemotaxis • Prostaglandins: Vascular permeability, mucus, nerve cells • Cytokines: chemotaxis, bactericidal killing, feedback Effector functions in immunity Innate • Vascular permeability, oedema • Immune cell recruitment • Bactericidals: cathelicidins, reactive O2 • Impede colonization, physical expulsion Adaptive • Activation and Ag presentation of DCs • Cell trafficking to draining lymph nodes • Lymph node hypertrophy TNF • Antigen presentation • Sensitization to Ag – immunological memory 1. Parasites • First study – helminths. Mast cell proliferation • Immune cell recruitment, gut permeability, parasite expulsion • Primary vs. secondary challenge • Leishmaniasis: T cell function, lesion size 2. Bacteria • Mouse model, peritonitis • Bacterial containment, prevention of dissemination • E. coli from peritoneum, bladder; K. pneumoniae from lungs; P. aeruginosa lesions • Cell trafficking, lymphocyte retention 3. Viruses • Less clear • Poly I:C: chemokines • CD8+ T cells, NK cells • Induced cytokine release • Cell mediated clearance Mast cells in vaccines • Enhancing adaptive immune response • Adjuvant activity • Mast cell activator (48/80) – humoral immunity • IgA production, mucosal immunity • Cellular mobilization, communication with draining lymph nodes Conclusions • Adaptive and innate immunity against pathogens • Kinetic advantage • Immunological memory • Functional outcome of heterogeneity • Long distance communication strategy • Vaccine design