Decreasing Inflammation in Athletes

by
Dr. Jen Mundt
This presentation is protected under copy-right and is not to be copied, distributed, or used in any way without the express written consent of Dr Jen Mundt
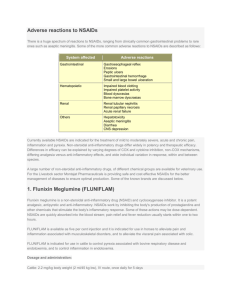
Immune response to overwork of a joint, injuries, bad diet, pathogens, etc.
Prolonged inflammation, known as chronic
inflammation, is characterized by simultaneous destruction and healing of the tissue from the inflammatory process.
Increased inflammation causes:
Joint destruction
Cardiovascular disease
Chronic Allergies
Nutrient deficiencies
What to eat
& What NOT to eat!
Cow’s milk, beef, liver, pork, lamb
Arachidonic acid is the direct precursor to proinflammatory and pain-promoting immune markers
Saturated fats: activates pro-inflammatory markers
Cream: marked oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation that lasts for 3 hours after you eat
Corn oil: rapidly activates pro-inflammatory effect
High glycemic OR carbohydrate dominant foods (white bread, sugar, high-carb fast-foodstyle breakfast):
Oxidative stress
Inflammation
Suppressed immune function infection or dysbiosis
Promotes bacterial overgrowth – inherently proinflammatory
Chemical preservatives & artificial sweeteners
Whole Foods:
Fruits
Veggies
Seeds
Nuts
Whole grains
Omega-3, Omega-6 & Omega-9 Fatty acids
Lean Sources of Protein
Lean meats
Fatty cold-water fish
Soy
Whey proteins
Organic Foods
Non-genetically modified (usually, but not always)
Non-irradiated
Grown without pesticides, herbicides, non-organic fertilizers, antibiotics or hormones
More nutrients
Taste better
Meats: Grass-fed, grass-finished organic meats
Critical in detox process of liver
Toxic build up systemic manifestations
Maintains energy
Promotes healthy functioning of liver, kidneys & other organs
Provides liquid to lubricate joints
BEWARE of “sports drinks” OR “high energy drinks”
High in sugar (pro-inflammatory)
Try Electrolyte mix instead
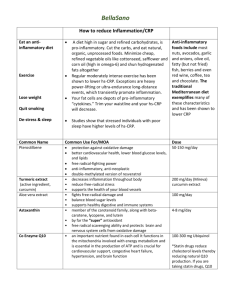
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA), EPA, DHA, GLA and oleic acid:
fatty acid supplementation
Anti-inflammatory
Maintains integrity and functionality of cells
Vitamin C
Anti-inflammatory
Builds & maintains collagen (component in all connective tissue, including cartilage)
Take with alpha lipoic acid
Vitamin D
Common deficiency
Chronic illness or chronic musculoskeletal pain
Anti-inflammatory
Immune boosting
Vitamin E
Natural (d-alpha) tocopherols OR
D-a-tocopherol succinate
Bioflavonoids
Decreases bruising
Decreases edema due to inflammation
Green tea
Antioxidant
Resveratrol
Antioxidant
Curcumin
Extremely anti-inflammatory
Quercitin
Anti-inflammatory
Antioxidant
Antihistamine
Ginger
Extremely anti-inflammatory
Bromelain
Glucosamine sulfate
Stimulates manufacture of GAGs by chondrocytes and promotes incorporation of sulfur into cartilage
Increases ability to absorb shock
Absorption rate 90-98%
Chondroitin sulfate, bovine cartilage
Mixed of intact or partially hydrolized GAGs
Absorption rate 13%
Jen Mundt, ND j.mundt@scnm.edu