urinary_system - MedCell at Yale
advertisement

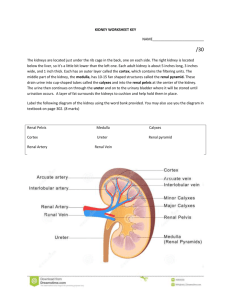
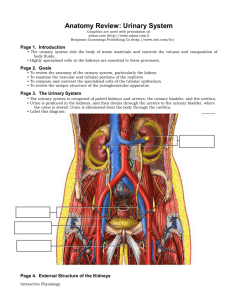
Histology Laboratories Molecules to Systems 2003 Compiled by James D. Jamieson, MD/PhD Thomas L. Lentz, MD No part of this image collection may be distributed outside of the Yale University Intranet. Acknowledgements Sources of Micrographs, Diagrams and Figures Alberts, B. et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th Edition, Garland Science, New York, 2002. Gartner, L. P. and Hiatt, J. L. Color Atlas of Histology, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1994. Kerr, J. B. Atlas of Functional Histology. Mosby, London, 1999. Kessel, R. G. and Kardon, R. H. Tissues and Organs: a text-atlas of scanning electron microscopy. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, 1979. Lentz, T. L. Cell Fine Structure. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1971. Lodish, H. et al. Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman, New York, 2000. Mizoguti, H. Color Slide Atlas of Histology. Nihon Shashin Shinbunsha, Tokyo. Young, B. and Heath, J. W. Wheater’s Functional Histology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 2000. Micrographs taken by George Palade, Marilyn Farquhar, James D. Jamieson, Nicolai Simionescu, Maya Simionescu, David Castle, Thomas L. Lentz. Web Resources http://info.med.yale.edu/webpath/webpath.htm Cushing Library Educational Software/Cell Biology/Several Histology Resources Urinary System Laboratory Some Handy Abbreviations G: glomerulus PCT: proximal convoluted tubule tDL: thin descending limb of Henle tAL: thin ascending limb of Henle TAL: thick ascending limb of Henle DCT: distal convoluted tubule (similar to TAL) CT: connecting/collecting tubule CD: collecting duct MD: macula densa AA: afferent arteriole (in) EA: efferent arteriole (out) Cortex BV RT G CD Renal Cortex and Medulla Medulla Vasa recta Organization of Renal Pyramid The Nephron Renal Tubules Renal Corpuscle (Glomerulus, afferent and efferent arterioles, Bowman’s capsule, beginning of proximal convoluted tubule) Diagram of Renal Corpuscle/Glomerulus Renal Corpuscle/Glomerulus Development of Renal Corpuscle PCT CD G DCT Renal Corpuscles Bowman’s space G PCT Renal Corpuscles Bowman’s capsule parietal layer visceral layer MD Vascular pole Bowman’s capsule parietal layer visceral layer G Bowman’s space PCT Renal Corpuscle Urinary pole Podocytes Bowman’s capsule parietal layer visceral layer PCT Bowman’s space (urinary space) Mesangial cells DCT Renal Corpuscle Beginning of PCT Urinary Pole of Renal Corpuscle Glomerular Filter Bowman’s space Podocyte Lumen of glomerular capillar Foot processes of podocytes Fenestrae Urinary space Glomerular BM Fenestrated Capillaries in Glomerulus Urinary space FS: filtration slits Glomerulus Podocyte Filtration slits with diaphragms Capillary space Components of Glomerular Filter Urinary space Scanning EM of Glomerulus Foot processes Filtration slits Renal Tubules in Sequence Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT): Epithelium: brush border; basal infoldings Loop of Henle: straight portion of PCT (or thick descending limb) (TDL)>thin descending limb (tDL)>loop>thin ascending limb (tAL)>straight portion of DCT (or thick ascending limb) (TAL) Epithelium: Simple squamous epithelium on thin segments; epithelium similar to PCT and DCT on thick segments Distal Convoluted Tubule: Continuous with TAL>macula densa>DCT Epithelium: No brush border, numerous mitochondria Collecting Tubule: Epithelium: cuboidal Collecting Duct: Epithelium: cuboidal Brush border Proximal Convoluted Tubule Brush border Proximal Convoluted Tubule M: mitochondria Mv: microvilli of brush border Proximal Convoluted Tubule PCT Vasa recta T T CD Thin Walled Tubules of Loop of Henle VR TAL tL TAL tL CD Relationhship Between CD, TAL, tL and Vasa Recta (VR) Basolateral infoldings with mitochondria Distal Convoluted Tubule Basolateral infoldings with mitochondria; few microvilli Distal Convoluted Tubule Collecting Ducts, LS Collecting Ducts, XS Site of urine outflow at renal papilla Renal pelvis Apex of Renal Pyramid Countercurrent Multiplier Countercurrent Multiplier Countercurrent Multiplier Juxtaglomerular Apparatus and Control of Blood Pressure and Volume JGA and Control of Blood Pressure Diagram of JG Apparatus JG Apparatus AA: afferent arteriole J: juxtaglomerular cells MD: macula densa DCT: distal conv. tubule DT JG Apparatus: Mg, mesangial cells; P, podocyte; JC, juxtaglomerular cells with secretory granules containing renin (arrowheads) Ureter, Bladder and Urethra Transitional epithelium Smooth muscle Ureter Transitional epithelium Relaxed Bladder Distended Bladder Male Urethra: transitional > stratified columnar epithelium Some Pathology Normal Glomerulus and Tubules PAS stain for basement membrane glycoproteins. Diabetic Kidney PAS stain. What component of the filtration apparatus might you see altered in an EM? Membranous Glomerulonephritis What structure is the membranous change affecting? The next EM taken at biopsy cinches the diagnosis. Membranous Glomerulonephritis Where is the pathology occurring? May be linked to chronic diseases and the immune system. What might the dark blobs be? Hint: look at the next immunofluorescence picture stained for IgG. Minimal Change Disease What is the most obvious change in this EM? EM is used routinely to diagnose kidney diseases. Acute Pyelonephritis. Where is the infection located? Renal cortex after drinking antifreeze. What is the main target of ethylene glycol and what might the patients’s urine show? Transplantation Rejection What does the histologic picture tell you about what went wrong?