ANEMIA DEFINITION & CLASSIFICATION

Maj Gen (R) Masood Anwar
Professor of Haematology
Functions of blood
◦ Transport of nutrients
◦ Transport of gases
◦ Haemostasis
◦ Defence
Composition of blood
◦ Cells ( RBC , WBC, Platelets)
◦ Plasma (Colloids, Crystalloids, Water)
PYSIOLOGICAL DEFINITION
◦ Decrease in oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
ANALYTICAL (PATHOLOGICAL) DEFINITION
◦ Reduction in total circulating red cell mass
◦ Reduction in Haemoglobin concentration and/or
Haematocrit
These are blood cells produced in the bone marrow from a pleuripotent haemopoietic stem cell by processes of division, differentiation and maturation and released in the circulation to function mainly to transport oxygen from lungs to other tissues of the body.
Haemoglobin (Hb)
Haematocrit (Hct)
[Packed Cell Volume (PCV)]
Total Red Blood Cell Count (TRBC)
Mean Cell Volume (MCV)
Mean Cell Haemoglobin (MCH)
Mean Cell Haemoglobin Concentration
(MCHC)
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
PARAMETER
Hb
TRBC
Hct/PCV
MCV
MCH
MCHC
ADULT MALE
13-17 g/dl
ADULT FEMALE
12-16 g/dl
4.5-6.5 X 10 12 /l 4.2-6.0 X 10 12 /l
40-54%/0.40-0.54 l/l 36-49%/0.36-0.49 l/l
76-96 fl
27-32 pg
31.5-34.5 g/dl
MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
Based on appearance of RBC under the microscope
OR red blood cell indices
PATHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
Based on abnormality of anatomical, biochemical or physiological abnormality
ETIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
Based on specific causative process/agent
Normocytic normochromic anaemia
Hypochromic Microcytic Anaemia
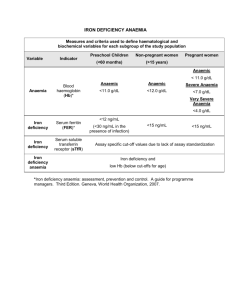
Iron deficiency anaemia
Thalassaemia minor
Sideroblastic anaemia
Anaemia of chronic disorders
Macrocytic anaemia
Megaloblastic anaemia
Aplastic anaemia
Myxoedema
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Liver Disease
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Blood loss
◦ Acute
◦ Chronic
Decreased production
◦ Disturbance of proliferation and differentiation
Of stem cells
Of erythroblasts
◦ Defective Hb synthesis
Increased destruction
◦ Intracarpuscular (Intrinsic) defects
◦ Extracarpuscular (Extrinsic) defects
Hereditary
◦ Blood loss – Hereditary Intestinal telengiectasia
◦ Decreased production – Pure Red Cell aplasia
◦ Increased destruction – Membrane, Enzyme and Hb defects
Congenital
◦ Defective production – Congenital dyserythropoietic anaemia,Congenital sideroblastic anaemia
◦ Increased destruction – Cardiac defects, vascular defects
Acquired
Blood loss
◦ Acute
◦ Chronic
Ulcerative lesions of GIT
Female reproductive system
Parasites – Ankylostoma duodenale, Schistosoma haematobium
Increased destruction of RBC
◦ Membrane defect (PNH)
◦ Mechanical trauma (Microangiopathies)
◦ Antibody mediated (Immune haemolytic anaemia)
◦ Parasites (malaria, Aroya fever)
Decreased production
◦ Deficiency anaemias
Iron deficiency
Vitamin B12 and Folate deficiency
◦ Bone marrow disease/infiltration
◦ Miscellaneous
Pyridoxin responsive anaemia
Sideroblastic anaemia