Anaemia
advertisement

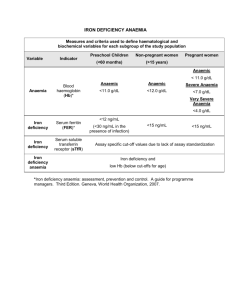
Anaemia Corrina Mc Mahon Normal Haematopoiesis Foetus – 0-2 mo; Yolk sac 2-7mo; liver/spleen 5-9mo; bone marrow Infants – Bone marrow of all bones Adults – Vertebrae, ribs, sternum, skull, sacrum, proximal ends of femur Haematopoiesis II Normal Values Haemoglobin 15-21g/dl; Neonate 9.5-12.5g/dl; 1-3mo >11g/dl; >3mo Platelets 150-450 x10^9/l Signs and Symptoms of anaemia Symptoms Pallor Poor feeding Tachypnoea Lethargy Signs Oedema Tachypnoea Tachycardia/systolic flow murmur/cardiomegaly Hepatosplenomegaly Hypotension Types of Anaemia Hypochromic/ microcytic MCV<80fl MCH<27 Iron deficiency Thalassaemia Chronic disease Lead poisoning Sideroblastic Macrocytic MCV>95fl Megaloblastic Alcohol Liver disease Myelodysplasia Aplastic Pregnancy Reticulocytosis Iron Deficiency Anaemia Commonest Anaemia Normally 5-10% of iron in food is absorbed C/F: Glossitis, Angular stomatitis, Brittle nails Generalised epithelial changes Causes of Iron Deficiency Blood Loss Increased Demands GIT Uterine Renal Prematurity Growth Pregnancy Malabsorption Coeliac disease Colitis Cows Milk Diet Intrauterine blood loss Twin/twin Foetal-Maternal Iatrogenic Blood Loss Investigations FBC and Blood Film Serum Iron and TIBC Ferritin Then find the cause! Failure to Respond Continued Haemorrhage Failure to comply Wrong diagnosis Mixed deficiency Malabsorption Slow release preparation Megaloblastic Anaemia Vitamin B12 deficiency Folate deficiency Abnormalities of B12 or folate metabolism, Anti-folate drugs, nitrous oxide, transcobalamin deficiency Defects of DNA synthesis, alcohol, hydroxyurea, chemotherapy Causes of B12 deficiency Nutritional 3 year supply Malabsorption Gastric causes Pernicious anaemia Abnormality of intrinsic factor Total or partial gastrectomy Intestinal Causes Ileal resection Crohns disease Stagnant loop syndrome Congenital malabsorption with preteinuria Tropical sprue Folate deficiency Nutritional Malabsorption Excess Utilisation Pregnancy and lactation Prematurity Haemolytic anaemia Inflammatory disease Malignancy Drugs Coeliac Disease Crohns disease Extensive jejunal resection Anticonvulsants Sulphasalazine Mixed Liver disease Alcoholism Haemolytic Anaemia Hereditary Membrane H. Spherocytosis H. Eliptocytosis Metabolism G6PD deficiency Pyruvate Kinase deficiency Haemoglobin Abnormal, HbS, HbC etc Acquired Immune Autoimmune Alloimmune Red cell Fragmenation TTP HUS DIC Infections Chemical and Physical agents PNH Signs and symptoms of HA s/s of Anaemia Jaundice Splenomegaly Abdominal pain Investigation of HA FBC & film Reticulocyte count Direct Coombes test Bilirubin & LDH Haptoglobins Urinary Hb/Haemosiderin Free serum Hb Specific tests Case 1 Newborn infant Pale,tachycardia Hepatosplenomegaly Jaundice FBC Hb 6g/dl WCC 15 x 109/l Platelets 200 x 109/l Reticulocytes 10% DCT positive Haemolytic disease of the newborn Passage of IgG antibodies Rhesus/ABO/Kell/Duffy/Kidd Mild, moderate, severe (Hydrops) May get worse with each pregnancy Case 2 2 week old boy Pale Tachycardia Prolonged Jaundice Splenomegaly Older brother jaundiced Father – cholecystectomy at 15 yrs FBC Hb 9g/dl WCC 9 x 109/l Platelets 210 x 109/l Retics 15% DCT negative LFTS Bilirubin 40 iu/l LDH 500 iu/l Case 2 Blood Film Other investigations Virology Cultures Heinz body prep Haemoglobin electrophoresis Red cell enzymes Red cell membrane studies Hereditary Spherocytosis Most common HHA in Northern Europeans Membrane defect Autosomal dominant (75%) Most severe cases – hydrops in utero Treatment; Blood transfusion Splenectomy Case 3 5yr old Nigerian boy Pyrexial URTI Treated Co-trimoxazole lethargy/jaundice FBC: Hb 8g/dl WCC 15 x 109/l Platelets 350 x 109/l Reticulocytes 15% Examination of Urine G6PD Deficiency Sex – linked West African, Mediterranean, middle East, SE Asia Neonatal jaundice Episodes of IV haemolysis Heinz Bodies NADPH regenerates glucathione which protects Hb against oxidative damage Haemoglobinopathy Thalassaemia Failure to produce adequate globin chains Sickle cell Disease Production of an abnormal Hb B-Thalassaemia Major B-Thalassaemia Major Failure of B-Chain production Anaemia in 1st year Chronic transfusion Iron overload Growth failure Sickle Cell Anaemia Valine for glutamine substitution at position 6 globin chain Sickling; Abnormal adherence of RBC to endothelium Hb polymerisationelongated filaments semi-solid gel Reversible sickling/irreversible changes HbS - Sickling HbF/HbA - sickling Factors precipitating RBC sickling Deoxygenation Dehydration Infection Acidosis Cold Vigorous exercise Menstruation Problems associated with SCD Hyposplenism Anaemia Vasoocclusion Bone Chest Abdominal Splenic sequestration Cerebrovascular events Renal Disease Life expectancy 45yrs Bony Abnormalities in SCD Diagnosis FBC/Film/Reticulocytes Sickledex (not in under 6 mo) Hb Electrophoresis Also G6PD Analysis Presence of another haemoglobinopathy