Chapter 4 Notes
advertisement

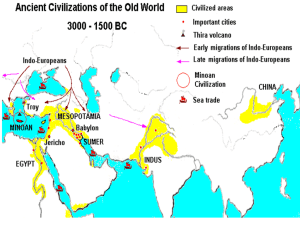
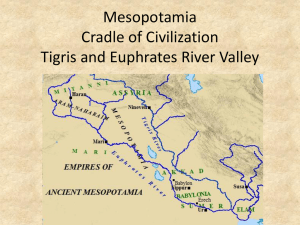
Chapter 4 First Age of Empires 1570 BC – 200 BC I. The Egyptians and Nubians A. Nomadic Invaders Rule Egypt Hyksos ruled Egypt from 1640 to 1570 BC Had chariots 1. Hebrews Migrate to Egypt Arrived around 1650 BC 2. Expulsion and Slavery By 1600 BC, the Egyptians grew strong Under Queen Ahhotep and Pharaoh Kamos Drove the Hyksos out and enslaved the Hebrews B. The New Kingdom in Egypt 1570-1075 BC Built an empire: control of several peoples or states under one ruler 1. Hatshepsut's Prosperous Rule She began ruling in 1472 BC Encouraged trade instead of war Her fleet started trade w/ Punt (Somalia) 2. Thutmose the Empire Builder Stepson, who may have murdered Hatshepsut Thutmose III armies took Syria and northern part of the Euphrates Pushed into Nubia Conquered an empire Grow rich, no longer isolated B. The New Kingdom cont. 3. The Egyptians and the Hittites Conflict erupted over Syria and Palestine Armies clashed at Kadesh in 1285 BC Ramses II and their king signed a treaty The two empires became allies 4. An Age of Builders Hidden tombs in desert cliffs Valley of the Kings near Thebes Ramses commissioned monumental statues and temples Ramses’ tomb was found in 1995 with 50 of his 52 sons buried with him C. The Empire Declines 1. Invasions by Land and Sea 1208 BC, Mediterranean sea raiders weakened the area Also faced Palestinian revolts and Libyan invaders 2. Egypt’s Empire Fades It never recovered its previous power or prestige Libyans ruled from 950 to 730 BC Adopted The Egyptian culture Nubians later do the same thing D. The Kushites Conquer the Nile Egypt dominated Nubia and Kush for centuries The region emerged during the Hyksos reign Conquered Egypt 1. The People of Nubia People overcame the cataracts to trade on the Nile Linked the Mediterranean world to Africa 2. The Interaction of Nubia and Egypt Forced rule on Nubia during the New Kingdom Heavily influenced Nubia Nubian princes lived in Egypt and adopted their culture Regained independence around 1200 BC D. The Kushites cont. 3. Piankhi Captures the Egyptian Throne 751 BC, Piankhi overthrew the Libyan pharaoh United the entire Nile River valley Started the 25th dynasty of Egypt Erected a monument in Kush to celebrate The Assyrians conquered Egypt in 671 BC, ending the dynasty E. The Golden Age of Meroë The Kushite royal family moved to Meroë 1. The Wealth of Kush Traded with Africa, India, and Arabia Plentiful rainfall and iron supplies 2. The Decline of Meroë Declined around 250 to 150 BC Another city, Aksum, dominated their trade II. The Assyrians A. A Mighty Military Machine Learned to fight while defending their land Most feared and hated empire in the region Foot soldiers, chariots, iron weapons, cavalry Treated People poorly Burned cities, tortured and killed captives, heavy taxes Deported entire populations One king, Sennacherib, claimed to destroy 89 cities and 820 villages 1. Military Organization and Conquest Nineveh the capital Start conquering 900 BC Well equipped with iron weapons Tiglath-pileser and Ashurbanipal led campaigns The Assyrians Cont. B. The Empire Expands Conquered Syria, Palestine, Babylonia, Anatolia, and Egypt 1. Assyrian Rule Peaked around 650 BC Royal Roads Divided empire into provinces w/ local rulers Crushed revolts quickly markers so others wouldn’t revolt Destroyed cities and exiled the people in places who refused to pay tribute Burned cities, hung skin on walls, piled skulls Left Never found a niche for making money, only knew conquering and pillaging Nineveh did have a huge library C. The Empire Crumbles A universal hatred of Assyria led to an alliance conquering Nineveh in 612 BC The army of Medes, Chaldeans, and others burned and leveled the city 2. Rebirth of Babylon Under the Chaldeans Started a revival for Babylon Built into a monumental city Reached its height under King Nebuchadnezzar II (605-562) Extended the empire Deported the Jews Built the Hanging Gardens Loved astronomy and maps Poor harvest and slow trade hurt them III. The Persians A. The Rise of Persia Modern day Iran 1. Cyrus Founds an Empire Conquered the Medes in the 540s Swept down from the mountains of Iran in 539 BC Cyrus II conquered Babylon Allowed the Jews to return to their homeland in 538 BC Eventually took over Mesopotamia, Syria, Canaan, Phoenicia, Lydia, and Greek citystates of Asia Minor (Ionia) Tolerant to others cultures Allowed to retain their own language, religions, and customs Killed in battle on the eastern border B. Persian Rule 1. Cambyses and Darius Conquered Egypt in 525 BC Ruled harshly, unlike his father Died eight years later, revolts erupted Darius seized the throne with the help of the Ten Thousand Immortals in 522 BC Spent the next three years putting down revolts Then began conquering Afghanistan • Empire went from the Nile to the Indus River, 3,000 miles with 50 million people B. Persian Rule cont. 2. Provinces and Satraps Divided it into provinces or satraps Military officials and tax collectors helped the king Inspectors were the “eyes and ears” of the king People only had to pay a tribute They would crush a rebellion quickly though Brought artisans from the various regions to build Persepolis Encouraged trade: used coins The Royal Road stretched 1,677 miles and had stops every 14 miles with food, water, and horses Messengers could travel it in seven days C. The Persian Legacy 1. Zoroaster’s Teachings Had a strict moral code Stressed bravery and honesty Before 500s BC, they worshipped many gods 570 BC, Zoroaster reformed the religion Talked about a struggle between good and evil Ahura Mazda: good, Ahriman: Bad Humans had to choose Teachings linked to glorifying the kings Lots of pomp and pageantry Zoroaster influenced Judaism, Christianity, and Islam: heaven, hell, Last Judgment 2. Political Order Tolerance and good govt. brought order to the region IV. The Unification of China A. Confucius and the Social Order Born Kongfuzi in 551 BC 1. Confucius Urges Harmony Good govt. and social harmony achieved if people used ethics Reciprocity Golden Rule Five Relationships For moral behavior Learn by example Stressed filial piety Family a mini society After his death, 479 BC, work collected for the book Analects 2. Confucian Ideas About Govt. Education could transform anyone into a gentleman Laid the groundwork for bureaucracy A trained civil service A. Confucius cont. 3. Legalism Rejected Confucianism Strict laws and harsh punishments Hanfeizi Humans evil by nature Favored by the Qin Vanished with their dynasty A. Confucius cont. Harmony w/ nature 4. Taoist Ideas Laozi, 500s BC Could be a Taoists and Confucianists Govt. vs. individual 5. Yin and Yang Two opposing forces Yin: cool, dark, female, submissive Yang: warm, light, male, aggressive Need balance B. The Qin Dynasty Local lords revolted against the Zhou 1. A New Emperor By 221 BC, Qin wiped out the Zhou Qin Shi Huangdi United the area under a strong, central govt. Attacked invaders north of the Huang He and pushed as far south as Vietnam 36 Military districts, standardized coins, laws, and writing Commanded all nobles live in his capital Uprooted 120,000 families Forced labor for roads and canals Legalists murdered hundreds of Confucian scholars to prevent criticism Burned useless books B. The Qin cont. 2. A Program of Centralization Built a network of 4,000 miles of roads Trade Set boomed standards throughout China for writing, law, currency, and weights and measures 3. Great Wall of China 300,000 troops worked to build the 4,000 mile wall Keep Mongolians out Thousands died 4. The Fall of the Qin Cruel tyrant 210 BC, Qin died, so did the dynasty Peasants rebelled against the son By 202 BC, the Han Dynasty replaced the Qin