Human Resource Management (HRM) Overview
advertisement

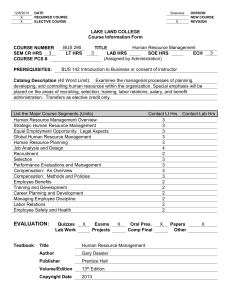
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Introduction Human Resource Strategy Human Resource Planning Recruitment and Selection Training and Development Performance Management Compensation Employee Benefits Employee Relations Career Planning HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IS ALL ABOUT: GROUP EFFICIENCY INDIVIDUAL PERFORMANCE INDIVIDUAL EFFECTIVENESS INDIVIDUAL EFFICIENCY Doing things the right way Doing the right things Individual Performance – Outputs of a high quality and quantity Doing things the right way: Executing a task correctly Doing more than the standard Rendering outputs of high quality and quantity Restricting wastage and interruptions Doing the right things: Involvement in goals set for work groups and organisation Positive attitude High morale Innovation HR Predictions for 2008: Definition of jobs Organisations will not pay for the value of the job but for the value of the person Versatility will be a key factor in determining employee value Compensation systems will be linked to business outcomes All jobs will require higher levels of computer skills Positions will be organised in teams focused on a task Positions will be defined by competencies needed to be performed (Grobler et al, 2006) HRM Issues and Challenges Worker productivity Quality improvement Downsizing, delayering, decruiting Changing workforce Globalisation Impact of legislation Quality of working life (QWL) Technology and training HIV Aids Human Resource Strategy A strategic approach to HRM: recognises impact of external environment recognises impact of competition recognises impact of labour market dynamics a long range focus (3 – 5 years) focuses on choice and decision-making considers all personnel is integrated with overall corporate strategy Strategic Human Resource Management Strategic Human Resource Management – The process by which managers design the components of a human resource system to be consistent with each other, with other elements of organizational structure, and with the organization’s strategy and goals. – The objective of strategic HRM is the development of an HRM system that enhances the organization’s efficiency, quality, innovation, and responsiveness to customers. Human Resource Planning HRP as part of strategic organisational planning The impact of good HRP Steps in the planning process Forecasting demand Estimating supply – skills inventories Components of a Human Resource Management System Recruitment and Selection Factors that influence recruitment Recruitment sources Recruitment methods Legal considerations Factors that influence the selection decision Selection Process Employment tests Checks The Recruitment and Selection System Training and Development Training Development Strategic Training Approaches: Traditional training vs Virtual Training 3 principles of VT: Employees are responsible for their growth Most powerful learning takes place on the job Improved performance hinges on the relationship between manager and employee Performance Management Purpose of Performance Management Performance Evaluation Legal considerations Performance management and QA: “if the system itself prevents good work, individuals will not be able to improve their performance, even if they want to” (Deming) Compensation Why compensation? Factors influencing compensation Elements of total compensation Job hierarchies – evaluation systems Tenets of dynamic compensation: Pay is a people issue Pay is a communication tool Pay must support vision, values, strategies Pay must be aligned to a work culture No single pay strategy is right for everyone Employee Benefits of benefits – mandatory voluntary Benefit planning Types Employee Relations Addresses the employer-employee relationship Three parties in this relationshipdirectly – employee and employer indirectly – the state Rights of workers Rights of management Career Planning By the individual: An individual sets career goals and identifies the means to achieve them By the organisation: (HR Planning) Recruitment and Selection Grooming people for posts Career Development Assignment Case Study 5 questions Examination Questions HRM professional will need to focus on the creation of value for the organisation. With reference to this, discuss the current issues and challenges facing Human Resource Managers in contemporary business organisations. Critically discuss the factors influencing human resource recruitment and selection policies within an organisation. Examination Questions Instructional Systems Design (ISD) is the basis for the most commonly used training and development process used within organisations. Discuss the five phases of a training process based on ISD. Examination Questions Discuss compensation as a human resource practice under the following headings: 4.1 The nature of compensation (5) 4.2 Factors influencing the determination of compensation (14) 4.3 Job-based compensation structures (6) Critically discuss the following statement: “Performance appraisal is the human resource function most often criticised and whose systems carry the greatest risk of either failing, falling into disuse or degenerating towards a meaningless, paperwork exercise.” Examination Questions Define the concept “employment relations” (4) Describe the parties involved in employment relations and their roles, rights and duties (12) Discuss the approaches to employment relations (9)