Progettazione di Sistemi Embedded Goals Embedded Systems
advertisement
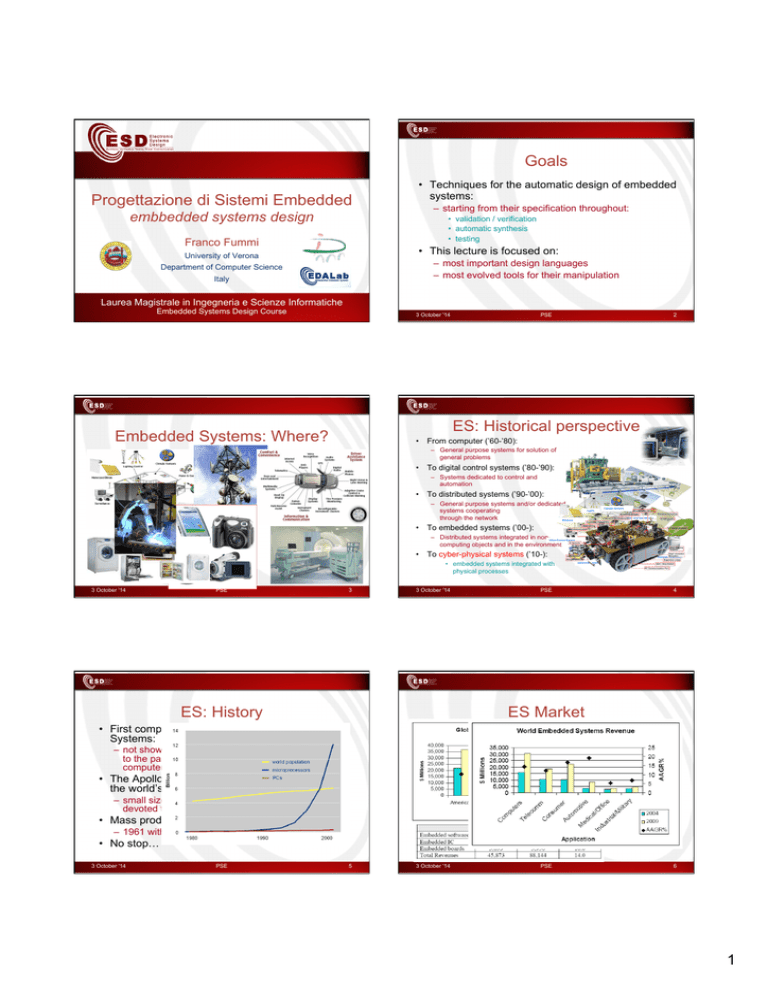
Goals Progettazione di Sistemi Embedded embbedded systems design • Techniques for the automatic design of embedded systems: – starting from their specification throughout: • validation / verification • automatic synthesis • testing Franco Fummi • This lecture is focused on: University of Verona – most important design languages – most evolved tools for their manipulation Department of Computer Science Italy Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche Embedded Systems Design Course 3 October '14 PSE 2 ES: Historical perspective Embedded Systems: Where? • From computer (’60-’80): – General purpose systems for solution of general problems • To digital control systems (’80-’90): – Systems dedicated to control and automation • To distributed systems (’90-’00): – General purpose systems and/or dedicated systems cooperating through the network Lights Climatic Sensors Water and Gas security Windows • To embedded systems (’00-): Irrigation – Distributed systems integrated in noncomputing objects and in the environment Video-Control System • To cyber-physical systems (’10-): • embedded systems integrated with physical processes 3 October '14 PSE 3 3 October '14 ES: History HVAC control Domestic Appliances audio/video systems PSE 4 ES Market • First computers in 1940’s were all Embedded Systems: – not showing the today characteristics, but devoted to the particular application of being programmable computers and embedded into a… room • The Apollo Guidance Computer is considered the world’s first modern Embedded System: – small size for a tremendous computational power devoted to guide Apollo • Mass production of Embedded Systems: – 1961 with the Autonetics D-17 • No stop… 3 October '14 PSE 5 3 October '14 PSE 6 1 How Relevenat (I) ES Market: trend • Expected to increase from $92.0 billion in 2008 to $112.5 billion by the end of 2013: – a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% – embedded hardware from $89.8 billion in 2008 to $109.6 billion in 2013 – embedded software from $2.2 billion in 2008 to $2.9 billion in 2013, for a CAGR of 5.6%. 3 October '14 PSE 7 4 October '13 How Relevant (II) PSE 8 ES: How to design? • & progetti europei completati e attivi: • We cannot design embedded systems like general purpose systems – Angel, Vertigo, Coconut, C4C, Complex, SMAC, Contrex – Different design constraints, different goals – Embedded design is about the system, not about the computer • 2 progetti europei in FP6 – ANGEL (mobile gateway for sensors network) – VERTIGO (HW formal verification) • E.g. • 5 progetti europei in FP7 – In general purpose computing, design often focuses on building the fastest CPU – In embedded systems the CPU simply exists as a way to implement control algorithms communicating with sensors and actuators – COCONUT (embedded systems design and verification) • best evaluation of the overall embedded systems track – C4C (control for coordination of distributed systems) – COMPLEX (platform-based design space exploration) – SMAC (smart systems design) – CONTREX (mixed-criticality systems) 3 October '14 PSE 9 3 October '14 ES: Design constraints 10 ES: Designer knowledge • Size and weight • HW architecture alternatives – for a correct HW/SW trade-off – Hand-held electronics – Weight costs money in transportation – Human body cannot eat desktops • SW design skills – lots of languages continuously extending • HW/SW interaction mechanisms • Power – O.S., MW, HdS for efficient SW development – Buttery power instead of AC • Network infrastructure • Harsh environment – all ES are now networked embedded systems – Power fluctuation, RF interferences, heat, vibration, water, … • Computation effort estimation – theory is important when used in practice • Safety critical and real time operations • Low costs 3 October '14 PSE PSE • Join 3C: computation, control & communication 11 3 October '14 PSE 12 2 Course Structure Modalità di Esame (I) • 34 lectures: • Teoria + lab. + opzioni: – 32 theory hours – teoria • 22 lectures • scritto con votazione /30 – 24 practical hours – relazione laboratorio 6 credits • 12 lectures • People: • +3 punti max – on demand • elaborato 0 +∞ • (orale) +3 -∞ – Franco Fummi (theory) – Michele Lora (laboratory class) • Regole generali: – … for practical elaborations 3 October '14 – elaborato dura 1 anno accademico – consegna in date stabilite PSE 13 3 October '14 PSE Modalità di Esame (II) Pre/post Condizioni • Precedenze Indispensabili: • Alternative: – Architettura degli Elaboratori – Programmazione – Linguaggi ... – Sistemi (Metodi di specifica) – Elaborato personale • stage aziendale • tesi – Teoria • Fondamentale per • no way :-) – Curriculum sistemi embedded (magistrale in Ingegneria) • Design&Reuse: • laboratorio di Informatica (ordinamento 509/99) • tesi • stage pre-tesi 3 October '14 • Sistemi operativi avanzati, Architetture avanzate, Software per Sistemi Embedded, Sistemi Embedded Multimediali, Sistemi Embedded di Rete… PSE 15 2014/2015 news ?:'08H')G:'&.#1:9F:'*'/(# -*9:%;# 5:DE&%*# 6FF.+)&G:'# -.+/*0123# @'*%I;# 5/:%&I*# J*,+)*# 2:E*%# 5:H%)*# 435#7'/*%8&)*# 435#624# 435#7'/*%8&)*# • Laboratorio Ciberfisico: 36!$# <=6>+(# 435#7'/*%8&)*# !"## $%&'()*+,*%# 5*%+&.#7'/*%8&)*# ?@$AB!C# – Secondo piano CV2 3 October '14 435#7'/*%8&)*# PSE 3 October '14 data 1-Oct 3-Oct 8-Oct 10-Oct 15-Oct 17-Oct 22-Oct 24-Oct 29-Oct 31-Oct 5-Nov 7-Nov 12-Nov 14-Nov 19-Nov 21-Nov 26-Nov 28-Nov 3-Dec 5-Dec 10-Dec 12-Dec 17-Dec 19-Dec 7-Jan 9-Jan 14-Jan 16-Jan 21-Jan 30-Jan hours credits • Smart devices: – The Open Source Test Case (SMAC project) 14 17 day Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. Wed. Fri. 56 6,0 3 October '14 PSE lecture Detailed Program lab. 3 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 2 32 4,0 16 topic NO Course introduction; Embedded systems modeling Embedded systems modeling II; SystemC-based design NO SystemC-based design II; SystemC-based design III Platform-based design; Transactional-based design; TLM 2.0 standard TLM 2.0 standard II; SystemC/AMS support SystemC modeling at RTL SystemC compilation/execution/debugging SystemC timing evolution SystemC modeling at TLM High-level synthesis (HLS): scheduling; High-level synthesis: allocation Automatic synthesis from TLM Software embedded synthesis; Model-based design (MBD) of embedded software; HMI design SystemC / AMS intermediate exam Mixed RTL/TLM/AMS SystemC VHDL introduction; VHDL syntax Platform, testbench and device driver (OSTC) VHDL modeling; VHDL timing simulation Embedded software: radCASE VHDL timing simulation II; VHDL synthesis VHDL modeling at RTL Cyber-physical systems: bioaspects + interfaces VHDL timing simulation Networked embedded systems (NES); Middleware for embedded systems Automatic synthesis from RTL VHDL Introduction to embedded systems verification; Introduction to embedded systems testing NO final exam 24 2,0 PSE 18 3 Topics (theory) • Specification: • – Embedded software generation – SystemC-based design – Automatic device driver generation – TLM design introduction – Middleware for embedded systems – HMI deisgn – VHDL syntax • – Networked embedded systems (NES) • Veriifcation & testing: – Introduction to testing • – VHDL timing simulation – Introduction to TLM design – RTL-TLM mixed simulation – High-level synthesis – Embedded software verification PSE 19 Software synthesis: 3 October '14 Teaching supports (I) @'*%I;# 5/:%&I*# J*,+)*# 2:E*%# 5:H%)*# 435#624# 435#7'/*%8&)*# 435#7'/*%8&)*# 36!$# <=6>+(# 435#7'/*%8&)*# !"## $%&'()*+,*%# 5*%+&.#7'/*%8&)*# ?@$AB!C# PSE • Theory slides: – – – – – – – – – – Detailed program – Complete program • E-learning web page – Slides – Laboratory instructions – Questions/answers • Seminars – Indications during the course PSE -.+/*0123# 20 Teaching supports (II) • Course web page 3 October '14 ?:'08H')G:'&.#1:9F:'*'/(# 5:DE&%*# 6FF.+)&G:'# Hardware synthesis: – Testbench and device driver – Model based design: radCASE – HMI design: radGUI – Automatic VHDL synthesis 3 October '14 Compiling / executing /debugging SystemC Modeling SystemC TLM Modeling SystemC RTL Timing evolution in SystemC -*9:%;# Analog modeling in SystemC/AMS Mixed modeling RTL/TLM/AMS 435#7'/*%8&)*# Timing modelingin VHDL – Automatic synthesis from TLM – VHDL modeling at RT – Automatic synthesis from RTL VHDL – Introduction to verification HW synthesis: Specification: – – – – – – – – Model-based design – VHDL modeling • SW synthesis: – Embedded systems modeling – TLM 2.0 standard Topics (lab.) • 21 • Theory slides: 0.CourseIntroduction 1.EmbeddedSystemsModeling 2.SystemCBasedDesignFlow 3.PlatformBasedDesign 4.TLMBasedDesign 5.Smart device SystemC/AMS 6.HighLevelSynthesis 7.EmbeddedSoftware 8.ModelBasedDesign 3 October '14 More information – – – – – – – – 9.VHDLDesignIntroduction 10.VHDLSyntax 11.VHDLSpecification 12.VHDLSimulation 13.VHDLSynthesis 14.NESDesign 15.EmbeddedMW 16.VerificationAndTesting PSE 22 For the stronger ... http://www.di.univr.it/~fummi Tuesday 8:30 – 10:30 7994 In the corridors... running franco.fummi@univr.it 3 October '14 PSE 23 3 October '14 PSE 24 4 For the strongest… Monday 10.00 – 11.00 7048 On the e-learning michele.lora@univr.it 3 October '14 PSE 25 5