condition-monitoring-through-non-destructive
advertisement

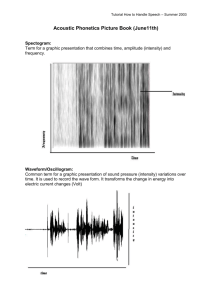
CONDITION MONITORING THROUGH NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTINGS OF MACHINES AND PLANTS INTRODUCTION • CONDITION MONITORING • SIGNATURE ANALYSIS • NON-DESTRUCTIVE EVALUATIONS(NDE) • IN-SERVICE INSPECTIONS (ISI) • SAFTEY fig 1.c detection methods of failures vibration vibration 45% oil analysis oil analysis 23% temperature rotational speed temperature 10% rotational speed 6% others 4% acoustic emission 3% torque 6% fluorescence 3% torque fluorescence acoustic emission others CONDITION BASED MAINTENANCE 2.PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE 1.BREAK DOWN 3.PREDICTIVE NDE TECHNIQUES 1.VIBRATION MONITORING 2.ACOUSTIC EMISSION (AE) 3.INFRARED THERMOGRAPHY (IRT) 4.FERROGRAPHY 5.FIELD SIGNATURE MAPPING (FSM) VIBRATION MONITORING INSTRUMENTATION • VIBRATION MEASURING AND ANALYSIS SYSTEM MACHINE VIBROMETER CHANNEL SELECTOR FREQUENCY ANALYSER fig,(1.a) SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM • MINI COMPUTERS • PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION ANALYSIS (PDF) • BY INSPECTION RECORDER ANALYSIS OF RESULTS 1. VIBRATION CAUSE IDENTIFICATION Sl No FAULT FREQUENCY DIRECTION OF VIBRATION 1 ROTATING UNBALANCE SAME AS RUNNING SPEED RADIAL 2 MISALIGNMENT OF BEARINGS 2*SPEED RADIAL AND AXIAL 3 ROLLER BEARING DEFECT AT BALL OR ROLLER SPEEED RADIAL AND AXIAL ULTRA SONIC FREQUENCIES(20-60KHz) 4. OIL FILM WHIRL IN HIGHSPEED 0.5*SPEED TURBO MACHINES RADIAL 5 DAMAGED OR WORN GEARS RADIAL No: OF TEETH* RPM VIBRATION METER (HAND HELD) SPM VIB-11 by SKF Vibration Meter : for imbalance, structural weakness, loose parts etc INDUSTRIAL MACINERY CLASSIFICATION Class 2: Medium size machines without special foundation Class 3: Large machines on rigid foundations Class 4: Large machines on soft foundations. fig 1.c detection methods of bearing failure vibration vibration 45% oil analysis oil analysis 23% temperature rotational speed temperature 10% rotational speed 6% others 4% acoustic emission 3% torque 6% fluorescence 3% torque fluorescence acoustic emission others APPLICATIONOF VIBRATION MONITORING IN PLANTS • • MONITORING AT ‘ROURKELA STEEL PLANT’ maintenance cost 10-15% of prod: cost valve fig2. failure rate of different machineries of plant others 24% valve 6% sliding bearing 6% seal 7% gear 7% sliding bearing seal gear oil pump slide way oil pump 8% rolling bearing 29% slide way 13% rolling bearing others GROWTH THROUGH CBM ACTIVITIES AT RSP BREAK DOWNS PREVENTED-10-102 120 EQUIPMENTS INCLUDED - 40-140 100 break downsprevented 60 40 insitu balancing 20 trend line 0 No: of machines 80 savings 94-95 year 95-96 96-97 97-98 98-99 99-00 ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORING AE sensors respond with amazing sensitivity to motion in the low ultrasonic frequency range (10 kHz - 2000 kHz). Motions as small as 10-12 inches and less can be detected ACOUSTIC-EMISSION METHOD This method is based on the registration of the elastic compression waves that are emitted by the defects developing in the stressed constructions. ACOUSTIC EMISSION SYSTEMS AE data collection systems •Laptop based AE system •DiSP Systems (any number of channels can be used) • Portable AE test system (lunch box) CASE STUDY AE DURING HYDROTESTING OF A HORTON SPHERE MAX: PRESSURE 22 Kg/cm2 Pressurization (Stage 1) Random AE activity due to 1. Mechanical rubbing between support structure and vessel 2. Paint layer peel-off . Re pressurization (Stage 2) No significant AE activity •AE SIGANLS FROM NEWER AREA local plastic deformation ) •NO SIGNAL DURING SUBSEQUENT PRESSURIZATION ( Fig.2(f) AE monitoring during hydro testing of Horton sphere IR THERMOGRAPHY • Infrared thermography is based on the principle of detection and measurement of infrared radiations QR) arising from the natural or stimulated thermal radiation of an object21 I R MEASURING SYSTEMS VARIOSCAN 3021 ST Type Spectral [µm] range 8 ... 12 Detector material Hg, Cd, Te Detector cooling Stirling-cooler ThermaCAM S60 : Real-Time Thermal •highly sensitive thermal imaging, •precision temperature measurement, •enhanced connectivity options including •high speed data transfer •extensive thermal analysis capabilities CASE STUDY raw thermo graphic data. data after removing the noise and vertical gradient. correspond to low strength welds. high strength welds data processed for the local gradient in surface temperature. Fig setup for infrared testing of lap joints FERROGRAPHY 1.WEAR DEBRIS ANALYSIS MODE: ABRASION, IMPACT, FATIGUE, EROSION, CORROSION RATE : CONCENTRATION OF WEAR DEBRIS SEVERITY : SIZE OF DEBRIS INDICATES LOCATION : COLOUR OF THE PARTICLES 2.SPECTROMETRIC ANALYSIS •OIL ELECTRICALLY EXCITED TO THE POINT WHERE LIGHT IS EMITTED. •ELEMENT EMITS A LIGHT OF ITS OWN PARTICULAR COLOR AND FREQUENCY. •SPECTROMETERS TRANSLATES THE INTENSITY OF THIS RAINBOW OF COLORS INTO A COMPUTERIZED READOUT. HOW IS THE TEST PERFORMED Tests # Conditions Detected Abnormal Wear Fuel Dilution Dirt Water Glycol Test Incorrect Oil Oxidation Additive Depletion * Viscosity * Appearance/Odor * Spectrometric Analysis Coolant * * * * * * * Alkaline Reserve * * * Blotter Spot Test * Water Content * * Distillation * Flash Point * * * WEAR METAL ORIGIN TABLE METAL WEAR POSSIBLE ORIGIN. ALUMINIUM BEARINGS,BLOCKS,BLOWERS,BUSHINGS, CLUTCHES,PISTONS. CHROMIUM BEARINGS,PUMPS,RINGS,RODS. COPPER BEARINGS,BUSHINGS,CLUTHES,WASHERS. IRON BLOCKS,CRANK SHAFTS, CYLINDERS,DISCS. SILVER SOLDERS. TIN PISTONS. MEASURING INSTRUMENT ModelT2FMAnalytical Ferrograph. This measure the effects of Contamination and electro-chemical changes that occur in synthetic and petroleum based oils Bi chromatic microscope. Video camera. Video capture card. Image capture software. industrial standard personal computer. FIELD SIGNATURE MAPPING • The FSM Inspection Tool (FSM) is a new technology for monitoring and inspection of metallic pipes and structures, pipelines and storage vessels • Reduce life cycle inspection costs • Reduce inspection time FIELD PATTERN Graphical plots indicating the severity and location of corrosion, and calculates actual corrosion and metal loss Sensing pins (electrodes) in an array over the monitored area to detect changes in the electrical field pattern. The voltage = the signature. INDUSTRIAL ARRANGEMENT A typical refinery monitors high temperature areas such as heater bends in the distillation unit. CONCLUSION SUMMARY OF APPLICABILITY AND CAPABILITY OF VARIOUS NDT TECHNIQUES NDT TECHNIQUE DETECTION CAPABILITY NON CONTACT INSPECTION AUTOMATED INSPECTION DEFECT SIZING VIBRATION VOLUMETRIC POSSIBLE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE ACOUSTIC EMISSION VOLUMETRIC POSSIBLE POSSIBLE NOT POSSIBLE I R THERMOGRAPHY SURFACE , NEAR SURFACE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE FERROGRAPHY VOLUMETRIC POSSIBLE POSSIBLE FSM SURFACE, NEAR SURFACE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE POSSIBLE