Lecture 1
advertisement

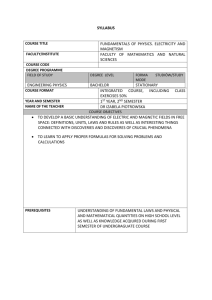
Power System Fundamentals EE-317 Lecture 1 27 September 2010 Aims Meeting Logistics Course Introduction & Overview A Background on the Modern Power System If Time Permits….. Broaden Understanding of the History of Electricity Technology Development Exploitation Meeting Logistics Lectures Mondays 1:40---12:00 AM Wednesdays 10:40—12:00 Course Overview (continued) Lectures Text Problem Assignments Term Research Paper ‘Electric Utility of the Future’ Course Syllabus Online / updated weekly http://sst.umt.edu.pk/newsite/courses/Fall2010/in dex.html Lectures History and Key Inventions in the Development of the Electric Power Industry Mechanical and Electromagnetic Fundamentals Three Phase Circuits Transformers AC Machinery Fundamentals Synchronous Machines Induction Motors DC Machines Transmission Lines Lectures – Introduction to Power Flow Course Syllabus (cont.) System Reliability - Relay and Control Engineering Power Generation Fuels Fossil, Nuclear, Solar, Geothermal and Tidal Advanced Generation Technologies PV System Design, Fuel Cells, Piezo/Thermoelectrics Utility Industry Organization and Deregulation Remote/Stand-Alone Electric Power Systems End-Use Devices, Systems and Efficiency Sustainable Designs for Electric Power Course Syllabus (cont.) Readings – TEXT: Electric Machinery and Power System Fundamentals - Stephen J. Chapman, McGraw Hill 2002 Electrical Power Systems Volume One by A. E. Guile & W. Paterson Wave Propagation By F.R. Connor Grading Class Participation and Attendance – 5% Homework Assignments – 10% Quizzes – 15% Mid-Term Examination – 20% Final Research Paper –50% Logistics Two Weekly Lectures 60-75 mins/each. Homework due at beginning of Class Quizzes as Course goes along U.S. Energy Use by Sector Electricity Industrial Transport Res. & Comm. SOURCE: Ristinen and Kraushaar 1999 U.S. vs. World 30 U.S. consumes 25% of the World’s Energy and 28% of the World’s Electricity % of Total 25 20 15 10 5 0 Electric Capacity Electric Use All Energy North America W. Europe FSU / E.E. CSA ME / Africa Asia / Oceania electric power to the cities generation transmission distribution the network of electric power Basic Components of Electric Power: How electricity gets to you When electricity leaves a po wer plan t (1), its voltage is increased at a “ste p-up” substation (2). Next, the energ y tr ave ls along a transmi ssion line to the area where the p ower is neede d (3 ). Once th ere, the vo ltag e is decreased, or “ stepped -down,” at a noth er substati on ( 4), and a distribution power line (5) carr ies the electricity until it reaches a home or business (6). – EEI, Getti ng Ele ctri city Whe re It’s Ne ede d, May 20 00 Electric Power Delivery Efficiency Source: PJM Website Electric Power Production Technologies Source: EPRI Website