Here are the PowerPoint slides with links - Auto
advertisement

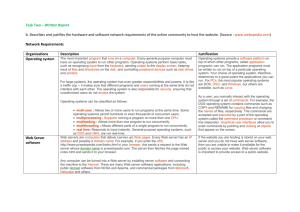
Information Security Fundamentals David Veksler Who is this talk for? • Non IT experts • Those working with confidential information • Especially in parts of the world with high informational security risks Why should I care about security? • Can’t I just hire someone and/or install software to protect myself? Why should I care about security? • • In most organizations, any IT administrator can read and alter any other employees email without any knowledge or record. Mr Smith was an executive building a new manufacturing plant in China. The support technicians in his IT department have access to the corporate mail server. One of them was hired by a competitor. Before he left, he logged on to the mail server and downloaded the entire mail archive for Mr Smith, including the design plans for the new assembly line. The company did not discover about the leak until the competitor built their own production line and release a competing product on the market. Why should I care about security? • • A tiny device with a build-in cellular modem can act as a Trojan horse to open your network to outsiders. Widget Corp produces software for sale worldwide. A agent for their competitors walked into one of their offices and installed a plugbot (theplugbot.com). The plugbot was able to sniff a domain password and send it over the built-in cellular modem. From there, the attacker established remote access to the corporate data server. A few months later, Widget Corp's suddenly had a new competitor in the market. Why should I care about security? • • "It has become the Wild West on that other side of the globe. There is little or no respect for Intellectual Property. Copyrights and patents are ignored. Accounting issues have recently also come into question for many Chinese companies that have bought U.S. shell corporations to simplify the process of going public in the West. Rough and tumble attitudes must be expected. Any American company doing business in China must anticipate the worst even as it hopes for the best in expanded marketing opportunities." http://www.forbes.com/sites/joanlappin/2011/09/21/americansuperconductor-destroyed-for-a-tiny-bribe/ Why should I care about security? • • "In terms of outright theft of intellectual property, there is growing evidence that China’s intelligence agencies are involved, as attacks spread from hits on large technology companies to the hacking of startups and even law firms. “The government can basically put their hands in and take whatever they want,” says Michael Wessel, who sits on the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission that reports to Congress. “We need to take more actions and protect our intellectual property.” Inside the Chinese Boom in Corporate Espionage (http://www.businessweek.com/articles/2012-03-14/inside-thechinese-boom-in-corporate-espionage) Why should I care about security? • “There have been a large number of corporate spying cases involving China recently… as the toll adds up, political leaders and intelligence officials in the U.S. and Europe are coming to a disturbing conclusion. “It’s the greatest transfer of wealth in history,” General Keith Alexander, director of the National Security Agency, said at a security conference at New York’s Fordham University in January.” Why should I care about security? • “There have been a large number of corporate spying cases involving China recently… as the toll adds up, political leaders and intelligence officials in the U.S. and Europe are coming to a disturbing conclusion. “It’s the greatest transfer of wealth in history,” General Keith Alexander, director of the National Security Agency, said at a security conference at New York’s Fordham University in January.” Contents • • • • Part 1: Secure web browsing Part 2: Secure networks Part 3: Secure email and IM Part 4: Securing operating systems & mobile devices • Part 5: Securing organizations • Conclusion: limitations of security measures Choosing a web browser Why web browsers matter Internet Explorer: upgrade to 9+ or switch to: Chrome: recommended for personal use Get HTTPS Everywhere & AdBlock Firefox as a multi-tool Plugging privacy leaks Keep your browser up to date Disable unused plugins AdBlock: it’s not just for blocking ads Block third party cookies Using Private Mode Cleaning your tracks with CC Cleaner Securing your surfing HTTPS Everywhere OpenDNS/Google DNS DNSCrypt VPN (details later) Advanced: monitoring web traffic Outgoing firewalls: Zone Alarm (Windows) Little Snitch (OS X) Monitoring network traffic with Wireshark Part 2: Secure Networks: Virtual Private Networks VPN options PPTP: simple, supported by mobile devices, only safe for personal use L2TP: best for corporations: supports digital certificates Open VPN: free, open-source Alternative VPN Solutions LogMeIn Hamachi: simple ad-hoc and hub and spoke VPN SSH Tunneling Browser helpers for VPNs Proxy Switchy (Chrome) Foxy Proxy (Firefox) Proxy Scripting – works with Proxy Switchy when configured in Chrome (IE) Advanced: Running your own proxy • Why run a proxy locally? • Optimize, secure, accelerate traffic • Control access to outside network Privoxy (recommended) GlimmerBlocker (OS X) Squid (Unix) Polipo (Unix, Windows, OS X) Part 3: Secure Email and IM: Encryption Tools Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Secure Email Corporate E-mail: Digital Certificates & Signing Get a free cert at http://startssl.com/ PGP: PGP Desktop ,GnuPG Secure Instant Messaging Corporate Instant Messaging: Microsoft: Skype, Lynx, Office Communication Server Personal Instant Messaging Off-The-Record plugin for: Pidgin (Windows), Adium (OS X) Part 4: Securing Operating Systems: OS Hardening Basic OS Hardening • Secure your login mechanism • • Password protect access to your desktop Admin privileges & user level accounts: run as a userlevel account; require password to login • Disable file sharing on the network • Enable automatic updates • Disable unused user accounts Anti-Virus Options • Do you need Anti-Virus software? • Anti-Virus for Individuals • • Windows Defender • Avast • Many free options • F-Secure, Trend Micro Office Scan Tip: Don't use Norton or McAfee! Anti-Malware Options • Do you need Anti-Malware software? • Recommended Anti-Malware: • Microsoft’s Windows Defender • Spybot S&D (Free) • Malware Bytes (Free/Pro) Whole disk encryption • What is it? Do you need it? • True Crypt (multiplatform) • Bitlocker (Windows) • File Vault (Apple) • PGP Whole Disk Encryption • Symantec Endpoint Encryption Advanced: Tips from the Pros • OS Hardening guides from the NSA • Windows: • OS X • Security tips from the NSA for all OS’s Advanced: OS Isolation • Portable (Live) OS • Portable apps • Virtual Machines • Only an “air gap” is safe for mission critical data! OS Specific Considerations • OpenBSD: when security is mission-critical • Linux • Windows Server 2008 • Windows XP • Windows 7 • OS X Securing your smartphone • Notes on locking: • Only protects against casual theft • Cloud storage risks • Remote wipes Part 5: Secure Organizations: physical security, social engineering, and other considerations Physical security • Human factors • Physical security • International travel • Asset management & theft prevention Social Engineering • Inside threats • Social engineering • “Need to access” policies Advanced: Threat discovery • Process Explorer • Rootkit detectors: • Microsoft: Rootkit Revealer • Avast: GMER • RootkitHunter Conclusion: Limitations of Information Security • Limitations of software measures • Limitations of hardware measures • Cost vs. benefit of security measures The End Technologies mentioned in this presentation have links to more information – get a copy of the PowerPoint from me (david.veksler@ef.com).