BLADE SERVERS 4
advertisement

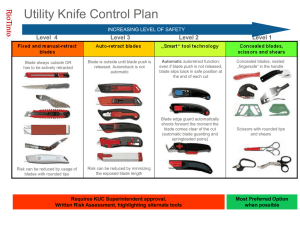
BLADE SERVERS PRESENTED BY:NEETHI NARAYANAN ROLL NO:39 INTRODUCTION Blade servers are stripped down computer servers with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space. Blade server saves space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be a computer. The blade architecture allows a number of servers, on the blade cards, to be housed with a single chassis. The blade server combines the hardware of the computer server, such as a processor, a memory and a network connection, in one extension card, also known as one server blade. The blade server has a higher calculation capacity and higher stability, and occupies less space than a traditional computer server. The blade server reduces the cost and the working temperature; moreover many functions and performance thereof are better than those of traditional computer servers. Network access for all server blades in a chassis reduces cabling complexity and allows for relocation of server resources. A server blade, along with storage, networking and other blades, are typically installed in a rack-mountable enclosure that houses multiple blades that share common resources such a cabling, power supplies and cooling fans. ORDINARY SERVER & BLADE SERVER… Regular server or a personal computer or a laptop includes at least a mother board, processor, memory, hard drive, keyboard, display, network adapter, video card, and power supply. A blade server on the other hand has many components removed for space, power, and other considerations while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. A blade server in the narrow definition is a thin, modular electronic circuit board capable of performing computational tasks. A blade server in this sense is literally a server on a board containing processors, memory, integrated network controllers, an optional fiber channel host bus adaptor (HBA), and other input/output (IO) ports. Server blades typically come with 1 to 4 processors and integrated Ethernet. Blade servers typically have a front panel containing a number of informational LEDs, relating to power and system activity. There may additionally be indicators of system failure, which may be general or specific to blade components. Together these components form a blade system, or shortly often called a blade server. FEATURES Hot swapping Power Cooling Storage SPECIFICATIONS BLADE CHASSIS: Blade chassis shall be 19" Width rack mountable and provide appropriate rack mount kit. Blade chassis shall support at least ten 1 height unit (1U) hot swappable Blades. Blade chassis shall be shipped with all cables and parts required to attach all included peripherals to other blade chassis as required for normal operation. Blade chassis shall provide a device capable of reading a 1.44 MB floppy. Blade chassis shall provide a device capable of reading a CD-ROM disc at a minimum 48x speed or provide an alternate way of installing operating system and application software. The Blade Chassis power supply shall operate at a nominal input voltage of 200VAC to 240VAC. BLADE: Each blade shall have a minimum of two CPUs. The blade shall be hot swappable. They use pentium chipset BLADE MEMORY: Blade shall contain a minimum Random Access Memory of 2GB and can be expanded to at least 8GB without requiring replacing the initial memory. Blade Random Access Memory (RAM) shall include an error correcting feature. The cache contains the data that is accessed most often the CPU and memory. Cache memory accounts for a small amount of high-speed RAM and is the memory that the processor most often uses. The cache runs almost as fast as the processor. CONNECTIVITY: The possible network connections are: 10Base-T Ethernet 10Base-2 Ethernet Fast Ethernet Token Ring Fibre Channel Fieldbus BLADE OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE: Microsoft windows Unix Linux Mac OS BENEFITS OF BLADE SERVERS Lower acquisition cost. Lower operational cost for deployment and troubleshooting and repair. Lower power,cooling and space requirements. Reduced cabling requirements. More efficient out-of-band management. Allow for faster server-to-server communications. ADVANTAGES OVER ORDINARY SERVERS Condensed, high-density. Load balancing and failover capabilities. Power consumption & power management. Lower management cost. Network and other cabling. Flexibility, modularity, and ease of upgrading. Deployment and scalability. Disaster management. DISADVANTAGES Expensive configuration. Expensive tool, i.e. economies of scale. Vendor-lock. Business case. Heating and cooling. APPLICATIONS Web page serving and caching. SSL encrypting of Web communication. Infrastructure applications such as DNS or Active Directory. Streaming audio and video content. File sharing and serving. Terminal services. Email messaging. Databases hosting. ERP hosting. Virtualization. FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS Blade infrastructures are maturing to address the most pressing issues that trouble CIOs, data center architects and facilities managers with emerging technologies for virtualization, converged I/O and networks, and systems management for power and cooling. According to the official, blade servers are the "growth engine" of the server market, citing an International Data Corporation (IDC) study which said the growth rate for blades in the next five years is continuously rising, posing 235 percent year-on-year growth in sales as of the second quarter of this year. Also in mid-2007, HP's blade server segment grew no less than 200 percent year-on-year. CONCLUSION With the blade server, you can build vital solutions to support your business that are more affordable, take less time to maintain, use less power and are ready to grow with you. In an all-in-one design, you have the essentials to build and maintain your infrastructure from start to finish. You can host a choice from thousands of applications on Windows, Linux, HP-UX and more. We can connect to a variety of the most popular networking brands and standards including Ethernet, Fibre Channel. THANK YOU….