HEB1
advertisement
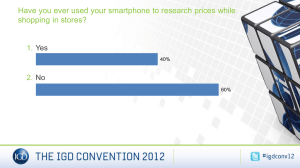
H.E. Butt Grocery Company Jae-Young Chung Ian Kwan Doris Lim WonShik Woo Company Overview 12th largest grocery retailers Over 7 billion in sales 260+ supermarkets, mostly in Texas Gas 'N Go outlets. Operates facilities for processing milk, meat, ice cream, and baked goods. Industry Overview A wave of Consolidation - Through acquisition to increase efficiencies and strengthen market positions - Some small & localized stores – bankrupt Online grocery - customer segment - save time and the trouble involved in going to the store. Total Electronic Grocery Spending Dollars: billions $12 $9 $6 $3 $0 1998 1999 2000 Specialty 2001 2002 2003 Full-service Percentage of industry total 1999 0.11% 2000 0.23% 2001 0.49% 2002 0.98% 2003 2.05% Suggested Services by HEB Online Service - Provide info services: recipes, food safety info. - Kiosks in the stores for web site access - Provide value added services & retain customers Transactional Pharmacy Web Site - Order online and receive delivery via direct mail - Leverage existing assets, build e-commerce expertise Pick Up Service - Pick up from the stores or convenient location Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) Industry cost-reduction initiative Responsive, consumer-driven systems – combine manufacturers, brokers and distributors – maximize consumer value & minimize the supply chain cost. Example: use of paperless system between retail checkout & the manufacturing line. Structure of new supply chain Store Replenishment System - Use POS data to produce a perpetual inventory - SRS – judges stock-outs at the shelf level, not warehouse level. Fast – Slow Warehousing - To manage fast & slow-moving items from different distribution centers & delivery systems Intranet & B2B infrastructure - Use of Extranet – collaborate with suppliers - Use of Intranet for info exchange within HEB Differences of its approach Avoid last mile delivery by having depots Kiosks inside the stores to provide access to their web site Launch transactional pharmacy web site Use Internet to accompany its retail store business Focus on improvements in its retail store Comparison between HEB and others HEB Own Peapod Contracted Homegrocer No Physical Store: Sell groceries Build expertise in the Sell groceries Core: SW and logistics surrounding Internet grocery home delivery Delivery No last mile Deliver door-to-door Deliver door-todelivery door method: Delivery Use Depots Use refrigerated trucks Use refrigerated trucks vehicle: NetGrocer No Offer national services, but only sell shelf-stable products Deliver door-todoor Use Shipment carriers Benefits created by its approach Reduce shipping cost by avoiding last mile delivery Depots could be used as cross-docks to enable home delivery model in the future Tap into new market Deepen relationship with customers Increase data volume for internal marketing analysis Give options to customers Challenges of the approach: Process Engineering Huge Investment (8 digit) Increase in fixed costs Electronic Tagging Currently no electronic tagging due to expensive price and ethical concerns Should implement in the future Price decreases Customers are willing to allow HEB to check down on their behaviors Conclusion HEB’s approach (establish online presence and improvements in operations and supply chain) will work given the benefits outweigh the costs Implement electronic tagging and loyalty card program in the future




![HEB Market Analysis[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485404_1-54cabf3bf07d6c92d73f2b15077d5f55-300x300.png)