The Lodging Industry
advertisement

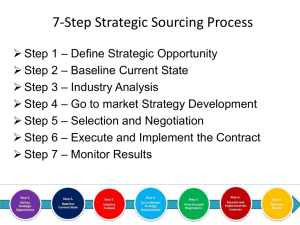
The Lodging Industry Understanding Lodging The lodging industry in the United States has always been strongly influenced by changes in transportation. Mid-1600s Stage coach routes established Coaching inns became popular resting places for travelers Expected a bed and a meal for the evening 1794-1828 1794 City Hotel in New York City opens The first building in the US designed specifically as a hotel. 1828 The Tremont House, first grand hotel, was built in Boston. First hotel to offer private rooms with locking doors. The Railroad Inns, taverns and foodservice facilities located near railway stations began to grow. Famous resorts because of the railway include Hotel del Coronado near San Diego and the Greenbrair Resort in West Virginia. Yellowstone was also a railway resort. Conrad Hilton A banker in New Mexico purchased his first hotel around 1900. It was in Cisco Texas. This began his chain of hotels. Other hotels around this time: Ritz Carlton in Boston and the Plaza in New York City. 1950’s Increased availability and popularity of the automobile and a new interstate freeway system made cross country vacations a popular option. Motels sprang up along highways offering travelers a place to bathe, sleep and eat. The Airline Industry 1958 commercial airlines became popular. Builders moved toward airports for hotels and restaurants. Lodging Operations Organization Front of the house: employees who have direct contact to the public Back of the house: supporting operations, behind the scenes OR Administrative Departments: Manage business (accounting, human resources, training, marketing, sales) Service Departments: responsible for serving guests directly Administrative Departments General Manager (GM) Accounting and Financial Management (Controller) Human Resources Marketing and Sales Service Departments Front Office Housekeeping Engineering and Facility Maintenance Security Food and Beverage (F & B) Leisure Travelers On vacation Shopping, fine dinning, sightseeing, sports events, relax May provide activities for children, on-site recreation or health facilities Business Travelers Looking for well lit work spaces, telephones, modems, copiers, fax machines. Meeting facilities 24 hour service - valet parking, secure lodging Amenities Restaurants Parking Garages Boutiques Barber shops Dry Cleaners Florists Swimming pools Room service Cable Television Pay per view Bathrobes Gift shops Kitchens Computer modems Spa Recreational activities Types of Properties Full Service Luxury Economy Mid-priced All-suite Resorts Bed and Breakfast Terms to Know Folio- The written record of a hotel guest's account. CRS Central Reservation System- A central reservation system (CRS) is a computerized system that stores and distributes information on a hotel, resort, or other lodging facility Room Inventory- Total number of rooms a lodging property has to sell Block- In a hotel, a number of rooms set aside or reserved for a group. Rooms Forecast- Analysis of anticipated room inventory that is based on past room sales; allows front office manager to determine projected revenues and make decisions about rates and reservations. No-Shows- A passenger who doesn't arrive for a flight or a hotel guest who reserves but never arrives. Overbook- The practice of taking more reservations than there are seats, rooms, or space in the expectation that no shows will bring the number of reservations actually used below maximum occupancy. Understays- Guests who leave before their anticipated date of departure Yield Management- The practice of adjusting prices up or down in response to demand in order to control yield. This process is usually computerized. Rack Rate- Highest rate category offered by a lodging property. Hubbart Formula Helps managers set rates Operating expenses + Desired return on investment-Other Income _______________________________________________________ Projected room sales = Room Rate