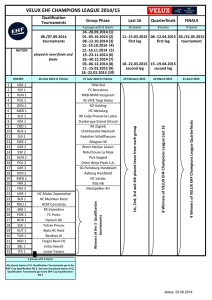
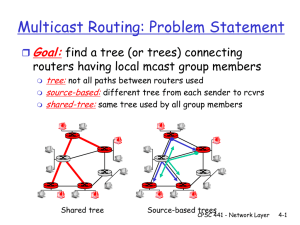
Topic 21 ADNS inst rev 0609 25 Jun 09
advertisement

Topic 21 ADNS Overview and Basic IP Routing Enabling Objectives 21.1 DESCRIBE the basic IP routing process. 21.2 DESCRIBE an Autonomous System (AS). 21.3 DESCRIBE the routing protocols used in a CSG/ESG environment. 21.4 DESCRIBE the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. 21.5 DISCUSS the ADNS concept of operations and vision. 21.6 DIFFERENTIATE major capabilities between Increment I and Increment II. 21.7 DISCUSS Increment I capabilities and constraints. 21.8 DESCRIBE Increment II capabilities, components, hardware, and software. 21.9 DISCUSS Increment II features. 21.10 EXPLAIN the various organizations that provide ADNS support. What is ADNS? • ADNS is an integral part of a complex communications system that provides an automated pathway for information to travel along any available transit link. • Provides for optimal use of bandwidth assigned by the system to: – – – – – UNCLAS SECRET SCI Coalition Other afloat networks and their shore counterparts ADNS “Vision” • Provide assured gateway availability for critical paths/applications • Guarantee 100% end-to-end delivery of selected voice, video, and data • Provide restore capabilities • Increase information transfer efficiency • Reduce manning and operation costs • Provide joint interoperability EIGRP OSPF OSPF ADNS DWTS DSCS CWSP Inmarsat “B” HSD EIGRP ADNS EHF MDR OSPF ADNS ADNS NOC OSPF EIGRP JWICS ASBR BGP-4 SIPRNET DISA Autonomous Systems NIPRNET CENTRIXS Application ROUTER Transport Application Transport Network Network Network Data Link Physical Data Link Physical Data Link Physical 205.1.2.0 205.1.3.0 ANDing Destination IP Address 205.1.3.1 = 11001101 . 00000001 . 00000011 . 00000001 ANDING ANDING ANDING 255.255.255.0 = 11111111 . 11111111 . 11111111 . 00000000 11001101 . 00000001 . 00000011 . 00000000 = 205.1.3.0 Subnet Mask Network address Local Machine Address = 205.1.2.12 Autonomous Systems NOC SIPRNET NIPRNET CSG OSPF & EIGRP JWICS ESG OSPF & EIGRP ROUTER 1 ROUTER 2 Operating System Operating System OSPF OSPF 89 89 IP Data Link IP Data Link Physical Physical 205.32.9.8 205.38.8.8 ROUTER ROUTER OSPF ROUTER ROUTER ROUTER ROUTER 205.33.1.8 205.46.4.8 205.34.9.8 205.1.16.8 AUTONOMOUS SYSTEM 205.32.9.8 ROUTER 7 ROUTER 205.33.1.8 2 205.38.8.8 1 ROUTER 2 ROUTER 205.46.4.8 2 1 ROUTER 205.34.9.8 11 6 ROUTER 205.1.16.8 Destination Next Hop(s) Cost 205.33.1.8 205.46.4.8 4 205.46.4.8 205.46.4.8 2 205.34.9.8 205.46.4.8 3 205.38.8.8 3 205.38.8.8 205.38.8.8 1 205.1.16.8 205.46.4.8 9 205.38.8.8 9 ADNS Increment I Capabilities • Consolidated WAN access for Multi-security level networks (via NES, TACLANE) • Link preference: DSCS, CWSP, EHF, IMS • Hot-standby Link Failover • Bandwidth Reservation per security level • Ship-to-Ship LOS links w/IP (VTC over DWTS) • Ship-to-Shore MAGTF support • Pier-side network access Constraints • IP traffic uses only one RF link even if more are connected • Best Effort delivery (i.e. no application has priority) • Fixed bandwidth allocation to each enclave Justification for Change • Increased demand requires more efficient use of RF bandwidth • Need to prioritize network traffic • Must be able to monitor and control network traffic based on applications Inc II Capabilities • Increment II = Inc I plus: – Traffic distribution over multiple links – Adjustable bandwidth guarantees – Application prioritization – Improved link monitoring tools – Application monitoring Components • Integrated Network Management (INM) – LQoSMAN • Routing and Switching – Cisco router – Packetshaper • TACLANE Software • • • • • • • • • • • Windows 2003 Server + patches Internet Explorer (IE) + patches Apache Web Server Adobe Acrobat Reader WinZip mIRC Chat Client (and patches) Tera Term Pro Norton Antivirus IT-20 Security scripts Cisco IOS PacketWise PacketShaper Tool • 32 bit, secure, Network Operating System that controls system hardware and provides a platform for running applications. Monitors ADNS software and controls ADNS devices. • Industry standard for large networks. • IAVA’s and FAMs are issued with directions to download and perform updates and patches. • Apache Web Server – Provides support for storing, managing, and displaying of HTML based content to local and network users. – Enables network users to access the local ADNS INM functionality using the IE browser. • • • • Monitor network connectivity Configure information display Configure and generate reports Configure QoS and bandwidth management settings mIRC • mIRC is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) program that connects to a host chat server at NCTAMS PAC and LANT. • Chat room to allow users to communicate with each other for testing and troubleshooting. LQoSMAN 3.x Software Tool Kit • Standalone IBM compatible workstation running Windows Server software • Provides status information • Monitors via Ethernet link • Uses SNMP • Provides remote access and monitoring via SIPRNET web access. User Levels • Administrator (Monitor/Manage) – Access all software modules and monitoring – Manage the entire ADNS • Operator (Monitor) – Monitor performance – Generate reports – Change screen preferences • Read-Only – Web access to view how ADNS is working Policy-Based Routing (PBR) • • • • Source-Based Transit Provider Selection Quality of Service (QOS) Cost Savings Load Sharing Quality of Service (QoS) • Control over resources • More efficient use of network resources. • Tailored Services – Grades of service differentiation to the customers. • Coexistence of mission-critical applications – Bandwidth and minimum delays required by timesensitive multimedia and voice applications are available, and that other applications using the link get their fair service without interfering with missioncritical traffic. • Foundation for a fully integrated network in the future Inc 2 Enhancement # 1 • Traffic Distribution – Benefits • Using multiple links increases effective bandwidth • Improves overall system reliability Traffic Distribution for Force Level Platforms RF Links Available DSCS Pt-to-Pt (256k – 1536k) CWSP Pt-to-Pt (1024k – 1536k) DSCS and CWSP SECRET, SCI, CENTRIXS, CWSP Failover DSCS and EHF MDR SECRET, SCI, CENTRIXS, JCA, UNCLAS DSCS and EHF TIP SECRET, SCI, CENTRIXS, JCA, UNCLAS DSCS, CWSP, and EHF MDR SECRET, SCI, CENTRIXS, CWSP Failover JCA, UNCLAS, DSCS Failover DSCS, CWSP, and EHF TIP SECRET, SCI, CENTRIXS, CWSP Failover JCA, UNCLAS, DSCS Failover EHF MDR Pt-to-Pt (128k – 1024k) EHF TIP Shared (128k – 1024k) JCA, UNCLAS, DSCS Failover DSCS Failover SECRET ship to ship, DSCS Failover Failover on loss of CWSP and DSCS Failover on loss of CWSP and DSCS Inc 2 Enhancement # 2 • Selectable Enclave Bandwidth Allocation – Baseline Configuration – SIPR-Favored – SCI-Favored Percent Bandwidth Allocation (Force Level) Baseline JCA NIPR SCI SIPR UDP/ICMP Total DSCS 1 20 25 24 128k max 70 CWSP 45 5 10 10 128k max 70 EHF 1 20 25 24 8k max 70 1 1 5 67 74 DWTS SIPRFavored DSCS 1 15 20 39 128k max 75 CWSP 35 5 10 25 128k max 75 EHF 1 15 20 39 8k max 75 1 1 5 67 74 DWTS SCIFavored DSCS 1 15 35 24 128k max 75 CWSP 35 5 20 15 128k max 75 EHF 1 15 35 24 8k max 75 1 1 5 67 74 DWTS Inc 2 Enhancement # 3 • Application Prioritization – Based on source application – Packets dropped depends on: • Degree of congestion • Priority of packets – ADNS Inc II uses PacketShaper (Packeteer) Unclassified Application Priorities Priority Application or Traffic Type 6 Reserved for future use 5 Chat and DNS 4 Reserved for future use 3 CRIT_WEB, Aircraft Logistics 2 E-Mail 1 Medical 0 Default Traffic -1 Web and SSL Inc 2 Enhancement #4 • Application Monitoring and Blocking – PacketShaper Overview • Traffic and Bandwidth Management system that delivers predictable efficient performance for applications running over the WAN • 7 Layer classification, analysis, control, and reporting capabilities. – Enables managers to keep critical traffic moving at an acceptable pace through bottlenecks and prevents any single type of traffic from monopolizing the link. The Bottleneck High-Speed DISA/HSGR Backbone 64 kbps – 1.5 Mbps OC-3, OC-12, OC-48, OC-192 10/100/1000 Mbps Problem: Traffic on the high-speed LAN hits the low-speed WAN access link before getting to the really high-speed shore infrastructure. Inc 2 Enhancement #5 • RF Link Monitoring – PacketShaper – LQoSMan • Trend reporting • Future requirements • Reports LQoSMAN Reports LQoSMan Alarms Support Organization Function In-Service Engineering Activity (ISEA Organization Phone SPAWAR SSC SD, Code 619.524.2623 2631 Software Support Activity SPAWAR SSC CHAS, Code 50 843.208.4108 Fleet Support Desk SPAWAR SSC SD 619.524.3717 Configuration Management SPAWAR SSC SD, Code 619.524.2623 2631 ILS Management PEO C4I and Space 858.537.0642 Support Organization Function In-Service Engineering Activity (ISEA Organization Phone SPAWAR SSC SD, Code 619.524.2623 2631 Software Support Activity SPAWAR SSC CHAS, Code 50 843.208.4108 Fleet Support Desk SPAWAR SSC SD 619.524.3717 Configuration Management SPAWAR SSC SD, Code 619.524.2623 2631 ILS Management PEO C4I and Space 858.537.0642