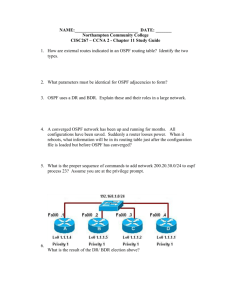
OSPF

LAN Switching and WAN Networks
Topic 6 - OSPF
What we have done so far!
Looked at the basic switching concepts and configuration from the Cisco IOS CLI
Looked at VLANs and seen how to configure basic VLANs on switches
Looked at VLAN trunking and seen how to setup trunks between switches and routers
Looked at switch port security features
Looked at the Virtual Trunking Protocol
***
2 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Objectives
Be able to describe OSPF characteristics
Be able to define what an area is
Be able to describe what the OSPF metric is and how it is used
Be able to describe how a router using OSPF is uniquely identified
Be able to describe how a router using OSPF form
adjacencies with out routers also using OSPF
***
3 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
OSPF characteristics
Developed in reference to the limitation of RIP in large enterprise networks
Based on open standards
Runs on most routers
Uses the SPF algorithm to provide a loop-free topology
Fast convergence with triggered and incremental updates via LSA’s (it’s a link state protocol)
Classless protocol allowing for VLSM and route summarisation
However, requires more memory, extra CPU processing power, careful design, complex to troubleshoot and configure (multi-area designs)
4 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
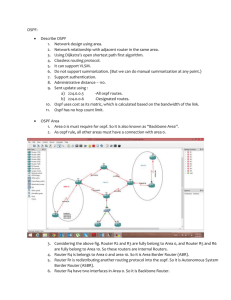
OSPF areas
OSPF uses Autonomous Systems and areas
Areas basically control when and how much routing information is shared across a network
Area 0 is the backbone
Areas 1-65,535 are “areas off the backbone”
***
5 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
OSPF areas
6
Route summarisation would mean that Area 1, 2 and 3 do not need to know all the subnets in each others area, only their own areas
Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Metric
OSPF uses cost
Cost is the inverse of the bandwidth of a link
The faster the speed of the link, the lower the cost
Preferred path is the one with the lowest cost
OSPF supports load-balancing
Six equal-cost paths to a single destination
On synchronous serial links the bandwidth defaults to
1544Kbps despite the clock rate settings
Bandwidth needs configuring specifically so that load-balancing works properly
This is important is there are multiple synchronous serial paths to a destination and the paths have different clock rates
7 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
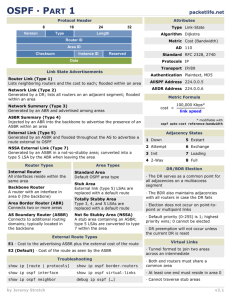
Router identities
Each router in an OSPF network requires a unique ID
The ID is included in OSPF messages
The ID is based on:
The highest IP address on any loopback interfaces, OR
The highest IP address on it’s active interfaces
If there are no active interfaces or loopback interfaces then the OSPF process will not start
Loopback interfaces are recommended because they are always up
***
8 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Finding neighbours
OSPF uses LSA’s to learn about neighbours
OSPF generates hello LSA’s every 10 seconds
If a router does not receive a hello LSA within 40 seconds from a neighbour it declares that neighbour dead
OSPF routers build an adjacency that makes them neighbours
To do this the following must match on both routers:
The area number and its type
The hello and dead interval timers
The OSPF password, if configured
The area stub tag
OSPF routers go through three states to form an adjacency:
Down state – no exchanges
Init state – destination router receives a hello and adds it to it’s neighbour list
Two-way state – new and destination routers exchange hello packets
9 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Designated and backup routers
OSPF also uses a client/server design when establishing adjacencies
Each segment will have a designated router (DR) and a backup designated router (BDR)
New routers form adjacencies with the DR and BDR
A router talks to the DR using 224.0.0.6
DR and BDR talk to routers using 224.0.0.5
The router with the highest router ID (IP address) becomes the DR
BDR is based upon the next highest router ID (IP address)
If the DR fails the BDR takes over and another router becomes the BDR
10 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Summary
OSPF is an open routing protocol and very popular
It works on most routers
It uses areas to control how much routing information is passed around a network
It uses cost (an inverse of bandwidth) as it’s metric
It uniquely identifies a router using either the highest IP address on a loopback interface or the highest IP address on an active interface
Using a loopback address for identity purposes is recommended
11 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Tutorial
Click on the icon below to run the tutorial and work through it until completion
12 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
So, what do you know now?
How does a router in an OSPF network become a designated router?
What happens if a designated router fails
How often are OSPF LSA hello messages sent?
What happens if a neighbour doesn't receive a hello LSA packet from it’s neighbour after 40 seconds?
What must be configured to prevent errors with the load balancing feature of OSPF?
***
13 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
How all this relates to the assignment
You will need to know how to configure OSPF for the case study and the skills test
You need to be able to perform these configuration on physical Cisco kit
***
14 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
Questions...
...are there any?
15 Richard Hancock 17/04/2020
16
End!
Richard Hancock 17/04/2020