necessary to the functionality or production
advertisement

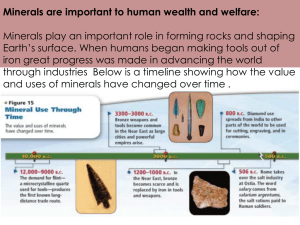
Conflict Minerals Rule Detroit Chapter of the IIA in Partnership with Experis Finance Presents CONFLICT MINERALS RULES January 16, 2013 Experis | January 16, 2013 1 Conflict Minerals Rule If you have questions during the webcast: – If necessary, exit Full Screen View by pressing the Esc key – Submit questions through the “Ask a Question” button – Questions will be answered after the presentation portion is concluded Experis | January 16, 2013 2 Conflict Minerals Rule Earning CPE Credit In order to receive CPE credit for this webcast, participants must: – Attend the webcast on individual computers (one person per computer) – Answer polling questions asked throughout the webcast When answering polling questions, select your answer and then click “Vote” button (next to the “Ask a Question” button) to submit / save your answer. CPE certificates will be sent to the e-mail address on your BrightTALK account within two weeks of this webinar. Experis | January 16, 2013 3 Conflict Minerals Rules Overview & Compliance Considerations Michelle Search-Winters, CPA National Director, Technical Accounting and Financial Reporting Center of Expertise January 16, 2013 Conflict Minerals Rule Conflict Minerals Rule Experis | January 16, 2013 5 Conflict Minerals Rule Conflict Minerals Rule • SEC adopted the rule, mandated by the Dodd-Frank Act, in August 2012 – Likely to directly impact half of all public companies – Rule may indirectly impact 10x that many public and non-public companies • Rule attempts to use securities law to effect social policy change – Exploitation & trade of conflict minerals provides funding for armed groups responsible for violence and human rights violations in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and surrounding region Experis | January 16, 2013 6 Conflict Minerals Rule Conflict Minerals Rule • The new rule requires issuers with “conflict minerals” that are necessary to the functionality or production of a product manufactured or contracted to be manufactured by such issuer to conduct supply chain due diligence and make annual disclosures in a new Form SD related to whether any of those conflict minerals originated in the Democratic Republic of Congo or an adjoining country. • Adjoining or covered countries include DRC, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Angola, Republic of the Congo and Cabinda. DRC is separated from Tanzania by Lake Tanganyika. Experis | January 16, 2013 7 Conflict Minerals Rule Reference map of Africa Experis | January 16, 2013 8 Conflict Minerals Rule Conflict Minerals Rule • What are “Conflict Minerals”? – Currently include tantalum, tin, gold and tungsten, regardless of where they have originated • and other minerals that the US Secretary of State names in the future • Sometimes referred to as 3T’s and a G • Use of these minerals is pervasive – Most products containing electronic components – Industries impacted include technology, electronics, aerospace, automotive, industrial products, jewelry, and consumer goods • Cell phones, computers, televisions, cars, planes, boats, jewelry, appliances, clothing, shoes, toys….. Experis | January 16, 2013 9 Conflict Minerals Rule Applicability of New Rule • An issuer is subject to the new rule if: – The issuer files Exchange Act reports with the SEC and – Conflict Minerals are necessary to the functionality or production of a product that it manufactures or contracts to manufacture. • An “issuer” for this rule includes any company (other than a registered investment company) that files periodic Exchange Act reports with the SEC – Includes domestic companies, foreign private issuers, smaller reporting companies, and voluntary filers (including debt-only filers) Experis | January 16, 2013 10 Conflict Minerals Rule Polling Question #1 How many public companies is the Conflict Minerals Rule likely to directly impact? 1. About 25 percent 2. About 50 percent 3. Almost 75 percent Experis | January 16, 2013 11 Conflict Minerals Rule Conflict Minerals Rule • Three-step process Step 1) Determine if conflict minerals are necessary to the functionality or production of products manufactured, or contracted to be manufactured. If yes… Step 2) Based on a reasonable “country of origin” inquiry, determine whether there is reason to believe that the conflict minerals may have originated in the DRC region • If no, or minerals come from recycled sources, file Form SD describing the inquiry and results • If yes… Step 3) Exercise due diligence on the source and chain of custody of conflict minerals following a nationally or internationally recognized due diligence framework. • Include an audited Conflict Minerals Report as an exhibit to Form SD. Experis | January 16, 2013 12 Conflict Minerals Rule Step One • To determine whether a mineral is necessary to the functionality or production of a product an issuer should consider: – Whether the mineral is contained in and intentionally added to the product (not a naturally occurring by-product); or – Necessary to the product’s function, use or purpose – Incorporated for the primary purpose of ornamentation, decoration or embellishment • The rule does not define “necessary to the functionality,” or “necessary to production.” Experis | January 16, 2013 13 Conflict Minerals Rule Necessary to Functionality • Issuers that do not meet the definition have no further requirements under the rules • This could be a highly complex analysis – For example, a piece of clothing has a zipper that contains tin • Is the zipper functional (required to use the product) or decorative (on a sleeve for decoration)? – All generally expected functions, uses or purposes of a multi-use product need to be evaluated – Analysis may have to be performed on a product by product basis • Same zipper could be functional in one product and decorative in another Experis | January 16, 2013 14 Conflict Minerals Rule Necessary to Production • Conflict minerals must be contained in the final product sold or offered for consideration by the issuer to be in scope of the rule • Minerals used as catalysts in production must be completely removed from the final product to be excluded from the rule – Even trace amounts would be considered applicable • Conflict minerals indirectly used in production are excluded from the provision – If present in tools or machines used in production but not contained in the final product Experis | January 16, 2013 15 Conflict Minerals Rule Manufacture and Contract to Manufacture • SEC believes term “manufacture” to be generally understood – Referenced dictionary definition • Noted that issuers who only service, maintain or repair products containing conflict minerals are not considered “manufacturers” for application of the rule • Mining issuers are generally excluded from the scope of “manufacturer” – Mining companies that manufacture product in addition to mining are subject to the rule Experis | January 16, 2013 16 Conflict Minerals Rule Manufacture and Contract to Manufacture • Issuers that contract to manufacture products containing conflict minerals must evaluate the degree of influence over the manufacturing process – If terms don’t directly relate to manufacturing, limited to adding brands or logos, or include only servicing or maintaining, may be excluded from the rule – SEC views influence on a sliding scale from ‘none” to “significant” – Companies will need to carefully assess influence, often on a contract by contract basis Experis | January 16, 2013 17 Conflict Minerals Rule Polling Question #2 The “Necessary to Production” category includes those conflict minerals used in any production machinery as well as those contained in the final product. 1. True 2. False Experis | January 16, 2013 18 Conflict Minerals Rule Step Two • If conflict minerals are necessary to the functionality of products manufactured or contracted to manufacture, must determine if minerals originated in covered countries – “Reasonable Country of Origin Inquiry (RCOI)” • Rule does not define RCOI but provides guidance – “must be reasonable designed to determine whether the issuer’s conflict minerals did originate in covered countries or did come from recycled or scrap sources and must be performed in good faith” • Consider obtaining representations from suppliers – Indicate originating mine or facility – Indicate if from covered countries or not – Indicate if scrap or recycled sources – If from covered countries, identity as “conflict free” or not Experis | January 16, 2013 19 Conflict Minerals Rule Supplier Responses • Issuers must also consider if responses from supplies are reasonable – Consider “red flags” that may indicate exceptions to responses • May not need to receive representations from ALL supplies – Need to make a good faith effort to receive representations – Will need to do some reasonable analysis of suppliers where representations are not received • Other approaches to RCOI can be considered depending on the nature of supply chain, etc. Experis | January 16, 2013 20 Conflict Minerals Rule Conclusion of Step Two • No need to move to due diligence if conflict minerals: – Did not originate from covered countries or no reason to believe so – Came from recycled or scrap sources or reason to believe so • Scrap or recycled materials – Reclaimed end-user or post consumer products or scrap processed materials created during manufacturing – Includes scrap material that contained refined or processes metals that are appropriate in the production of 3Ts and G – Unprocessed, partially processed and by-product production are explicitly excluded from the definition of scrap or recycled material. – If supplier asserts minerals are from recycled / scrap sources, issuer must ensure that statement is reasonable Experis | January 16, 2013 21 Conflict Minerals Rule Step Three • If issuer knows or has reason to believe that its conflict minerals originated in covered countries and are not scrap/recycled sources, must perform due diligence – Due diligence includes procedures to determine the origin and chain of custody of its conflict minerals • Due diligence must follow a nationally / internationally recognized framework and be consistent with Generally Accepted Governmental Auditing Standards (GAGAS) – Currently only framework for conflict minerals is the OECD’s “Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas”. – OECD framework has a supplement for the 3Ts and also for gold Experis | January 16, 2013 22 Conflict Minerals Rule Step Three • OECD framework includes five elements: – Establish Strong Company Management Systems – Identify and Assess Risk in the Supply Chain – Design and Implement a Strategy to Respond to Identified Risk – Carry out Independent 3rd Party Audit of Supply Chain – Report on Supply Chain Due Diligence • http://www.oecd.org/ • http://www.oecd.org/investment/guidelinesformultinationalenterprises/46 740847.pdf Experis | January 16, 2013 23 Conflict Minerals Rule Due Diligence Outcomes • Three outcomes from Due Diligence 1) Minerals are scrap / recycled sources or not from covered countries • No Conflict Minerals Report is required • Must disclose description of due diligence, results and final determination in form SD 2) Minerals originate from covered countries • Must include Conflict Minerals Report in form SD • Report must be audited • Additional disclosures required Experis | January 16, 2013 24 Conflict Minerals Rule Due Diligence Outcomes 3) Source of conflict minerals is undeterminable • Assertion can only be made after due diligence is performed • Still must file Conflict Minerals Report in form SD, including description of due diligence, steps taken to minimize risk that conflict minerals benefit armed groups, identify facilities used to process minerals if knows and efforts to determine location of origin • May indicate “undeterminable” for 2 years (4 years for smaller reporting companies) • Subsequently must apply full provisions of the rule Experis | January 16, 2013 25 Conflict Minerals Rule Outside of Supply Chain • Rule provides exclusion for conflict minerals “outside the supply chain” prior to January 31, 2013 • Exclusion includes: – Minerals already smelted – Gold fully refined – Conflict minerals located outside the covered countries • Provides relief for issuers who may already have stockpiles of conflict minerals in the supply chain • Products made with pre-January 31, 2013 stockpiles would be excluded from the 2013 From SD disclosure Experis | January 16, 2013 26 Conflict Minerals Rule Polling Question #3 Please tell us your IIA member status 1. Member Detroit Chapter 2. Member Other Michigan Chapter (Not Detroit) 3. Non-member 4. Student Experis | January 16, 2013 27 Conflict Minerals Rule Filing and Transition • New Form SD is due by May 31 of each year, regardless of the registrant’s year end – Audited Conflict Minerals Report with Form SD if source believed to be DRC region • Transition Period – 2 years (4 years for smaller reporting companies) – Describe products as “DRC conflict undeterminable” • No audit required • Must perform due diligence & file Form SD • Initial form SD for calendar year 2013 due May 31, 2014 • Form SD is considered “filed” (not just “furnished”) and creates liability to companies who may be sued for false or misleading statements • No financial statement or 10-K/10-Q disclosure requirements Experis | January 16, 2013 28 Conflict Minerals Rule Independent Audit Requirements • Rule requires an independent private sector audit to express an opinion on: – Appropriateness of design of the due diligence framework – Accuracy of the description of the execution of the due diligence process undertaken by the issuer • Auditor is not required to express an opinion on: – Effectiveness of the due diligence measures performed – Whether the issuer’s conflict minerals are DRC conflict free • Audit must be performed in accordance with GAO standards and likely under existing GAGAS rules Experis | January 16, 2013 29 Conflict Minerals Rule Compliance Considerations • Issuers subject to the rule should conduct a comprehensive assessment of their supply chain activities to determine whether their conflict minerals originated from a covered country • Materiality of content of the conflict minerals doesn’t matter – How much gold is in the product, for example, doesn’t matter to the compliance requirements • Finance groups will likely not have the expertise to manage compliance on their own – Many organizations are looking to supply chain and purchasing executives to lead the effort • Sales, purchasing, operations, legal and finance must all work together Experis | January 16, 2013 30 Conflict Minerals Rule Compliance Considerations • Other participants in an issuer's supply chain are affected by the rule, regardless of whether they are public or nonpublic companies – component manufacturers, smelters, and mining companies performing mineral extraction • The SEC estimates that companies (and their affected suppliers) will likely incur significant compliance costs. • Non-Public companies will be significantly impacted – Products containing conflict minerals may be components of other products – Asked by customers to provide information about supply chain and may be asked to provide certifications on an on-going basis. – Could incur significant cost for compliance even though not directly required to comply with the rule Experis | January 16, 2013 31 Conflict Minerals Rule Polling Question #4 Requirements include that an independent auditor opine on: 1. Appropriateness of the due diligence framework 2. Effectiveness of the due diligence measures 3. Whether the issuer’s minerals are DRC conflict free 4. All the above Experis | January 16, 2013 32 Conflict Minerals Rule Steps for Compliance • Identify if issuer is subject to the rule • Identify what products may contain conflict minerals • Determine functionality of conflict minerals to products • Design a plan to perform the RCOI • Integrate the OECD framework into company processes • Nonpublic companies should be proactive in working with customers to determine their information requirements • Consider working with industry groups to determine industry specific best practices for compliance Experis | January 16, 2013 33 Conflict Minerals Rule SEC decision tree for applying conflict minerals rule http://www.sec.gov/rules/final/2012/34-67716.pdf Experis | January 16, 2013 34 Conflict Minerals Rule Questions Experis | January 16, 2013 35 Conflict Minerals Rule For more information Michelle Search-Winters, CPA National Director Technical Accounting & Financial Reporting Center of Expertise (303) 885-9796 michelle.search@experis.com Experis | January 16, 2013 36 Conflict Minerals Rule THANK YOU! Please join us for additional chapter events: – February 15th – Chapter Meeting • Our Chapter’s 70th anniversary celebration • Doug Anderson, Dow Chemical, and Mike Peppers, IIA North America Board – March 11 – 13 – Annual Spring Conference at U of M Dearborn – April 9th – Chapter Meeting • Student Night Visit www.iiadetroit.org for additional information and registration details Experis | January 16, 2013 37 Conflict Minerals Rule Please Take a Moment to Rate the Webinar • • • • Click on “Rate This” Rate this webinar with 1 to 5 stars Provide any comments Click “Send Rating” Experis | January 16, 2013 38