Quality Function Deployment - Masters in Engineering Management
advertisement

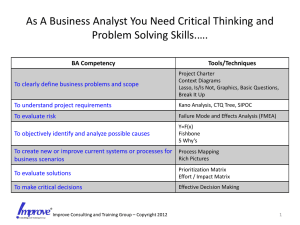
A Quality Function Deployment methodology for product development Ryan Craig Graduate Student Industrial and Systems Engineering Ohio University Presented by Dr. David Koonce, PHD Overview – Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is an Industrial and Systems Engineering tool used in product development – Developed by Dr. Yoji Akao in 1966 – Comprised of a number of processes, notably the House of Quality, and Kano’s model (Hauser and Clausing, 1988) Background: QFD Tools House of Quality – A series of matrices that define the relationship between product features and customer driven quality/satisfaction – Takes direct customer input data to help design the product, as well as input from cross function product development teams – – – – Marketing Engineering Sales Management (Hauser and Clausing, 1988) Background: House of Quality Basic House of Quality matrix (Revelle Moran and Cox, 1995) Background: House of Quality Customer Input Quality score output (choose largest for optimal product design) Completed House of Quality (Improvement Encyclopedia, 2007) Background: House of Quality Customer inputs are typically marketing surveys (web based and paper) – Customers typically ask for all possible features with no concept of trade offs and production costs. Leads to end product similar to “Swiss Army Knife.” These types of products have difficulty in the market. Potential area for improvement Quality output score determines which product will be produced along with the related features (Hauser and Clausing, 1988) Background: House of Quality How does the HOQ work into the overall product development and manufacturing process? Background: House of Quality House of Quality throughout the manufacturing/development process (Qimpro Standards Association) Background: Kano’s Model Model of customer satisfaction for product features and attributes. Essential to developing products for respective benefit segments Three types of features Attractive Quality: Cutting Edge (Exponential Increase) One Dimensional Quality: Standard Features (Linear) Must-Be Quality: Required Features (Exponential approaching sufficient quality) Leads to three types of customer segments Kano, 2003 Background: Kano’s Model Problem Statement How can the customer input of the house of quality be improved as to produce a sellable, marketable product that avoids the “Swiss Army Knife” result of running HOQ/QFD? How can the overall product development process be streamlined for the consumer electronics industry and the various types of customers? Methodology By using industry standard web surveys, the voice of the customer can be easily capture and analyzed In order to avoid the “Swiss Army Knife” problem, an orthogonal design is used to structure the questions and responses Capturing the Voice of the Customer Using SPSS, an orthogonal design of the desired features is created – – For this example of designing a consumer electronics internet radio audio product, 8 features were compared 8 features, 2 levels (Yes/No) Orthogonal Design/Survey Design The orthogonal design creates 8 ‘cards’ which are composed of different combinations of features – Each card is a different combination based on the orthogonal design of the original number of attributes Survey respondents are asked to rate likeliness to purchase each product presented by one of the 8 cards Survey Design Example: – If you could purchase a home audio product that allows you to listen to Pandora (www.pandora.com) Internet radio without a computer that does the following: -Sets up out of the box automatically when you plug it in -Connects to wired (Ethernet) Internet -Can be moved around the home or office freely -Includes over 11,000 Internet radio stations for free including news, sports, and talk radio from around the world (in addition to Pandora Internet radio) How likely would you be to purchase this product? (Scale of 1-7) Survey Results After obtaining the desired number of respondents and survey results, optimal feature sets can be determined Likeliness to purchase (sum of the number of respondents that respond higher than ‘undecided’) is added to each survey card Clustering Algorithm Using a 2-stage clustering method of Wards and K-Means++, multiple feature sets based on the voice of the customer are created for input into the house of quality\ Optimally 3 feature sets in order to match Kano’s model House of Quality With the customer input section of the house of quality completed with the voice of the customer, input from the cross functional teams can be collected – Marketing, Management, Sales, Engineering Optimizing the HOQ Using Moskowitz and Kim’s QFD optimizer software, the product design can be analyzed and improved using the VOC and input from the cross functional teams Maximizes quality score Result Using the obtained quality scores, the cross functional team can make an informed decision on which product to proceed developing Questions?