Industry Briefing, Webinar (Jun 2013)
advertisement

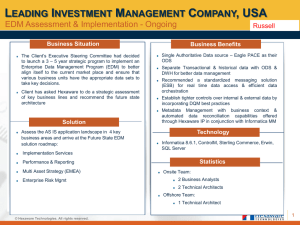
EDM Council Webinar Update and Outlook Michael Atkin Managing Director, EDM Council June 12, 2013 Confidential 1 Regulatory Drivers Mandatory Basel Requirements • Transparency (Dodd-Frank, Regulation AB2, EMIR, UCITS, AIFMD, COREP, FINREP, ACORD) Governance and Infrastructure (Board of Directors accountability, independent validation, integrated data taxonomies, aligned metadata, standard identifiers, standard naming conventions, mechanism for data alignment and comparability (semantics) ● • Systemic Risk Oversight (Basel Risk Data Aggregation Principles, SBSG Report on Risk Appetite Frameworks, FSB Key Attributes, FRY-14Q, FRY-9C) • Capital Requirements (Basel III, CCAR, Solvency II) • Functional Areas (collateral flows, leverage and liquidity measures, guarantee and transmission of risk, degree of diversification, systemic contagion) • Surveillance (shadow banking, electronic execution, concentration of power, structural vulnerability, consumer protection, hedge funds, insurance and reinsurance) ● Risk Data Aggregation (data quality - timely, accurate, comprehensive, clear), data lineage and root cause remediation, on-demand and ad hoc reporting capabilities, automated risk aggregation all relevant business units and functions, near real time reporting Supervisory Tools (mandatory tools, independent audit, capital add-ons, activity limits, pre-authorization, cross regulatory agency coordination) ● Internal Assessment (2013) Mandatory Compliance (2016) Business Drivers • Data Errors and Repairs (reconciliation, exception processing, convoluted models, trade repairs, valuation miscalculation, settlement instruction mismatches, bad corporate action processing) • Data Utilization (manual processes, maintenance of proprietary feeds and interfaces, redundant systems, duplicate master files, duplicate accounts, integration and transformation challenges) • Business Development (upselling opportunities, enhanced client service, new product engineering, contextual big data mining, process automation, product and client ROI) • Data Reporting (links between instruments (what we trade) entity (with whom we do business) obligations (based on role) and holdings (what’s in our portfolios) Pillars of Data Operations Content Infrastructure Standards for the unique and precise identification of instruments, entities, language of the contract and classification schemes (LEI, loan ID, universal product ID, cash flow, sector classification, instrument categorization) (Identifiers and Ontologies) Data Management Strategy IT Environment Governance, funding model, TCO and measurement, requirements management, resource strategy, business semantics, business process flows, data flows, data quality, executable business rules, integration strategy Data workflow, process capabilities and limitations, technical architecture, legacy reconciliation, messaging standards, metadata management, data management platform, supply chain management (Data Management Maturity and Capability Assessment) (Technical Architecture, Framework Standards and Process Engineering) EDM Council Highlights • Initial FIBO specifications to be released June 17 (Foundations and Business Entitles) • FIBO Technical Summit held June 4-5 in San Francisco (collaboration with semantic processing community) • Liquidity template mapping to FIBO (Bank of England) Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 3 EDM Council Highlights • DMM pilot with Microsoft successfully completed • EDM Council to offer facilitated DMM assessment workshops to members • Office of Financial Research (OFR) Financial Research Advisory Committee (FRAC) initial recommendations Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 4 Core Regulatory Initiatives • Dodd-Frank Act = total revision of U.S. financial regulatory environment (transparency, financial stability and market surveillance implications) • Regulation AB2 = the SEC’s new regulations on mortgage backed/Asset Backed securities (must be able to unravel links between loan, tranches, pool, etc.). • UCITS = Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities (EU Directive on simplification of prospectus and their expression using clear, accessible and standardized data). • AIFMD – Alternative Investment Fund Managers Directive (EU proposed law to provide more oversight and transparency to hedge funds and private equity). • Basel III – global regulatory standard on bank capital adequacy, stress testing and market liquidity risk. • CCAR = Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (stress test methodology in the US; CCAR reporting is putting lots of pressure on data alignment and comparability. This includes the FR Y-9C (Bank Holding Company Capital Report) and FR Y-14Q (detailed ‘show your calculation methodology work for BHC). This is the US version of Basel III. • Solvency II – EU Directive that harmonizes insurance regulation (requirements for capital reserve and reduction of risk of insolvency) – to be implemented January 2014. • ACORD – Insurance standards development body (UK) likely to be mandated as the format for reporting. • COREP = Common Reporting requirements (developed by Committee of European Banking Supervisors (CEBS) with the goal of developing a supervisory reporting framework based on common data standards and formats. • EMIR – European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EU version of Dodd-Frank Title VII on derivatives transparency). • MiFID II – Revised Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (mostly about trading, but does require common instrument identification for consolidated pricing). • FSB Templates = Common Data Template for G-SIB’s seeking to harmonize the data compounding methodology for reporting. • Basel Principles for Effective Risk Data Aggregation and Reporting = new principles related to the implementation of a “data control environment” and healthy “risk appetite framework” within systemically important financial institutions. Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 5 Common Data Themes Data Harmonization – alignment of definitions and the ability to aggregate consistently across the industry Data Production – understanding of what it takes to create new information and link content for scenario-based analysis Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 6 Basel Principles for Risk Data Aggregation • Governance: ownership at the BOD and executive management level for enterprise-wide adoption of control environment • Data Infrastructure: facilitate comparability and ability to aggregate on consistent basis • Ad-Hoc Reporting: data that regulators have confidence in to facilitate comparability without reconciliation Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 7 Derivatives Transparency • Validate and Normalize Data (across SDR’s and across geography) • Standardize Product Identification (719(b), SDR aggregation and OFR instrument database) • Aggregate and Classify (type, counterparty, cash flow, obligation) • Align with Messaging Standards (FpML, FIX derivatives, ISO 20022) • Support Complex Analytics (filter, sort, search, link, query based on ad-hoc scenarios and on-demand) Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 8 Stress and Liquidity Testing • Data: alignment of terms and definitions, product type classification, integration of acquisitions • Communication: clarity of requirements, data usage, data production process • Timing: change requests, submission deadline conflicts Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 9 Hierarchical Reporting • Remember: LEI is a building block for reporting • Separate the characteristics of “entities” from the types of “relationships” that exist among entities from the “roles” performed in the transaction • This is about describing contractual “facts” and “relationships” in a formal manner – – – – What an “entity” is The types of “entities” that exist What “ownership” means What “control” means Relationship Types, Definitions, and Descriptions Entity B Entity A Confidential Copyright © 2012 EDM Council Inc. THIS Relationship 10 FRAC Data Committee (core themes) • Focus on the practical objectives of OFR (advisory capacity only) • Manage contagion and support predictive analysis • Implement standards to support core capability objectives (identify, describe, classify and link) • Facilitate data comparability among FSOC member agencies • Improve data collection process (reduce cost, improve quality, support analytical flexibility) Confidential Copyright © 2010 EDM Council Inc. 11 FRAC/DTS Short-Term Goals • LEI quality standards (necessary to fulfill the entity database obligation) • Employ “legal criteria” for reporting about relationships (the application of LEI) • Instrument database is a precise description of all instrument types (what they are and how they work) • Loan ID and classification are pressing standards objectives Confidential Copyright © 2010 EDM Council Inc. 12 Data Management Maturity Model • Core Model Released (June 2012) – SIFI request to address MRIA orders on data quality and governance – Hybrid of SCAMPI methodology – Early adoption (30+) and detailed feedback • Revised DMM (April 2013) – Elimination of redundancies and simplification – Alignment of approach across process areas – Concept clarification and translation to non-specialists – Enhanced relationship to artifacts – Dependency mapping and value band categorization • Confidential Pilot Initiatives and Validation Copyright © 2010 EDM Council Inc. 13 DMM: Alignment with Basel RDA “If the DMM is something our bankers would like us to consider in the context of the BCBS Risk Aggregation Reporting Principles, let them know we are open to having a dialogue with them.” Basel RDA Data Principles • Accountability for risk aggregation at BOD and executive management level • Integrated data taxonomies and aligned metadata • Standard identifiers and naming conventions • Data lineage and root cause remediation • On-demand and ad-hoc reporting capabilities • Automated risk aggregation across relevant business units • Scenario-based analysis and near real-time reporting Molly Scherf Risk Appetite Working Group Senior Banking Supervisors Group Large Bank Supervision Office of the Comptroller of the Currency U.S. Department of Treasury May 2, 2013 Internal Assessment (2013) Mandatory Compliance (2016) Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 14 Understanding the DMM • Structure of DMM – – – – Top level is organized into core categories Categories contain a number of primary components Components are organized into process areas (containing goals, core questions and capability practice statements) Capability practices are organized into levels that are used as the basis for assessment (with expected artifacts/work products) Capability Practice Levels • Level 0: Incomplete (not performed or unstable processes) • Level 1: Performed (ad hoc processes. Emphasis on data repair. Reactive and transitory improvements) • Level 2: Managed (formalized processes. Infrastructure supports at business unit. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities) • Level 3: Defined (Established processes. Tailored to meet specific needs. Predictable and consistent) • Level 4: Measured (Established metrics. Variance management across the process lifecycle) • Level 5: Optimized (processes are improved on a continuous basis and advocated at the executive management level) Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 15 DMM Facilitated Assessment • CMMI Institute and EDM Council service offering (on request by members) • Workshop Methodology – – – – • Confidential Collaborative, interactive and shared understanding Consistent view of the breadth and depth of data management within the organization Shared language about components, capabilities, core principles and objectives Consensus scoring with interaction on rationale Four Step Process 1. Preparation: define objectives and recruit stakeholders 2. Assessment Plan: establish sequence, define deliverables, determine responsibilities and set timeframes 3. Workshop: managed interviews, verification of requirements, analysis of business processes/data flows, review of artifacts and analysis of governance 4. Recommendations: current state assessment, gap analysis, composite scoring, final report and executive briefing Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 16 Financial Industry Business Ontology Facilitates complex queries for risk and transitive exposure analysis Enables risk data aggregations across multiple dimensions Represents real world facts (terms and standard definitions) and relationships about financial instruments, business entities and 1 transactions 7 Integrates easily within existing environments and aligns with other standards 2 6 Enables classification of financial instruments into categories and supports quality assurance 3 Can be used to visually express all forms of data relationships 5 Confidential Provide common reference point for mapping from data 4 repositories to a common business data standard 17 FIBO Developments • Initial Standards Milestone Passed – FIBO Foundations and Business Entities combined with OMG architectural rigor – Standardization of FIBO methodology in RDF/OWL • FIBO Development – Wave two: securities, loans and derivatives – Wave three: market data, corporate actions and transactions • Migration to Adaptive Metadata Repository Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 18 FIBO Use Case Activities • Derivatives Transparency (live POC demo) – – – – • Liquidity Reporting (underway) – – – • Evaluation of FIBO as a common data language for standardized and granular reporting Test of liquidity forms FSA 047-054 (data definitions and classification) Potential to reduce reporting burdens and generate comparable data in support of ad-hoc analysis Loan Lifecycle (in discussion) – – – Confidential Operational ontology showing the intersection of interest rate swaps, credit default obligations and legal entities Classification based on contractual facts for UPI Queries about legal entity control and ownership Alignment with FpML, FIX and ISO 2022 messaging taxonomies Align loan and MBS lifecycle with FIBO to support reporting consistency Support accurate and consistent mapping to MISMO messaging taxonomy Rationalize FR Y-14 data production process and reporting Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 19 FIBO Technical Summit FIBO Summit Technical Objectives Adaptive Inc Alion Science and Technology Black Diamond Research Cambridge Intelligence Cambridge Semantics CAPSICUM Business Architects Carnegie Mellon Citigroup EDM Council Entropy Management Limited Expert Systems FacetApp Fincore Ltd FrankelConsulting Franz Global IDs Google IHMC Intellegent Software Solutions Johns Hopkins University Manulife Financial Confidential Michigan State University/REA MphasiSy NIST OCLC Ontolog & CIM3 Ontology Engineering Group (OEG)/ Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Oracle Philadelphia University Price Waterhouse Coopers Quantum4D Raytheon-BBN Semantic Arts Smart Cloud Inc SRI International Tahoe Blue Thematix Top Quadrant Bank of America University College Cork, Ireland W3C Wells Fargo Wizdom Systems 1. The generation of operational ontologies in RDF/OWL from conceptual ontologies 2. Convert requirements (i.e. regulatory rules) into executable semantic rule statements 3. Visually represent all forms of semantic content with enough rigor to support reasoning 4. Facilitate the sharing of semantics and analytics at the scale of the financial system Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 20 Next Steps for Collaboration Process • Organize: Create a Semantic Coordination Leadership team with a fixed membership and published meeting schedule • Fund: Identify sources and a coordination process for semantic technology funding • Sustain: Implement a Semantic Technology Laboratory (Center of Excellence) as a formal mechanism for the advancement of semantic technology • Link: Build and maintain a directory of participants and a listing of publications/resources for the advancement of semantic technology • Meet: Implement an annual Semantic Technical and annual Semantic Applications Summit as checkpoints • Publish: Provide a mechanism for participants to publish articles and research related to semantic technology implementation Confidential 21 Get Ready For … On-Demand and Ad-Hoc Reporting Meeting the needs of macroprudential oversight is not possible without a trusted data infrastructure Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 22 Don’t Forget the … Mandatory Alignment with Standards The goal is automated, enterprise-wide risk reporting. Concordance and data reconciliation is no longer viable Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 23 Built Upon … Enterprise-Wide Governance Board of Directors and executive management is responsible for managing the intractable relationship between risk appetite and data management Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 24 Designed Around … Data Flows and Business Processes Provenance over data and how it flows from process-to-process with SOX-like certification of capability Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 25 Managed Through … Better Supply Chain Management The goal is to manage the flow of data from originator source system transformation process transaction reporting Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 26 Propelling Vendors … To New Concepts of Added Value The data management mandate will propel data vendors and suppliers to innovate and integrate in support of clients enhanced requirements Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 27 Opportunity for … Partnerships and Collaboration Between business silos, with vendors, with regulators and across geographic boundaries Confidential Copyright © 2013 EDM Council Inc. 28