Chapter 4: Adolescence
Section 1: Physical and Sexual
Development
Main Idea
All Adolescents experience dramatic
changes in their physical size, shape, and
capacities, as well as biological
development related to reproduction.
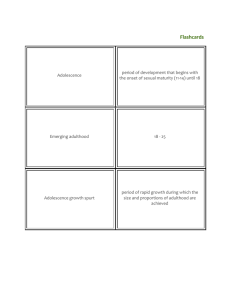
Adolescence
The transition period between childhood
and adulthood
Outlooks on adolescence
Time period of mixed abilities and responsibilities
Other societies – Not a separate stage of life
Move directly from childhood to adulthood
Initiation Rite (rites of passage)
Informal- 16th, 18th or 21st birthday
Formal- high school/college graduation, weddings
Theories of Adolescence
G. Stanley Hall- Transitional Stage
Period of “Storm and Stress”
A marginal being, confused, troubled and highly
frustrated.
Theories of Adolescence
Margaret Mead- Anthropological Studies
In some cultures adolescence is a highly
enjoyable time of life not marked by Storm
and Stress
Storm and Stress- byproduct of industrialized
society (Culture may play a role in development)
11% experience serious difficulties
32% have sporadic problems
57% positive and healthy development during teenage
years
Theories of Adolescence
Robert Havighurst
Challenges in the form of developmental tasks (p. 95)
Acquiring a gender role- Masculine or Feminine
Developing appropriate relations with age-mates of both
sexes
Emotional dependence from parents and other adults
Most face stress but tend to cope with it
Influential Factors for Individual
Adolescent Development
Adjustments in Childhood
Level of adjustment of his/her parents and
peers
Changes that occur during adolescence
Physical, social, emotional and intellectual
Physical Development
Sexual Maturation (puberty) The biological
event that marks the end of childhood.
Hormones- trigger internal/external
changes
Females
Start to mature physically as early as 8
Puberty between 8-10
Growth Spurt
Fat tissue develops (making the girl look
chubby) retain and add as they spurt
Grow 2-3 ½ inches in a year
Breasts and hips begin to fill out
Females
Reach sexual maturity at the end of
growth spurt
10-17 she has her first menstrual period or
menarche (beginning of womanhood)
12-18 months later her period becomes
regular and she can conceive a child.
Males
Start to mature physically at age 9-10
Puberty between 9-16
Growth spurt- around age 12 last 2 years
Fat tissue develops but is quickly lostprogress to a lean and lanky phase
Age 12-13- first ejaculation or spermarche
Physical Development of Males
Broader Shoulders and thicker trunks
More muscle tissue
Larger heart and lungs than women
Voice deepens
Hair growth- face and later on chest
Asynchrony- uneven growth of body parts
Hands/feet may be too large or small
compared to the rest of the body
Reactions to growth
Sudden body changes make all
adolescents somewhat self conscious
Want to be accepted by their peers
Conform to how males and females their age
should act, look and dress.
Research on maturation and
success
Boys who mature early have an
advantage
Hero’s in sports
Leaders in social activities
Boys look up to them- girls have crushes
Adults treat them as more mature
More self-confident and independent
Research on maturation and
success
Girls who mature early may feel
embarrassed rather than proud of their
height and figure at first.
Dating older boys
Bossy with people their own age
Research on maturation and
success
Self-fulfilling prophecy
The boy who believes he does not meet his
culture’s physical ideal may think less of
himself and not pursue success as diligently
as the next person.
His belief brings about the failure he feared
Sexual Development
Developing attitudes about sex and the
gender role he/she will fill.
Some societies keep children in the dark
about sex until just before marriage
Other cultures encourage preadolescents
children to engage in sexual play to foster
mature development
Teen Sex Stats
870,000 pregnancies/year
3,000,000 cases of STDs
Factors Contributing to Teenage
Pregnancy
Problematic
Relationships
Emotional Problems
Problems in School
Loosening of Prohibitions
Peer Pressure
Lack of Knowledge
Fights with or rebelling
against parents
Feelings of emptiness
Lack of educational goals
Portrayal of sexual themes in
the media
Friends engaging in sexual
activity
Misunderstanding or ignorance
about the facts of reproduction
ABSTINENCE
A choice to avoid harmful behaviors
including premarital sex and the use of
drugs and alcohol.
Visual Representations
Robert Havighurst’s research indicated
that all adolescents face developmental
challenges (p.95). Your assignment is to
illustrate one of the tasks Havighurst
identified. The illustrations can take the
form of a single drawing or a cartoon.