Urbanization, and Industrialization
advertisement

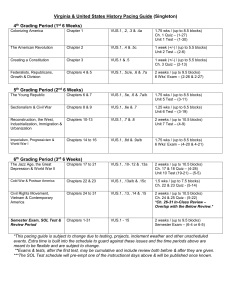
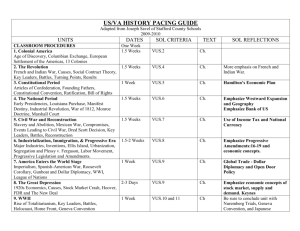
Urbanization, and Industrialization What You Need to Know Urbanization and the Growth of Cities (VUS.8a) Industrial growth led to urbanization and the rise of large cities such as Chicago, New York, Detroit, and Pittsburgh. Urbanization and the Growth of Cities (VUS.8a) Cities served as manufacturing and transportation centers. Factories provided jobs – long hours, low pay, dangerous working conditions (ex. - Triangle Shirtwaiste Fire). Urbanization and the Growth of Cities (VUS.8a) Workers families lived in crowded tenements and slums. Urbanization and the Growth of Cities (VUS.8a) The Cliff Dwellers, by George Bellows illustrates tenement life in New York Urbanization and the Growth of Cities (VUS.8a) Urbanization led to new public services such as sewage and water treatment systems and subways. Jacob Riis, Children sleeping in Mulberry Street (1890) Admission of New States (VUS.8a) As the population moved westward new states were added in the Great Plains and Rocky Mountains. All of the lower 48 states had been added by the early 20th century (“closing of the frontier”). Industrialization (VUS.8b) Technological change spurred the growth of industry primarily in northern cities. • Corporation (limited individual liability) • Bessemer process (steel) • Light bulb and electricity (Thomas Edison) • Telephone (Alexander Graham Bell) • Airplane (Wright Brothers) • Assembly line manufacturing (Henry Ford) Industrialization (VUS.8b) • Light bulb and electricity (Thomas Edison) Industrialization (VUS.8b) • Airplane (Wright Brothers) Industrialization (VUS.8b) • Assembly line manufacturing (Henry Ford) Industrialization (VUS.8b) Industrial leaders and the growth of monopolies and trusts: Andrew Carnegie (steel) J.P. Morgan (finance) John D. Rockefeller (oil) Cornelius Vanderbilt (railroads) Andrew Carnegie Industrialization (VUS.8b) Reasons for Industrialization and Economic Growth Government policies based on laissez-faire capitalism Monopolies and trusts (vertical/horizontal integration) Special considerations – e.g. land grants to railroads Increasing labor supply (immigration) Natural resources – coal, iron ore, petroleum – and navigable rivers Industrialization (VUS.8b) And that is what you need to know! The Monopoly Man!